Light-Scattering Study of the Normal Human Eye
... shifts, and n is the refractive index of the lens. Thus, the spatial variation of the bulk modulus K = ρλ2 f 2 /4n2 is directly obtained from the measured Brillouin shift f, and knowledge of n and ρ as the incident laser beam probes at different positions within the lens. The precision and accuracy ...
... shifts, and n is the refractive index of the lens. Thus, the spatial variation of the bulk modulus K = ρλ2 f 2 /4n2 is directly obtained from the measured Brillouin shift f, and knowledge of n and ρ as the incident laser beam probes at different positions within the lens. The precision and accuracy ...
RAY OPTICS NOTES - RIT Center for Imaging Science
... to manipulate “light” in useful ways. This presupposes the definition of “light,” which I specify as electromagnetic radiation of any “color,” temporal frequency, and wavelength. This is more general than the definition put forth by humanocentrics (e.g., color scientists), but is much more reasonabl ...
... to manipulate “light” in useful ways. This presupposes the definition of “light,” which I specify as electromagnetic radiation of any “color,” temporal frequency, and wavelength. This is more general than the definition put forth by humanocentrics (e.g., color scientists), but is much more reasonabl ...
Chapter 32 Optical Images
... the ways in which these two systems accommodate. That is, the difference between how an eye adjusts and how a camera adjusts (or can be adjusted) to form a focused image for objects at both large and short distances from the camera. ...
... the ways in which these two systems accommodate. That is, the difference between how an eye adjusts and how a camera adjusts (or can be adjusted) to form a focused image for objects at both large and short distances from the camera. ...
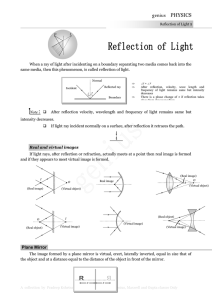
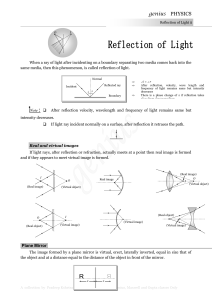
genius PHYSICS
... A ray of light makes an angle of 10 o with the horizontal above it and strikes a plane mirror which is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The angle for which the reflected ray becomes vertical is (a) 40o ...
... A ray of light makes an angle of 10 o with the horizontal above it and strikes a plane mirror which is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The angle for which the reflected ray becomes vertical is (a) 40o ...
Colours of opaque object - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
... A ray of light makes an angle of 10 o with the horizontal above it and strikes a plane mirror which is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The angle for which the reflected ray becomes vertical is (a) 40o ...
... A ray of light makes an angle of 10 o with the horizontal above it and strikes a plane mirror which is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The angle for which the reflected ray becomes vertical is (a) 40o ...
Measuring the Real Point Spread Function of High Numerical
... In confocal microscopy, where the signal is determined by the overlap of the effective excitation and detection PSFs, the loss of register between them should lead to a reduction of signal towards the edge of the field of view. It has to be said, though, that in most confocal microscopes, almost alw ...
... In confocal microscopy, where the signal is determined by the overlap of the effective excitation and detection PSFs, the loss of register between them should lead to a reduction of signal towards the edge of the field of view. It has to be said, though, that in most confocal microscopes, almost alw ...
lab 1 GEO Optics
... Your group is working to develop and study new proteins. To analyze the composition of a protein mixture you have produced, the protein solution is placed in an electric field. Proteins with different total charges will drift at different speeds in the solution, and can be separated for further anal ...
... Your group is working to develop and study new proteins. To analyze the composition of a protein mixture you have produced, the protein solution is placed in an electric field. Proteins with different total charges will drift at different speeds in the solution, and can be separated for further anal ...
PreDesigner Manual
... For example, if you know that your optical system must have a focal length of f, a magnification of m’ and an object height of h, PreDesigner will draw the system paraxial layout and calculate the related object/image distances, magnification throw, image height and angles. However you are not limit ...
... For example, if you know that your optical system must have a focal length of f, a magnification of m’ and an object height of h, PreDesigner will draw the system paraxial layout and calculate the related object/image distances, magnification throw, image height and angles. However you are not limit ...
Handout Building the demonstration refractor tube
... bag. http://scientificsonline.com/ http://scientificsonline.com/product.asp?pn=3009445 (accessed 5/2006) ...
