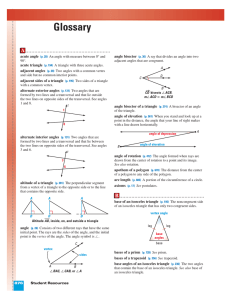
9/18 homework
... 3. Leg, Base = ½ m (Leg) 4. Base, Leg = ½ m (Base) 5. Base, Leg = 2 m (Base) 6. Base angle, Leg (therefore 2 angles , and 2 sides) 7. Base angle, Base 8. Given the vertex angle, find the base angles (by construction) 10/28 homework ...
... 3. Leg, Base = ½ m (Leg) 4. Base, Leg = ½ m (Base) 5. Base, Leg = 2 m (Base) 6. Base angle, Leg (therefore 2 angles , and 2 sides) 7. Base angle, Base 8. Given the vertex angle, find the base angles (by construction) 10/28 homework ...
Maths E3 GCSE - Churchill Park School
... Objective: To calculate the perimeter and area of quadrilaterals Success Criteria: Support: I can measure and calculate the perimeter of a rectilinear figure (including squares) in centimetres and metres. I can find the areas of rectilinear shapes by counting. (S14) Core: Calculate the area of quadr ...
... Objective: To calculate the perimeter and area of quadrilaterals Success Criteria: Support: I can measure and calculate the perimeter of a rectilinear figure (including squares) in centimetres and metres. I can find the areas of rectilinear shapes by counting. (S14) Core: Calculate the area of quadr ...
Statistics Test
... • When we join 6 equilateral triangles at a vertex, what happens? Can you make a polyhedron with 6 equilateral triangles at a vertex? __ • Is it possible to put more than 6 equilateral triangles at a vertex to form a polyhedron? __ • Name the only three regular polyhedra that can be made using cong ...
... • When we join 6 equilateral triangles at a vertex, what happens? Can you make a polyhedron with 6 equilateral triangles at a vertex? __ • Is it possible to put more than 6 equilateral triangles at a vertex to form a polyhedron? __ • Name the only three regular polyhedra that can be made using cong ...