Ajivikas An ascetic sect that emerged in India about the same time
... Nirvana. When one has achieved Nirvana, which is a transcendent state free from suffering and our worldly cycle of birth and rebirth, spiritual enlightenment has been reached. The Fourth Noble truth charts the method for attaining the end of suffering, known to Buddhists as the Noble Eightfold Path. ...
... Nirvana. When one has achieved Nirvana, which is a transcendent state free from suffering and our worldly cycle of birth and rebirth, spiritual enlightenment has been reached. The Fourth Noble truth charts the method for attaining the end of suffering, known to Buddhists as the Noble Eightfold Path. ...
What the Buddha Taught
... -23(8) Right Concentration The 3rd and last factor of Mental Discipline leads to The 4 Stages of Dhyana (Trance or ‘Higher’ Meditation) ...
... -23(8) Right Concentration The 3rd and last factor of Mental Discipline leads to The 4 Stages of Dhyana (Trance or ‘Higher’ Meditation) ...
Buddhism - Siegel Middle School
... luxury did not guarantee happiness he explored the different teaching religions and philosophies of the day to find the key to human happiness ...
... luxury did not guarantee happiness he explored the different teaching religions and philosophies of the day to find the key to human happiness ...
Buddhist Spirituality
... – Our cravings can never be fully satisfied – Control cravings rather than let cravings control you ...
... – Our cravings can never be fully satisfied – Control cravings rather than let cravings control you ...
Buddhism
... found the enlightenment he sought, when he realized the Middle Way. It is then that he became Buddha (the ...
... found the enlightenment he sought, when he realized the Middle Way. It is then that he became Buddha (the ...
Ancient India - Revere Local Schools
... Led by monks and nuns Worship in temples Symbol is the Lotus Plant Buddha’s teachings are in the Dharma ...
... Led by monks and nuns Worship in temples Symbol is the Lotus Plant Buddha’s teachings are in the Dharma ...
Buddhism - PhilosophicalAdvisor.com
... Siddhartha Gautama (563 BC - 483 BC) was born in ancient India (in tiny Lumbini which is now in Nepal, bordering India), a prince whose teachings resulted in the philosophy or religion of Buddhism. A ‘Buddha’ is an enlightened person whose teachings reveal the nature and path of salvation … Bu ...
... Siddhartha Gautama (563 BC - 483 BC) was born in ancient India (in tiny Lumbini which is now in Nepal, bordering India), a prince whose teachings resulted in the philosophy or religion of Buddhism. A ‘Buddha’ is an enlightened person whose teachings reveal the nature and path of salvation … Bu ...
What is Buddhism
... 2. Siddhartha Gautama was born a prince in Nepal. 3. On his journey Siddhartha saw four things for the first time ever. They were Old age, sickness, a funeral, and a religious man. 4. While meditating he realized that suffering was caused by desire. 5. The four noble truths are 1. Suffering is a par ...
... 2. Siddhartha Gautama was born a prince in Nepal. 3. On his journey Siddhartha saw four things for the first time ever. They were Old age, sickness, a funeral, and a religious man. 4. While meditating he realized that suffering was caused by desire. 5. The four noble truths are 1. Suffering is a par ...
Introduction to Religious Studies and Theology
... 1. Right Effort/Exercise—One makes an effort to improve (samyag-vyāyāma, sammā-vāyāma) 2. Right Mindfulness/Awareness—Mental ability to see things for what they are with clear consciousness (samyak-smṛti, sammā-sati) 3. Right Concentration/Meditation—Being aware of the present reality within oneself ...
... 1. Right Effort/Exercise—One makes an effort to improve (samyag-vyāyāma, sammā-vāyāma) 2. Right Mindfulness/Awareness—Mental ability to see things for what they are with clear consciousness (samyak-smṛti, sammā-sati) 3. Right Concentration/Meditation—Being aware of the present reality within oneself ...
Buddhism With as many as 500 million followers, Buddhism is the 4
... Buddhists must train and purify their mind by following the Four Noble Truths. The Four Noble Truths are: 1—Life is suffering 2—Suffering is due to attachment to things 3—Attachment can be overcome 4—There is a life path to accomplish all of this The "path" mentioned in the 4th Noble Truth is called ...
... Buddhists must train and purify their mind by following the Four Noble Truths. The Four Noble Truths are: 1—Life is suffering 2—Suffering is due to attachment to things 3—Attachment can be overcome 4—There is a life path to accomplish all of this The "path" mentioned in the 4th Noble Truth is called ...
