Unit 1, Chapter 1 Test Review Key Issue 1: How Do Geographers
... century to be the final arbiter of names on U.S. maps. In recent years the board has been especially concerned with removing offensive place names. Site The term site makes reference to the physical characteristics of a place. Important site characteristics include climate, water sources, topography ...
... century to be the final arbiter of names on U.S. maps. In recent years the board has been especially concerned with removing offensive place names. Site The term site makes reference to the physical characteristics of a place. Important site characteristics include climate, water sources, topography ...
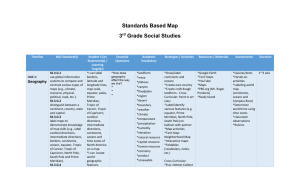
Chapter 1: Studying Geography
... • How many oceans are there? – Four: Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic ...
... • How many oceans are there? – Four: Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic ...
geography - South Stanley Junior School
... describe and understand key aspects of physical geography including climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, use the eight points of a compass, four and six‐figure grid references, symbols and keys (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom a ...
... describe and understand key aspects of physical geography including climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, use the eight points of a compass, four and six‐figure grid references, symbols and keys (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom a ...
Earth Science!!!!!! Chapter 1 – Intro to Earth Science Section 1.1
... either too small, too big, or out of place. Mapmakers have, however, found ways to limit the distortion of shape, size, distance, and direction. The Mercator Projection o Gerardus Mercator created this map to help sailors navigate the world in 1569 Figure 10 pg 12 Although the sizes and distance ...
... either too small, too big, or out of place. Mapmakers have, however, found ways to limit the distortion of shape, size, distance, and direction. The Mercator Projection o Gerardus Mercator created this map to help sailors navigate the world in 1569 Figure 10 pg 12 Although the sizes and distance ...
Spatial Skills Vocabulary
... GIS – geographic information system; any system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on the Earth’s surface. (NatGeo Education, 2014) GPS – global positing system; system of satellites and receiving devices used to determine the location of something on Earth. ( ...
... GIS – geographic information system; any system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on the Earth’s surface. (NatGeo Education, 2014) GPS – global positing system; system of satellites and receiving devices used to determine the location of something on Earth. ( ...
Introduction to Human Geography
... Once you think about different types of diffusion, you will be tempted to figure out what kind of diffusion is taking place for all sorts of goods, ideas, or diseases. Please remember any good, idea or disease can diffuse in more than one way. Choose a good, idea, or disease as an example and descr ...
... Once you think about different types of diffusion, you will be tempted to figure out what kind of diffusion is taking place for all sorts of goods, ideas, or diseases. Please remember any good, idea or disease can diffuse in more than one way. Choose a good, idea, or disease as an example and descr ...
a) See the second attach b) Two teams, one from tower A and
... two rays are. We could put two points A and B on the two rays, and the angle doesn’t ...
... two rays are. We could put two points A and B on the two rays, and the angle doesn’t ...
Unit 1 and 2 Study Guide Directions: Answer each question
... Step 1: Find the compass rose and scale on the map. Use these tools to estimate the size of Europe from north to south and from east to west. Step 2: Look at the natural resource symbols on the map. On the map legend, circle the three or four most common resources you see on the map. Step 3: Study t ...
... Step 1: Find the compass rose and scale on the map. Use these tools to estimate the size of Europe from north to south and from east to west. Step 2: Look at the natural resource symbols on the map. On the map legend, circle the three or four most common resources you see on the map. Step 3: Study t ...
Chapter 18 Asia and the Pacific Worksheet (1) File
... Chapter 18 Section 2 Climate and Vegetation Questions pages 580 to 583 13. Use the information under Key Terms section on page 580. What is the difference between monsoons and typhoons? 14. How do monsoons affect the climate of East Asia? Use page 581 for reference. Chapter 18 Section 3 Natural Reso ...
... Chapter 18 Section 2 Climate and Vegetation Questions pages 580 to 583 13. Use the information under Key Terms section on page 580. What is the difference between monsoons and typhoons? 14. How do monsoons affect the climate of East Asia? Use page 581 for reference. Chapter 18 Section 3 Natural Reso ...
