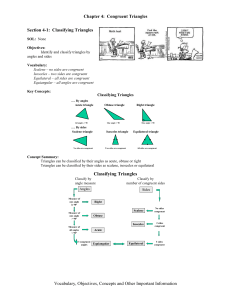
Chapter 4: Congruent Triangles Classifying Triangles
... Chapter 4: Congruent Triangles Section 4-2: Angles of Triangles SOL: None Objectives: Apply the Angle Sum Theorem Apply the Exterior Angle Theorem Vocabulary: Exterior Angle: is formed by one side of a triangle and the extension of another side Remote Interior Angle: interior angles not adjacent to ...
... Chapter 4: Congruent Triangles Section 4-2: Angles of Triangles SOL: None Objectives: Apply the Angle Sum Theorem Apply the Exterior Angle Theorem Vocabulary: Exterior Angle: is formed by one side of a triangle and the extension of another side Remote Interior Angle: interior angles not adjacent to ...
content domain geometry propoerties of shape
... whole turn (total 360°) - angles at a point on a straight line and ½ a turn (total 180°) - other multiples of 90° ...
... whole turn (total 360°) - angles at a point on a straight line and ½ a turn (total 180°) - other multiples of 90° ...
4 Right Triangle Geometry
... a building. Mrs. Hannon, the building’s owner, has given specific instructions that the plants and shrubs around the base of the building are not to be disturbed in any way. Carrie, a worker for Dish It Out, must choose a ladder that will be long enough to reach the roof of the building while not di ...
... a building. Mrs. Hannon, the building’s owner, has given specific instructions that the plants and shrubs around the base of the building are not to be disturbed in any way. Carrie, a worker for Dish It Out, must choose a ladder that will be long enough to reach the roof of the building while not di ...
Chapter 6 Halving segments
... halving segments. To show this, start with a vertical line p that crosses k halving segments. Assume without loss of generality that p has at most n/2 vertices on its left. Start translating p to the left. The number of halving segments intersected by p changes only when p passes through a vertex, a ...
... halving segments. To show this, start with a vertical line p that crosses k halving segments. Assume without loss of generality that p has at most n/2 vertices on its left. Start translating p to the left. The number of halving segments intersected by p changes only when p passes through a vertex, a ...