Document
... “The Buddha, the founder of Buddhism, was not God or a god. He was a human being who attained full enlightenment through meditation and showed us the path of spiritual awakening and freedom. Therefore, Buddhism is not a religion of God. Buddhism is a religion of wisdom, enlightenment and compassion. ...
... “The Buddha, the founder of Buddhism, was not God or a god. He was a human being who attained full enlightenment through meditation and showed us the path of spiritual awakening and freedom. Therefore, Buddhism is not a religion of God. Buddhism is a religion of wisdom, enlightenment and compassion. ...
File
... • To try to free one's mind from evil • To be in control of one's feelings and thoughts • To practice appropriate forms of concentration ...
... • To try to free one's mind from evil • To be in control of one's feelings and thoughts • To practice appropriate forms of concentration ...
Notes-on-Early-Buddhist-Discourses
... aware of anicca and the five aggregates that constitute the self and their mutability. (pp. 43-54) ...
... aware of anicca and the five aggregates that constitute the self and their mutability. (pp. 43-54) ...
Comparing World Religions - Townsend Harris High School
... Triptakanarratives scriptural text Buddha’s teaching (sutras) ...
... Triptakanarratives scriptural text Buddha’s teaching (sutras) ...
Buddhism Notes 16 pdf
... 1. Life is filled with _________________. 2. Suffering is caused by ____________________. 3. Suffering can be ended if people __________________________, like more pleasure or more power. 4. To stop wanting things, people must follow 8 basic laws, called the ______________________. The Eightfold Pat ...
... 1. Life is filled with _________________. 2. Suffering is caused by ____________________. 3. Suffering can be ended if people __________________________, like more pleasure or more power. 4. To stop wanting things, people must follow 8 basic laws, called the ______________________. The Eightfold Pat ...
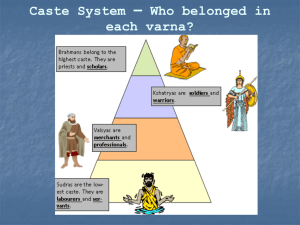
Caste System – Who belonged in each varna?
... 5. Do rewarding work. 6.Work for good and oppose evil. 7. Make sure your mind keeps your senses under control. 8. Practice meditation. ...
... 5. Do rewarding work. 6.Work for good and oppose evil. 7. Make sure your mind keeps your senses under control. 8. Practice meditation. ...
The Indian Subcontinent
... Eightfold Path • Eightfold Path is also called the Middle Path • Four Noble Truths: 1. Ordinary life is full of suffering 2. This suffering is caused by our desire to satisfy ourselves 3. The way to end suffering is to end our desire for selfish goals and to see others as an extension of ourselves. ...
... Eightfold Path • Eightfold Path is also called the Middle Path • Four Noble Truths: 1. Ordinary life is full of suffering 2. This suffering is caused by our desire to satisfy ourselves 3. The way to end suffering is to end our desire for selfish goals and to see others as an extension of ourselves. ...
Buddhism - TeacherWeb
... • Not very strict categories: *Main idea is that the inner life influences the outer life • 1.) Morality: moral action brings about good Meditation • 2) Meditation: brings about wisdom • 3) Wisdom: gives rise to right moral actions ...
... • Not very strict categories: *Main idea is that the inner life influences the outer life • 1.) Morality: moral action brings about good Meditation • 2) Meditation: brings about wisdom • 3) Wisdom: gives rise to right moral actions ...
Noble Eightfold Path
The Noble Eightfold Path (Pali: ariyo aṭṭhaṅgiko maggo, Sanskrit: āryāṣṭāṅgamārga) is one of the principal teachings of Śrāvakayāna. It is used to develop insight into the true nature of phenomena (or reality) and to eradicate greed, hatred, and delusion. The Noble Eightfold Path is the fourth of the Buddha's Four Noble Truths; the first element of the Noble Eightfold Path is, in turn, an understanding of the Four Noble Truths. It is also known as the Middle Path or Middle Way. Its goal is Arhatship. The Noble Eightfold Path is contrasted with the Bodhisattva path of Mahayana which culminates in Buddhahood.All eight elements of the Path begin with the word ""right,"" which translates the word samyañc (in Sanskrit) or sammā (in Pāli). These denote completion, togetherness, and coherence, and can also suggest the senses of ""perfect"" or ""ideal."" 'Samma' is also translated as ""wholesome,"" ""wise"" and ""skillful.""In Buddhist symbolism, the Noble Eightfold Path is often represented by means of the dharma wheel (dharmachakra), whose eight spokes represent the eight elements of the path.















![Buddhism[1]. - Mr. Fellens` World History Honors](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006442421_1-4b4dd9563a9db6afc434e94f46285d75-300x300.png)