A tutorial for designing fundamental imaging systems
... We should decide magnification of designed system according to the resolution of the image. We should decide it at first. Magnification for fundamental optical system is shown in Figure.3.1. There are 2 lenses and object with height of ho. Object is placed at front focal plane of an objective lens, ...
... We should decide magnification of designed system according to the resolution of the image. We should decide it at first. Magnification for fundamental optical system is shown in Figure.3.1. There are 2 lenses and object with height of ho. Object is placed at front focal plane of an objective lens, ...
Chapter 25
... The iris is the colored portion of the eye It is a muscular diaphragm that controls pupil size The iris regulates the amount of light entering the eye by dilating the pupil in low light conditions and contracting the pupil in high-light conditions The f-number of the eye is from about 2.8 to 16 ...
... The iris is the colored portion of the eye It is a muscular diaphragm that controls pupil size The iris regulates the amount of light entering the eye by dilating the pupil in low light conditions and contracting the pupil in high-light conditions The f-number of the eye is from about 2.8 to 16 ...
3.0Mb PDF - David Kleinfeld
... terms of minimizing the time to travel between two points is given in appendix A. We consider a ray that propagates from a material with index n1 to one with index n2. The ray is incident at an angle &1 relative to the normal to the interface. Snells’ law relates the exit angle, &2, to the indices a ...
... terms of minimizing the time to travel between two points is given in appendix A. We consider a ray that propagates from a material with index n1 to one with index n2. The ray is incident at an angle &1 relative to the normal to the interface. Snells’ law relates the exit angle, &2, to the indices a ...
Can Fermat`s Principle accurately predict lens focusing? - TEM-EELS
... Equation (1) is known as the Lensmaker’s Formula and its derivation involves small-angle approximations, meaning that fp is a paraxial focal length, only valid for rays that travel close to the optic axis. A thin-lens version of Eq.(1) is fp = (0.5)R /(n-1). The focusing power can be deduced much mo ...
... Equation (1) is known as the Lensmaker’s Formula and its derivation involves small-angle approximations, meaning that fp is a paraxial focal length, only valid for rays that travel close to the optic axis. A thin-lens version of Eq.(1) is fp = (0.5)R /(n-1). The focusing power can be deduced much mo ...
EE119 Homework 7: Microscopes, Projectors and Photomultiplier
... The positive solution to this quadratic equation is fo = 0.5. Notice that if the working distance were larger, then fo could be larger too. But let’s use fo = 0.5here. This means that the eyepiece focal length should be 8/(3×0.5)=16/3=5.333 cm. Now we need to find some diameters for these lenses. Fo ...
... The positive solution to this quadratic equation is fo = 0.5. Notice that if the working distance were larger, then fo could be larger too. But let’s use fo = 0.5here. This means that the eyepiece focal length should be 8/(3×0.5)=16/3=5.333 cm. Now we need to find some diameters for these lenses. Fo ...
mirrors and lenses - Appoquinimink High School
... OBJECTS FROM FAR AWAY If objects are infinitely far away from a mirror (The sun, the stars, etc), the rays would be precisely parallel. The law of reflection holds for each of the parallel rays, but they will not all reflect to be brought to a single point. This causes an unfocused image. ...
... OBJECTS FROM FAR AWAY If objects are infinitely far away from a mirror (The sun, the stars, etc), the rays would be precisely parallel. The law of reflection holds for each of the parallel rays, but they will not all reflect to be brought to a single point. This causes an unfocused image. ...
Spherical mirrors in the paraxial approximation [Pages 181-187]. Assignment 2
... (b) At what object distance (in terms of lens focal length) the magnification is one. What does this mean? In some cases in optical spectroscopy this configuration becomes important. Why? 3. Bessel Method: In this case the distance between the object and the screen, L, is fixed. If the lens is moved ...
... (b) At what object distance (in terms of lens focal length) the magnification is one. What does this mean? In some cases in optical spectroscopy this configuration becomes important. Why? 3. Bessel Method: In this case the distance between the object and the screen, L, is fixed. If the lens is moved ...
Lab 7, The Basics of Optics and Telescopes
... QUESTION: In the context of the previous question, which will be more effective for gathering light, a lens with a larger diameter, or a lens with a smaller diameter? ______________________________________________________________________________________ QUESTION: If two lenses have the same focal le ...
... QUESTION: In the context of the previous question, which will be more effective for gathering light, a lens with a larger diameter, or a lens with a smaller diameter? ______________________________________________________________________________________ QUESTION: If two lenses have the same focal le ...