... bag. http://scientificsonline.com/ http://scientificsonline.com/product.asp?pn=3009445 (accessed 5/2006) ...
lenses - Van Buren Public Schools
... small angle of view, as shown in Figure 30.4a. When you are closer, the same object is seen through a larger angle of view, as illustrated in Figure 30.4b. This wider angle allows the perception of more detail. Magnification occurs when the use of a lens allows an image to be observed through a wide ...
... small angle of view, as shown in Figure 30.4a. When you are closer, the same object is seen through a larger angle of view, as illustrated in Figure 30.4b. This wider angle allows the perception of more detail. Magnification occurs when the use of a lens allows an image to be observed through a wide ...
© NCERT not to be republished
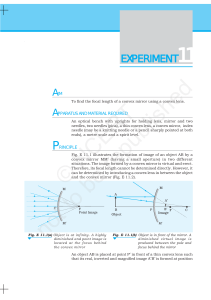
... A convex lens L1 converges the light rays starting from the object AB to form a real and inverted image A′B′ at position I1 [Fig. E 12.2(a)]. If a concave diverging lens L2 is inserted between the lens L1 and point I 1 as shown in Fig. E 12.2 (b), for concave lens L2 image A′ B′ behaves as virtual o ...
... A convex lens L1 converges the light rays starting from the object AB to form a real and inverted image A′B′ at position I1 [Fig. E 12.2(a)]. If a concave diverging lens L2 is inserted between the lens L1 and point I 1 as shown in Fig. E 12.2 (b), for concave lens L2 image A′ B′ behaves as virtual o ...
Ophthalmic lens
... To correct refractive errors along with ‘higher order aberrations’. Distortions that create problems such as double vision or halos at ...
... To correct refractive errors along with ‘higher order aberrations’. Distortions that create problems such as double vision or halos at ...
Strategies for the compensation of specimen
... however, one were able to choose any refractive index for the immersion medium, it would be possible, for a given focusing situation, to find the optimum value. If the immersion medium is not the same as that for which the lens was designed then the medium can be treated as an extra aberrating layer ...
... however, one were able to choose any refractive index for the immersion medium, it would be possible, for a given focusing situation, to find the optimum value. If the immersion medium is not the same as that for which the lens was designed then the medium can be treated as an extra aberrating layer ...
Lens Aberrations and Ray Tracing 1 Background
... point using a lens. The first “obvious” requirement is that the initial beam should be well collimated, sent along the axis of the optical system, and free of spherical aberrations. However, the power may still not be as high as you might expect at the focus. If you are using white light, the variou ...
... point using a lens. The first “obvious” requirement is that the initial beam should be well collimated, sent along the axis of the optical system, and free of spherical aberrations. However, the power may still not be as high as you might expect at the focus. If you are using white light, the variou ...
Ray Optics - Sakshi Education
... 1. Light is a form of energy which on striking the eye makes things visible (stimulates the sensation of vision). 2. A substance through which light can more or less pass is called optical medium. 3. A medium through which light can pass very easily is called transparent medium. 4. A medium through ...
... 1. Light is a form of energy which on striking the eye makes things visible (stimulates the sensation of vision). 2. A substance through which light can more or less pass is called optical medium. 3. A medium through which light can pass very easily is called transparent medium. 4. A medium through ...
Microscope
... Shorter wavelengths of light provide greater resolution. Under the best conditions, with violet light (wavelength = 0.4 um) and a numerical aperture of 1.4, the light microscope can theoretically achieve a limit of resolution of just under 0.2 pm. ...
... Shorter wavelengths of light provide greater resolution. Under the best conditions, with violet light (wavelength = 0.4 um) and a numerical aperture of 1.4, the light microscope can theoretically achieve a limit of resolution of just under 0.2 pm. ...
File
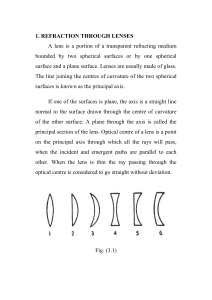
... 1. REFRACTION THROUGH LENSES A lens is a portion of a transparent refracting medium bounded by two spherical surfaces or by one spherical surface and a plane surface. Lenses are usually made of glass. The line joining the centres of curvature of the two spherical surfaces is know n as the principal ...
... 1. REFRACTION THROUGH LENSES A lens is a portion of a transparent refracting medium bounded by two spherical surfaces or by one spherical surface and a plane surface. Lenses are usually made of glass. The line joining the centres of curvature of the two spherical surfaces is know n as the principal ...
Variable Focus Video: Reconstructing Depth and Video
... scene motion on DFD algorithms. We show that, given accurate estimates of optical flow (OF), one can robustly warp the focal stack (FS) images to obtain a virtual static FS and apply traditional DFD algorithms on the static FS. Acquiring accurate OF in the presence of varying focal blur is a challen ...
