+ Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
... Describing Location in a Distribution The Practice of Statistics, 4th edition - For AP* ...
... Describing Location in a Distribution The Practice of Statistics, 4th edition - For AP* ...
+ Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
... The median of a density curve is the equal-areas point, the point that divides the area under the curve in half. The mean of a density curve is the balance point, at which the curve would balance if made of solid material. The median and the mean are the same for a symmetric density curve. They both ...
... The median of a density curve is the equal-areas point, the point that divides the area under the curve in half. The mean of a density curve is the balance point, at which the curve would balance if made of solid material. The median and the mean are the same for a symmetric density curve. They both ...
Machine Learning
... P(I,C) = P(I=True, C=True) • 30 like chocolate but not ice cream P(I’,C) = P(I=False, C=True) • 5 like ice cream but not chocolate P(I,C’) • 10 don’t like chocolate nor ice cream Prob(I) = P(I=True) Prob(C) = P(C=True) Prob(I,C) = P(I=True, C=True) ...
... P(I,C) = P(I=True, C=True) • 30 like chocolate but not ice cream P(I’,C) = P(I=False, C=True) • 5 like ice cream but not chocolate P(I,C’) • 10 don’t like chocolate nor ice cream Prob(I) = P(I=True) Prob(C) = P(C=True) Prob(I,C) = P(I=True, C=True) ...
Chapter 5 Working with Scores
... measure. We'll learn two formulas for the mean (1.) raw score, and (2) frequency distribution which requires creating an X[f(X)] column. The mean is represented as an X with a bar above it (Xbar) or M. Outlier - an extreme score (high or low) far away from the majority of the other scores. 3. Median ...
... measure. We'll learn two formulas for the mean (1.) raw score, and (2) frequency distribution which requires creating an X[f(X)] column. The mean is represented as an X with a bar above it (Xbar) or M. Outlier - an extreme score (high or low) far away from the majority of the other scores. 3. Median ...
File
... The median of a density curve is the equal-areas point, the point that divides the area under the curve in half. The mean of a density curve is the balance point, at which the curve would balance if made of solid material. The median and the mean are the same for a symmetric density curve. They both ...
... The median of a density curve is the equal-areas point, the point that divides the area under the curve in half. The mean of a density curve is the balance point, at which the curve would balance if made of solid material. The median and the mean are the same for a symmetric density curve. They both ...
TPS4e_Ch2_2.1
... The median of a density curve is the equal-areas point, the point that divides the area under the curve in half. The mean of a density curve is the balance point, at which the curve would balance if made of solid material. The median and the mean are the same for a symmetric density curve. They both ...
... The median of a density curve is the equal-areas point, the point that divides the area under the curve in half. The mean of a density curve is the balance point, at which the curve would balance if made of solid material. The median and the mean are the same for a symmetric density curve. They both ...
Error Propagation
... • Many measurements only seek to determine if any activity is present above background. • The minimum significant measurement determines the conditions to assert that there is activity above background. – Failure is false positive; type I error. • The minimum detectable measurement determines the co ...
... • Many measurements only seek to determine if any activity is present above background. • The minimum significant measurement determines the conditions to assert that there is activity above background. – Failure is false positive; type I error. • The minimum detectable measurement determines the co ...
7. Closed cone of curves Finally let us turn to one of the most
... of curves of X, denoted NE(X), is the cone spanned by the classes [C] ∈ H2 (X, R) inside the vector space H2 (X, R). The closed cone of curves of X, denoted NE(X), is the closure of NE(X) inside H2 (X, R). More generally, if X is normal but not necessarily smooth, one can define the cone of curves a ...
... of curves of X, denoted NE(X), is the cone spanned by the classes [C] ∈ H2 (X, R) inside the vector space H2 (X, R). The closed cone of curves of X, denoted NE(X), is the closure of NE(X) inside H2 (X, R). More generally, if X is normal but not necessarily smooth, one can define the cone of curves a ...
The Normal Distribution
... A continuous random variable X is one which represents measurements that (theoretically) can be made to any degree of accuracy. For example suppose X = the weight (in kg) of a randomly chosen newborn baby. Depending on the accuracy of our scale the weight X of a randomly selected baby could be recor ...
... A continuous random variable X is one which represents measurements that (theoretically) can be made to any degree of accuracy. For example suppose X = the weight (in kg) of a randomly chosen newborn baby. Depending on the accuracy of our scale the weight X of a randomly selected baby could be recor ...
C.2 Review Sheets D - Mrs. McDonald
... 9. Raw scores on behavioral tests are often transformed for easier comparison. A test of reading ability has mean 75 and standard deviation 10 when given to third-graders. Sixth-graders have mean score 82 and standard deviation 11 on the same test. (a) David is a third-grade student who scores 78 on ...
... 9. Raw scores on behavioral tests are often transformed for easier comparison. A test of reading ability has mean 75 and standard deviation 10 when given to third-graders. Sixth-graders have mean score 82 and standard deviation 11 on the same test. (a) David is a third-grade student who scores 78 on ...
TESTING A TEST
... LR for ECG 2.2 mm result = 10. – This raises post test probability to > 90% for coronary artery disease (see next slide) ...
... LR for ECG 2.2 mm result = 10. – This raises post test probability to > 90% for coronary artery disease (see next slide) ...
Block: ______ Chapter 3: Modeling Distribution
... One important distinction between histograms and density curves is most histograms show the _____________ of observations in each ___________ by the ______________ of their ______ and therefore by the _____________________________. We set up density curves to show the __________________________ ...