Chapter 25
... It is a muscular diaphragm that controls pupil size The iris regulates the amount of light entering the eye by dilating the pupil in low light conditions and contracting the pupil in high-light conditions The f-number of the eye is from about 2.8 to 16 ...
... It is a muscular diaphragm that controls pupil size The iris regulates the amount of light entering the eye by dilating the pupil in low light conditions and contracting the pupil in high-light conditions The f-number of the eye is from about 2.8 to 16 ...
Thin Lenses
... surfaces (R1 and R2) and to the index of refraction, n, of the lens material. Sign convention of lens radii R1 and R2 The signs of the lens radii indicate whether the corresponding surfaces are convex (R > 0, bulging outwards from the lens) or concave (R < 0, depressed into the lens). If R is infini ...
... surfaces (R1 and R2) and to the index of refraction, n, of the lens material. Sign convention of lens radii R1 and R2 The signs of the lens radii indicate whether the corresponding surfaces are convex (R > 0, bulging outwards from the lens) or concave (R < 0, depressed into the lens). If R is infini ...
Document
... Some stage micrometers are finely divided only at one end. One of the larger divisions is positioned at one edge of the field of view, so that the fine part of the scale overlaps the opposite side. The field diameter ca then be determined to the maximum available precision ...
... Some stage micrometers are finely divided only at one end. One of the larger divisions is positioned at one edge of the field of view, so that the fine part of the scale overlaps the opposite side. The field diameter ca then be determined to the maximum available precision ...
9-26 Geometrical Optics
... than the edges and it has a higher index than the surrounding medium) R>0 if the center of curvature is after the surface (i.e. the light rays are incident on a convex surface) so>0 and si>0 if they are on opposite sides of the mirror ...
... than the edges and it has a higher index than the surrounding medium) R>0 if the center of curvature is after the surface (i.e. the light rays are incident on a convex surface) so>0 and si>0 if they are on opposite sides of the mirror ...
Chapter 25
... It is a muscular diaphragm that controls pupil size The iris regulates the amount of light entering the eye by dilating the pupil in low light conditions and contracting the pupil in high-light conditions The f-number of the eye is from about 2.8 to 16 ...
... It is a muscular diaphragm that controls pupil size The iris regulates the amount of light entering the eye by dilating the pupil in low light conditions and contracting the pupil in high-light conditions The f-number of the eye is from about 2.8 to 16 ...
Lecture 31 - Purdue Physics
... Chief ray: any ray from an object point that passes through the middle of the aperture stop It is effectively the central ray of the bundle emerging from a point on an object that can get through the aperture. Importance: aberrations in optical systems ...
... Chief ray: any ray from an object point that passes through the middle of the aperture stop It is effectively the central ray of the bundle emerging from a point on an object that can get through the aperture. Importance: aberrations in optical systems ...
6.2 Refraction
... • the f-number of a lens is given by the focal length divided by the diameter, f/# = f/D • the f-number is used as a metric for the _____________ that can be gathered from a point source - the lower the value the higher the collection efficiency • referring to the figure it can be seen that the frac ...
... • the f-number of a lens is given by the focal length divided by the diameter, f/# = f/D • the f-number is used as a metric for the _____________ that can be gathered from a point source - the lower the value the higher the collection efficiency • referring to the figure it can be seen that the frac ...
Exam 4 Solutions
... 16. An individual has a near point of 13 cm and a far point of 40 | 35 | 45 cm. What is her new near point when her nearsightedness is corrected? Answer: 19 cm | 21 cm | 18 cm Solution: Nearsightedness is corrected by making the image of an object at infinity appear at the person’s far point. Let’s ...
... 16. An individual has a near point of 13 cm and a far point of 40 | 35 | 45 cm. What is her new near point when her nearsightedness is corrected? Answer: 19 cm | 21 cm | 18 cm Solution: Nearsightedness is corrected by making the image of an object at infinity appear at the person’s far point. Let’s ...
February 6 pptx
... and object distances can be measured from the eye. One wants the position of the virtual image of the correctional lens (q) q = - patient’s near point when p = 25 cm (normal near point): 1/f = 1/25cm - 1/near point. Example, if near point = 50 cm, one needs 1/f = 1/25cm - 1/50cm = +1/50cm f = 50 c ...
... and object distances can be measured from the eye. One wants the position of the virtual image of the correctional lens (q) q = - patient’s near point when p = 25 cm (normal near point): 1/f = 1/25cm - 1/near point. Example, if near point = 50 cm, one needs 1/f = 1/25cm - 1/50cm = +1/50cm f = 50 c ...
