PDF
... In a non-empty complete metric space, any countable intersection of dense, open subsets is non-empty. In fact, such countable intersections of dense, open subsets are dense. So the theorem holds also for any non-empty open subset of a complete metric space. Alternative formulations: Call a set first ...
... In a non-empty complete metric space, any countable intersection of dense, open subsets is non-empty. In fact, such countable intersections of dense, open subsets are dense. So the theorem holds also for any non-empty open subset of a complete metric space. Alternative formulations: Call a set first ...
Lecture 8: Curved Spaces
... was given to spaces where this postulate does not hold. Mathematicians such as, Gauss, Riemann, Lobachevskii formulated the field of non-Euclidean geometry. Let’s begin by examining the subspace R2 (the flat infinite plane) embedded into R3 . Or, to make a more concrete example, consider the flat un ...
... was given to spaces where this postulate does not hold. Mathematicians such as, Gauss, Riemann, Lobachevskii formulated the field of non-Euclidean geometry. Let’s begin by examining the subspace R2 (the flat infinite plane) embedded into R3 . Or, to make a more concrete example, consider the flat un ...
The Lebesgue Number
... defined to be the least upper bound of the set {d(x, y) | x, y ∈ S} of real numbers. We will denote the diameter of S by diam(S). Definition. A collection U of subsets ofSa topological space X is said to cover X, and is also called a cover of X, if its union U equals X. A collection of open subsets ...
... defined to be the least upper bound of the set {d(x, y) | x, y ∈ S} of real numbers. We will denote the diameter of S by diam(S). Definition. A collection U of subsets ofSa topological space X is said to cover X, and is also called a cover of X, if its union U equals X. A collection of open subsets ...
The path to General Relativity
... the same side less than two right angles, the two straight lines, if produced indefinitely, meet on that side on which are the angles less than the two right angles.” This can be shown to be equivalent to the statement that “the sum of angles in a triangle is 180◦ ” (Legendre). However, by the late ...
... the same side less than two right angles, the two straight lines, if produced indefinitely, meet on that side on which are the angles less than the two right angles.” This can be shown to be equivalent to the statement that “the sum of angles in a triangle is 180◦ ” (Legendre). However, by the late ...
General Relativity
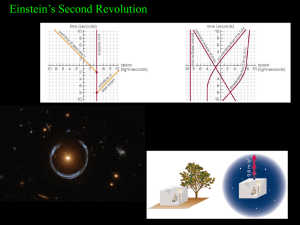
... Black holes form when there is enough mass to collapse spacetime and prevent light from escaping. This shows the spacetime bending as a star collapses creating a gravitational field strong enough to trap light. ...
... Black holes form when there is enough mass to collapse spacetime and prevent light from escaping. This shows the spacetime bending as a star collapses creating a gravitational field strong enough to trap light. ...
“Perfect” Cosmological Principle? - University of Texas Astronomy
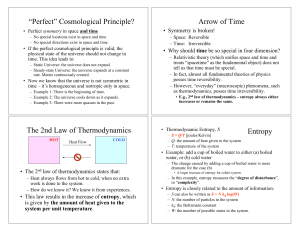
... • It’s basically the surface of a sphere. • All lines will eventually intersect: no parallel lines exist! – Euclid had to extend his “parallel” lines to very large distances on the Earth before he noticed this fact. ...
... • It’s basically the surface of a sphere. • All lines will eventually intersect: no parallel lines exist! – Euclid had to extend his “parallel” lines to very large distances on the Earth before he noticed this fact. ...
Day 3 Sections S3.1-3 Spacetime, A New View of Gravity
... 3) Astronaut Bill is hovering 15,000,000 miles above a neutron star while astronaut Susan is down close the surface making measurements. When Bill compares his clock to Susan’s, he says her clock is running slower than his. What does Susan say when she compares her clock to Bill’s? ...
... 3) Astronaut Bill is hovering 15,000,000 miles above a neutron star while astronaut Susan is down close the surface making measurements. When Bill compares his clock to Susan’s, he says her clock is running slower than his. What does Susan say when she compares her clock to Bill’s? ...
GR in a Nutshell
... The first equation has reproduced Einstein’s equations. The second equation involves a spin density tensor S and a modified torsion tensor T, and therefore couples spin with torsion. ...
... The first equation has reproduced Einstein’s equations. The second equation involves a spin density tensor S and a modified torsion tensor T, and therefore couples spin with torsion. ...