Seeing the World Like a Geographer
... GlobalVegetationZones Geographers study where different plants grow by dividing the world into vegetation zones. In each zone, a certain mix of plants has adapted to similar conditions. Like climate zones, vegetation zones are affected by their location on Earth. They range from the barren ice cap z ...
... GlobalVegetationZones Geographers study where different plants grow by dividing the world into vegetation zones. In each zone, a certain mix of plants has adapted to similar conditions. Like climate zones, vegetation zones are affected by their location on Earth. They range from the barren ice cap z ...
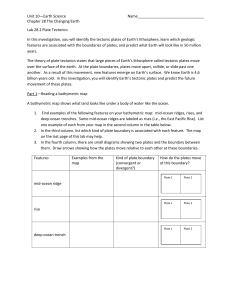
Chapter 28 Plate Tectonics Lab
... deep ocean trenches. Some mid-ocean ridges are labeled as rises (i.e., the East Pacific Rise). List one example of each from your map in the second column in the table below. 2. In the third column, list which kind of plate boundary is associated with each feature. The map on the last page of this l ...
... deep ocean trenches. Some mid-ocean ridges are labeled as rises (i.e., the East Pacific Rise). List one example of each from your map in the second column in the table below. 2. In the third column, list which kind of plate boundary is associated with each feature. The map on the last page of this l ...
Geography - Warren County Schools
... of geography we study in order to make connections to the world and how we interact with it: Location Place Movement Region Human-Environmental Interaction ...
... of geography we study in order to make connections to the world and how we interact with it: Location Place Movement Region Human-Environmental Interaction ...
Lesson 2 - A Spatial Way of Thinking
... one area as a business region, another as a shopping region, and still another as a residential region. Each region looks different, has a different purpose, and has different requirements. Geographers define regions in several ways. The Sunbelt is a region defined by physical, or natural, features. ...
... one area as a business region, another as a shopping region, and still another as a residential region. Each region looks different, has a different purpose, and has different requirements. Geographers define regions in several ways. The Sunbelt is a region defined by physical, or natural, features. ...
Classroom Activities KS2 A3
... DME: Planning for Tectonic Hazards - Activity Sheet Introduction 1. Put the section title Introduction. ...
... DME: Planning for Tectonic Hazards - Activity Sheet Introduction 1. Put the section title Introduction. ...
Post Assessment Grade 4
... C. It tells what the different symbols on a map mean. D. It shows the distance from one place to another. ...
... C. It tells what the different symbols on a map mean. D. It shows the distance from one place to another. ...
GEOL 10: Environmental Geology Activity 9: Topographic Maps and
... Activity 9: Topographic Maps and Mt. St. Helens Name: ________________________________________________ Date: ________________ ...
... Activity 9: Topographic Maps and Mt. St. Helens Name: ________________________________________________ Date: ________________ ...
Monday, June 13, 2016 INNER PLANET DELIGHT: MERCURY AND
... Preparing the First Global Geological Map of Mercury [#7027] Previous to the MESSENGER spacecraft mission to Mercury, only half the globe was mapped using the Mariner 10 spacecraft imagery. Preparation of the new global geological map is discussed. ...
... Preparing the First Global Geological Map of Mercury [#7027] Previous to the MESSENGER spacecraft mission to Mercury, only half the globe was mapped using the Mariner 10 spacecraft imagery. Preparation of the new global geological map is discussed. ...
Map projection

Commonly, a map projection is a systematic transformation of the latitudes and longitudes of locations on the surface of a sphere or an ellipsoid into locations on a plane. Map projections are necessary for creating maps. All map projections distort the surface in some fashion. Depending on the purpose of the map, some distortions are acceptable and others are not; therefore, different map projections exist in order to preserve some properties of the sphere-like body at the expense of other properties. There is no limit to the number of possible map projections.More generally, the surfaces of planetary bodies can be mapped even if they are too irregular to be modeled well with a sphere or ellipsoid; see below. Even more generally, projections are the subject of several pure mathematical fields, including differential geometry and projective geometry. However, ""map projection"" refers specifically to a cartographic projection.