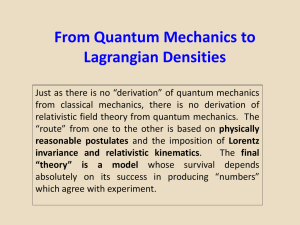
Lecture6.QM.to.Lagrangian.Densities
... Quantization arises from placing boundary conditions on the wave function. It is a mathematical result! ...
... Quantization arises from placing boundary conditions on the wave function. It is a mathematical result! ...
Molekylfysik - Leiden Univ
... constructive interference occurs when =2d sin. Davidsson and Germer showed also interference phenomenon but with electrons! ...
... constructive interference occurs when =2d sin. Davidsson and Germer showed also interference phenomenon but with electrons! ...
Lecture 1
... -Quantum theory may be more than a way of modeling the physical world… it may be a more accurate representation of reality than the physical objects we currently believe to exist -Quantum theory may be an imperfect representation of a physical world that we don’t yet understand -Our applications of ...
... -Quantum theory may be more than a way of modeling the physical world… it may be a more accurate representation of reality than the physical objects we currently believe to exist -Quantum theory may be an imperfect representation of a physical world that we don’t yet understand -Our applications of ...
Presentation - University of Colorado Boulder
... function simultaneously and do not read out the result until a useful outout is expected with reasonably high probability. Use entanglement: measurement of states can be highly correlated ...
... function simultaneously and do not read out the result until a useful outout is expected with reasonably high probability. Use entanglement: measurement of states can be highly correlated ...
Fiziev
... not from the interval. Thus we see that the notion of “black holes” is based on presence of Schwarzschild singularity, which is in contradiction of the basics of general relativity…” ...
... not from the interval. Thus we see that the notion of “black holes” is based on presence of Schwarzschild singularity, which is in contradiction of the basics of general relativity…” ...
Document
... ” …not a mechanical influence … … an influence on the very conditions which define the possible types of predictions regarding the future behavior of the system.” ...
... ” …not a mechanical influence … … an influence on the very conditions which define the possible types of predictions regarding the future behavior of the system.” ...
Feynman Lectures on Physics
... particle to add to the electron, the proton, and the neutron. That new particle is called a photon. The new view of the interaction of electrons and protons that is electromagnetic theory, but with everything quantum-mechanically correct, is called quantum electrodynamics. This fundamental theory ...
... particle to add to the electron, the proton, and the neutron. That new particle is called a photon. The new view of the interaction of electrons and protons that is electromagnetic theory, but with everything quantum-mechanically correct, is called quantum electrodynamics. This fundamental theory ...
Quantum phenomena
... Aim: Find rules for particles interactions and transformations. Method: Collide particles at high energy to produce interactions and transformations, then track and analyse resulting particles. Particle creation and annihilation follows E = mc2. ...
... Aim: Find rules for particles interactions and transformations. Method: Collide particles at high energy to produce interactions and transformations, then track and analyse resulting particles. Particle creation and annihilation follows E = mc2. ...
Quantum Complexity and Fundamental Physics
... “A quantum computer is obviously just a souped-up analog computer: continuous voltages, continuous amplitudes, what’s the difference?” “A quantum computer with 400 qubits would have ~2400 classical bits, so it would violate a cosmological entropy bound” “My classical cellular automaton model can exp ...
... “A quantum computer is obviously just a souped-up analog computer: continuous voltages, continuous amplitudes, what’s the difference?” “A quantum computer with 400 qubits would have ~2400 classical bits, so it would violate a cosmological entropy bound” “My classical cellular automaton model can exp ...
Quantum Mechanical Model - Elmwood Park Memorial Middle School
... Quantum Mechanical Model • From Heisenberg’s principle we know that we can’t exactly locate electrons • We can determine probable locations… general areas • Schrodinger created an equation for solving these locations, but it has only been completely solved for hydrogen Why hydrogen? The m ...
... Quantum Mechanical Model • From Heisenberg’s principle we know that we can’t exactly locate electrons • We can determine probable locations… general areas • Schrodinger created an equation for solving these locations, but it has only been completely solved for hydrogen Why hydrogen? The m ...
poster
... itself, and then collapses to a point upon detection. Copenhagen/Agnostic (C/A): Electrons are modeled in terms of waves or particles accordingly; emphasis on mathematical calculation (predicting features of the interference pattern) over interpretation. ...
... itself, and then collapses to a point upon detection. Copenhagen/Agnostic (C/A): Electrons are modeled in terms of waves or particles accordingly; emphasis on mathematical calculation (predicting features of the interference pattern) over interpretation. ...
Atomic Diffraction Dr. Janine Shertzer College of the Holy Cross
... The wave-particle duality is fundamental to quantum mechanics. Light can behave like a particle (photon); matter can behave like a wave. The wavelength associated with a particle is inversely proportional to its momentum p: λ = h / p, where h is Planck’s constant. For cold atoms, the wavelength is l ...
... The wave-particle duality is fundamental to quantum mechanics. Light can behave like a particle (photon); matter can behave like a wave. The wavelength associated with a particle is inversely proportional to its momentum p: λ = h / p, where h is Planck’s constant. For cold atoms, the wavelength is l ...