Homework 4
... function of t. How does the sectional curvature behave in the limit as t → 0 or t → ∞? (Note: a 3-sphere with one of the metrics gt is sometimes called a Berger sphere) Problem 3. A surface of revolution is a smooth surface in E3 obtained by rotating a smooth curve (called the generatrix) in the x–z ...
... function of t. How does the sectional curvature behave in the limit as t → 0 or t → ∞? (Note: a 3-sphere with one of the metrics gt is sometimes called a Berger sphere) Problem 3. A surface of revolution is a smooth surface in E3 obtained by rotating a smooth curve (called the generatrix) in the x–z ...
lecture06slides-schwarzschild
... We can discover this curvature by making geometric measurements. • Straight lines, initially parallel, cross near the star’s center • Angles of a triangle > 180° • Circumference < ( diameter) Quantitative details of “how much” are predicted by Schwarzchild’s solution. We can imagine extracting th ...
... We can discover this curvature by making geometric measurements. • Straight lines, initially parallel, cross near the star’s center • Angles of a triangle > 180° • Circumference < ( diameter) Quantitative details of “how much” are predicted by Schwarzchild’s solution. We can imagine extracting th ...
Hyperfunction Geometry
... Hyper-function geometry An old (1980) program of mine is to develop hyperfunction geometry. It was motivated by work of Hawking on Euclidean Quantum Gravity and of Penrose on Twistor Quantization. Hawking considers complex 4-manifolds. To begin with, they admit Lorentzian sections. But he goes on to ...
... Hyper-function geometry An old (1980) program of mine is to develop hyperfunction geometry. It was motivated by work of Hawking on Euclidean Quantum Gravity and of Penrose on Twistor Quantization. Hawking considers complex 4-manifolds. To begin with, they admit Lorentzian sections. But he goes on to ...
1. What is meant by spacetime?
... 2a. This will be just a straight line on a spacetime diagram. 3. What is the equivalence principle? 3a. The effects of gravity can be mimicked by accelerating appropriately. 4. What are the characteristics of a flat, open and closed geometry for spacetime? 4a. Flat: Angles in a triangle add up to 18 ...
... 2a. This will be just a straight line on a spacetime diagram. 3. What is the equivalence principle? 3a. The effects of gravity can be mimicked by accelerating appropriately. 4. What are the characteristics of a flat, open and closed geometry for spacetime? 4a. Flat: Angles in a triangle add up to 18 ...
Complete Metric Spaces
... Definition: A set D in a metric space is called nowhere dense if The closure has non-empty interior. Theorem(Baire): In a complete metric space the countable union of nowhere dense sets is again nowhere dense. ...
... Definition: A set D in a metric space is called nowhere dense if The closure has non-empty interior. Theorem(Baire): In a complete metric space the countable union of nowhere dense sets is again nowhere dense. ...
Document
... Quanta of gravity: In principle they are somewhat like photons with a higher spin, but specific predictions are hard to make and we are not close to being able to detect them as particles. Cosmology: The big bang singularity, expansion, imprints on the CMB. Black holes: Singularities, entropy and Ha ...
... Quanta of gravity: In principle they are somewhat like photons with a higher spin, but specific predictions are hard to make and we are not close to being able to detect them as particles. Cosmology: The big bang singularity, expansion, imprints on the CMB. Black holes: Singularities, entropy and Ha ...
Let K be a compact Lie group (or a finite group, if one desires) and
... Let K be a compact Lie group (or a finite group, if one desires) and assume that K acts linearly on W := Rn . An important question is to determine the quotient space of the K-action on W . Abstractly, the quotient space (denoted W/K) is the space of K-orbits in W and it is given the quotient topolo ...
... Let K be a compact Lie group (or a finite group, if one desires) and assume that K acts linearly on W := Rn . An important question is to determine the quotient space of the K-action on W . Abstractly, the quotient space (denoted W/K) is the space of K-orbits in W and it is given the quotient topolo ...
Euclidean/non-Euclidean Geometry
... In curved space, the shortest distance between any two points (called a geodesic) is not unique. In curved space, (for spherical (riemannian) or hyperbolic geometry)the concept of perpendicular to a line can be illustrated as seen in either of these pictures. ...
... In curved space, the shortest distance between any two points (called a geodesic) is not unique. In curved space, (for spherical (riemannian) or hyperbolic geometry)the concept of perpendicular to a line can be illustrated as seen in either of these pictures. ...