... One important distinction between histograms and density curves is most histograms show the _____________ of observations in each ___________ by the ______________ of their ______ and therefore by the _____________________________. We set up density curves to show the __________________________ ...
Density Curve
... The median: the “equal-‐areas point”, divides the curve into two halves of equal areas. • The quartiles divide the area under the curve into quarters. • The rough location of the quartiles can be done ...
... The median: the “equal-‐areas point”, divides the curve into two halves of equal areas. • The quartiles divide the area under the curve into quarters. • The rough location of the quartiles can be done ...
REVIEW
... This is related to Simpson's paradox. It is possible that the winning candidate will not have the majority of the student vote. One situation where this this may happen is the following: the candidate that wins more than half of the colleges does so by winning with a small margin in colleges where t ...
... This is related to Simpson's paradox. It is possible that the winning candidate will not have the majority of the student vote. One situation where this this may happen is the following: the candidate that wins more than half of the colleges does so by winning with a small margin in colleges where t ...
In-class Exercises on Normal Distributions October 29, 2007 Name
... (e) If the golfer had a drive that was 1.5 standard deviations below the mean, what is the z-score and how long was the drive? x = 850 − 1.5(25) = 812.5ft. ...
... (e) If the golfer had a drive that was 1.5 standard deviations below the mean, what is the z-score and how long was the drive? x = 850 − 1.5(25) = 812.5ft. ...
19. P-values, Power, Sample Size
... of not being able to reject H0 when it is false (false negative). The next section is related to this error probability. ...
... of not being able to reject H0 when it is false (false negative). The next section is related to this error probability. ...
Working with the Normal Model
... The normal model is commonly used in statistics. It is used to model data that is unimodal, bell-shaped and symmetric. In this class we will be working a lot with the Normal model. We can use STATA to calculate values similar to those found in the Normal Table in the back of the book. Suppose we wan ...
... The normal model is commonly used in statistics. It is used to model data that is unimodal, bell-shaped and symmetric. In this class we will be working a lot with the Normal model. We can use STATA to calculate values similar to those found in the Normal Table in the back of the book. Suppose we wan ...
Lecture 08. Mean and average quadratic deviation
... compared with a standard. Attributable risk or Risk difference is a measure of absolute risk. It represents the excess risk of disease in those exposed taking into account the background rate of disease. The attributable risk is defined as the difference between the incidence rates in the exposed an ...
... compared with a standard. Attributable risk or Risk difference is a measure of absolute risk. It represents the excess risk of disease in those exposed taking into account the background rate of disease. The attributable risk is defined as the difference between the incidence rates in the exposed an ...
z-score
... distribution using a density curve – The area under any density curve = 1. This represents 100% of observations – Areas on a density curve represent % of ...
... distribution using a density curve – The area under any density curve = 1. This represents 100% of observations – Areas on a density curve represent % of ...
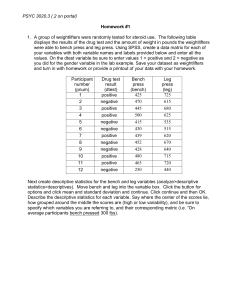
Homework1
... 2. Open the breakfast.sav dataset that we used for the class presentation (it can be found on the class portal under course materials). Create a histogram of the frequency distribution for the poptart variable (analyze/descriptive statistics/frequencies). Move poptart to the variable box. Be sure to ...
... 2. Open the breakfast.sav dataset that we used for the class presentation (it can be found on the class portal under course materials). Create a histogram of the frequency distribution for the poptart variable (analyze/descriptive statistics/frequencies). Move poptart to the variable box. Be sure to ...
Chapter 3 - Math TAMU
... mean at the end of the semester is 73 with a standard deviation of 12. He decides that the top 12% of the class should get an A, the next 24% should get a B, the next 36% a C, the next 18% a D and the last 10% of the class will get an F. What are the cutoffs for the ...
... mean at the end of the semester is 73 with a standard deviation of 12. He decides that the top 12% of the class should get an A, the next 24% should get a B, the next 36% a C, the next 18% a D and the last 10% of the class will get an F. What are the cutoffs for the ...
Lecture 12. Estimation of authenticity of statistical research
... compared with a standard. Attributable risk or Risk difference is a measure of absolute risk. It represents the excess risk of disease in those exposed taking into account the background rate of disease. The attributable risk is defined as the difference between the incidence rates in the exposed an ...
... compared with a standard. Attributable risk or Risk difference is a measure of absolute risk. It represents the excess risk of disease in those exposed taking into account the background rate of disease. The attributable risk is defined as the difference between the incidence rates in the exposed an ...
PSSA Review
... The normal curve is a symmetrical distribution of scores with an equal number of scores above and below the midpoint of the abscissa (horizontal axis of the curve). Since the distribution of scores is symmetrical the mean, median, and mode are all at the same point on the abscissa. In other words, t ...
... The normal curve is a symmetrical distribution of scores with an equal number of scores above and below the midpoint of the abscissa (horizontal axis of the curve). Since the distribution of scores is symmetrical the mean, median, and mode are all at the same point on the abscissa. In other words, t ...
Chapter 2
... has an area of exactly 1 underneath it O The area under the curve for any given interval is equal to the proportion of all observations ...
... has an area of exactly 1 underneath it O The area under the curve for any given interval is equal to the proportion of all observations ...