... scene motion on DFD algorithms. We show that, given accurate estimates of optical flow (OF), one can robustly warp the focal stack (FS) images to obtain a virtual static FS and apply traditional DFD algorithms on the static FS. Acquiring accurate OF in the presence of varying focal blur is a challen ...
PPT
... • So is pupil size compared to eye pupil – dark adapted pupil up to 7 mm diameter (2–3 mm in daylight) – sets limit on minimum magnification (if you want to use the full aperture) • 210 mm aperture telescope must have M > 30 • for f/5 scope, means f2 < 35 mm; f/10 scope means f2 < 70 mm • 3.5-m scop ...
... • So is pupil size compared to eye pupil – dark adapted pupil up to 7 mm diameter (2–3 mm in daylight) – sets limit on minimum magnification (if you want to use the full aperture) • 210 mm aperture telescope must have M > 30 • for f/5 scope, means f2 < 35 mm; f/10 scope means f2 < 70 mm • 3.5-m scop ...
Report Liquid Lens
... the camera is a CMOS imager with a 640-by-480-pixel sensor array. Directly in front of the CMOS imager is a plastic lens, which allows the image to be projected sharply onto the flat CMOS image sensor. The eye does not need such a lens because the image sensor in the eye (the retina) is curved. In f ...
... the camera is a CMOS imager with a 640-by-480-pixel sensor array. Directly in front of the CMOS imager is a plastic lens, which allows the image to be projected sharply onto the flat CMOS image sensor. The eye does not need such a lens because the image sensor in the eye (the retina) is curved. In f ...
What is a Fresnel Lens?
... These circular ridges give the Fresnel lens a zigzag or sawtooth cross-section. Each sawtooth creates a tiny prism. By choosing appropriate powers for these prisms, designers can define the focal length and control image quality. Fresnel lenses are molded from precision opticalgrade acrylic. Typical ...
... These circular ridges give the Fresnel lens a zigzag or sawtooth cross-section. Each sawtooth creates a tiny prism. By choosing appropriate powers for these prisms, designers can define the focal length and control image quality. Fresnel lenses are molded from precision opticalgrade acrylic. Typical ...
F - mjburns.net
... cm from the centre of the lens. You want to use this lens to form a erect virtual image that is 1/3 the height of the object. Where should the object be placed? f = -20cm ...
... cm from the centre of the lens. You want to use this lens to form a erect virtual image that is 1/3 the height of the object. Where should the object be placed? f = -20cm ...
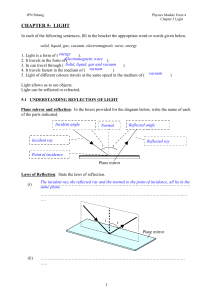
CHAPTER 5: LIGHT
... iii) The characteristics of the image formed by a magnifying glass are yang (real / virtual) ; (inverted / upright) ; (magnified /diminished) ; (on the same side as the object / on the opposite side of the object). iv) Greater magnification can be obtained by using a lens which has (long / short) fo ...
... iii) The characteristics of the image formed by a magnifying glass are yang (real / virtual) ; (inverted / upright) ; (magnified /diminished) ; (on the same side as the object / on the opposite side of the object). iv) Greater magnification can be obtained by using a lens which has (long / short) fo ...
INDIAN SCHOOL DARSAIT
... Image with magnification -1 means image is inverted and of the same size. Therefore, object is at 2F and the image is also at 2F on the other side of the lens. Therefore, distance between the object and its image is 4f = 60 cm f = 15 cm Object distance 2f = 30 cm. if the object is shifted towards th ...
... Image with magnification -1 means image is inverted and of the same size. Therefore, object is at 2F and the image is also at 2F on the other side of the lens. Therefore, distance between the object and its image is 4f = 60 cm f = 15 cm Object distance 2f = 30 cm. if the object is shifted towards th ...
Depth of field

In optics, particularly as it relates to film and photography, depth of field (DOF), also called focus range or effective focus range, is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image. Although a lens can precisely focus at only one distance at a time, the decrease in sharpness is gradual on each side of the focused distance, so that within the DOF, the unsharpness is imperceptible under normal viewing conditions.In some cases, it may be desirable to have the entire image sharp, and a large DOF is appropriate. In other cases, a small DOF may be more effective, emphasizing the subject while de-emphasizing the foreground and background. In cinematography, a large DOF is often called deep focus, and a small DOF is often called shallow focus.