Angles and the Pythagorean Theorem
... the distance from the floor to the landing.) and the total run is 12ft. (That is the total distance the stairs must travel parallel to the floor.) To find the stringer (the length of the board for the steps) So we would use the Pythagorean theorem because those three dimensions form a right triangle ...
... the distance from the floor to the landing.) and the total run is 12ft. (That is the total distance the stairs must travel parallel to the floor.) To find the stringer (the length of the board for the steps) So we would use the Pythagorean theorem because those three dimensions form a right triangle ...
Recall from yesterday the two conjectures that you derived about the
... ***Remember: The Reflexive Property of Congruence was covered in Chapter 2 page 106. An included angle is________________________________________________________. In order for the SAS Conjecture to be valid, the angle chosen MUST be the one included between the two chosen sides! Not just any old ang ...
... ***Remember: The Reflexive Property of Congruence was covered in Chapter 2 page 106. An included angle is________________________________________________________. In order for the SAS Conjecture to be valid, the angle chosen MUST be the one included between the two chosen sides! Not just any old ang ...
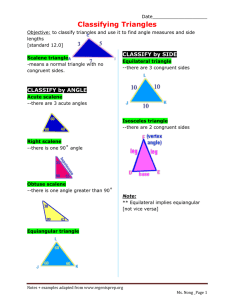
subject
... Students will be able to identify and use AA, SAS, and SSS similarity to solve a variety of problems including real world applications. Core Content for Assessment: MA-11-3.1.6 Students will apply the concepts of congruence and similarity to solve real world problems. ...
... Students will be able to identify and use AA, SAS, and SSS similarity to solve a variety of problems including real world applications. Core Content for Assessment: MA-11-3.1.6 Students will apply the concepts of congruence and similarity to solve real world problems. ...
Postulate 4-1
... If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. ...
... If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. ...