Introduction
... To visualize the f-number, consider a lens with a positive focal length illuminated uniformly with collimated light. The f-number defines the angle of the cone of light leaving the lens which ultimately forms the image. This is an important concept when the throughput or light-gathering power of an ...
... To visualize the f-number, consider a lens with a positive focal length illuminated uniformly with collimated light. The f-number defines the angle of the cone of light leaving the lens which ultimately forms the image. This is an important concept when the throughput or light-gathering power of an ...
Optical Term Definitions
... Often, positive lenses intended for use as simple magnifiers are rated with a single magnification, such as 4 x. To create a virtual image for viewing with the human eye, in principle, any positive lens can be used at an infinite number of possible magnifications. However, there is usually a narrow ...
... Often, positive lenses intended for use as simple magnifiers are rated with a single magnification, such as 4 x. To create a virtual image for viewing with the human eye, in principle, any positive lens can be used at an infinite number of possible magnifications. However, there is usually a narrow ...
lab9 - University of Puget Sound
... Or the right half, or what? Explain your observations. Describe what happens when the object distance is less than the focal length. Can you focus the image on a card? Can you see the image? If so, describe its properties. Finally, place the light source at one end of the optical rail and the white ...
... Or the right half, or what? Explain your observations. Describe what happens when the object distance is less than the focal length. Can you focus the image on a card? Can you see the image? If so, describe its properties. Finally, place the light source at one end of the optical rail and the white ...
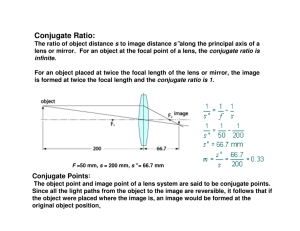
Conjugate Ratio:
... because only the first terms of the sine expansions are used. Design of any optical system starts with this approximation. The assumption that sin θ = θ is reasonably valid for θ close to zero (i.e., high f-number lenses). With more highly curved surfaces (and particularly marginal rays), paraxial t ...
... because only the first terms of the sine expansions are used. Design of any optical system starts with this approximation. The assumption that sin θ = θ is reasonably valid for θ close to zero (i.e., high f-number lenses). With more highly curved surfaces (and particularly marginal rays), paraxial t ...
Chapter 25: Optical Instruments
... objects do not become a blur on film), we want a small diameter lens opening. Different films are made to work faster or slower, in dimmer or brighter light with more or less grain. The choice of settings takes fine judgment about the desired image. A longer focal length lens produces a larger image ...
... objects do not become a blur on film), we want a small diameter lens opening. Different films are made to work faster or slower, in dimmer or brighter light with more or less grain. The choice of settings takes fine judgment about the desired image. A longer focal length lens produces a larger image ...
Ray Diagram PRELAB LAB
... Part 1: The Converging Lens: The Bench A. Set up the lens apparatus as shown by your instructor. Using focal length of your lens using an object that is very far away – across the street. B. Place the object light at a distance further than the focal length and move the screen until you bring the im ...
... Part 1: The Converging Lens: The Bench A. Set up the lens apparatus as shown by your instructor. Using focal length of your lens using an object that is very far away – across the street. B. Place the object light at a distance further than the focal length and move the screen until you bring the im ...
Depth-of-Focus in Microscopy
... these descriptions do not agree. In general, the authors propose that ∆z should be a function of the wavelength of light, λ , the numerical aperture of the objective lens NA, the index of refraction, n, and the total magnification of the optical system M. The numerical aperture is defined as NA = n• ...
... these descriptions do not agree. In general, the authors propose that ∆z should be a function of the wavelength of light, λ , the numerical aperture of the objective lens NA, the index of refraction, n, and the total magnification of the optical system M. The numerical aperture is defined as NA = n• ...
Depth of field

In optics, particularly as it relates to film and photography, depth of field (DOF), also called focus range or effective focus range, is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image. Although a lens can precisely focus at only one distance at a time, the decrease in sharpness is gradual on each side of the focused distance, so that within the DOF, the unsharpness is imperceptible under normal viewing conditions.In some cases, it may be desirable to have the entire image sharp, and a large DOF is appropriate. In other cases, a small DOF may be more effective, emphasizing the subject while de-emphasizing the foreground and background. In cinematography, a large DOF is often called deep focus, and a small DOF is often called shallow focus.





![Spherical mirrors in the paraxial approximation [Pages 181-187]. Assignment 2](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008539460_1-d375c81ee0822c3c0b88887d5bbb056f-300x300.png)