What Does Quantum Mechanics Suggest About Our
... Quantum indeterminacy is the unavoidable fact that not all quantities can simultaneously have determinate values. For example, if an electron has a location, then it simply has no speed – it is neither at rest, nor is it moving slowly, nor is it moving quickly. There simply is no fact of the matter ...
... Quantum indeterminacy is the unavoidable fact that not all quantities can simultaneously have determinate values. For example, if an electron has a location, then it simply has no speed – it is neither at rest, nor is it moving slowly, nor is it moving quickly. There simply is no fact of the matter ...
SAND Quantum Theory of What
... obtaining a specific result, such as position or velocity, in a specific measurement on a specific quantum object. • That’s all it says. • But there is no agreement on what a quantum object is! ...
... obtaining a specific result, such as position or velocity, in a specific measurement on a specific quantum object. • That’s all it says. • But there is no agreement on what a quantum object is! ...
Modern Physics Lesson 3
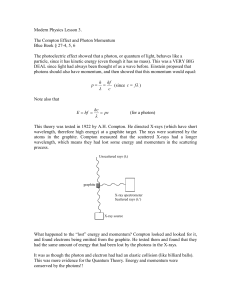
... Conclusion: A photon is a particle of light that has energy and momentum. However, photons have no mass and travel at the speed of light, c. deBroglie Wavelength Louis deBroglie proposed in 1923 that if waves behave like particles, then particles should also behave like waves! This was the beginnin ...
... Conclusion: A photon is a particle of light that has energy and momentum. However, photons have no mass and travel at the speed of light, c. deBroglie Wavelength Louis deBroglie proposed in 1923 that if waves behave like particles, then particles should also behave like waves! This was the beginnin ...
Chapter 7: Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
... • Werner Heisenberg - showed that it is impossible to know (or measure) precisely both the position and velocity (or the momentum) at the same time. • The simple act of “seeing” an electron would change ...
... • Werner Heisenberg - showed that it is impossible to know (or measure) precisely both the position and velocity (or the momentum) at the same time. • The simple act of “seeing” an electron would change ...
Document
... for any smooth function ("classical observable") f∈C∞(T*X). In other words, Hamilton's equations say that the rate of change of the observed value of f equals the observed value of {f, H}. Note that for a given Lagrangian, the unique function H (up to adding a constant) for which equations (21) are ...
... for any smooth function ("classical observable") f∈C∞(T*X). In other words, Hamilton's equations say that the rate of change of the observed value of f equals the observed value of {f, H}. Note that for a given Lagrangian, the unique function H (up to adding a constant) for which equations (21) are ...
A Vlasov Equation for Quantized Meson Field
... *Define creation/annihilation ops. & construct N×N Wigner functions: ...
... *Define creation/annihilation ops. & construct N×N Wigner functions: ...
CHAPTER 2. LAGRANGIAN QUANTUM FIELD THEORY §2.1
... the Euler-Lagrange equations. In general we will ignore these ordering questions at first and use the definition of operators and field equations suggested by the classical theory. So when a specific composite operator, like H or P µ , is defined we will keep the order fixed according to that defini ...
... the Euler-Lagrange equations. In general we will ignore these ordering questions at first and use the definition of operators and field equations suggested by the classical theory. So when a specific composite operator, like H or P µ , is defined we will keep the order fixed according to that defini ...
Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom
... • Photon emission occurs upon orbital trans. • Angular momentum is quantized. ...
... • Photon emission occurs upon orbital trans. • Angular momentum is quantized. ...
Document
... de Broglie’s intriguing idea of “matter wave” (1924) Extend notation of “wave-particle duality” from light to matter For photons, P E hf h ...
... de Broglie’s intriguing idea of “matter wave” (1924) Extend notation of “wave-particle duality” from light to matter For photons, P E hf h ...
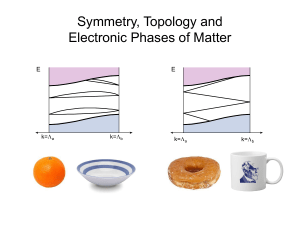
Symmetry, Topology and Electronic Phases of Matter
... strong interactions Strongly interacting systems can exhibit intrinsic topological order, which is distinct from band topology in insulators. ...
... strong interactions Strongly interacting systems can exhibit intrinsic topological order, which is distinct from band topology in insulators. ...
How Einstein Swept Retrocausality Under the Rug
... reason why no light is emitted by black holes. UÊ SÊ upercausal times would characterize systems in which diverging and converging forces are balanced. An example is offered by atoms and quantum mechanics. In these systems causality and retrocausality coexist, and time is unitary: past, present, and ...
... reason why no light is emitted by black holes. UÊ SÊ upercausal times would characterize systems in which diverging and converging forces are balanced. An example is offered by atoms and quantum mechanics. In these systems causality and retrocausality coexist, and time is unitary: past, present, and ...
First lecture, 7.10.03
... both properties defined – and give all those knowledge of Sz... and the wave function is all you can possibly know. EPR are cheating, discussing measurements they didn’t do. ...
... both properties defined – and give all those knowledge of Sz... and the wave function is all you can possibly know. EPR are cheating, discussing measurements they didn’t do. ...
Chapter 4: Symmetries
... simplifying calculations as well as results.1 For example, in most cases QFT’s have some symmetry of space and time. Particularly in fundamental particle physics all models have relativistic invariance or Poincaré symmetry. Symmetries are some transformations of the fields φ → φ0 that map solutions ...
... simplifying calculations as well as results.1 For example, in most cases QFT’s have some symmetry of space and time. Particularly in fundamental particle physics all models have relativistic invariance or Poincaré symmetry. Symmetries are some transformations of the fields φ → φ0 that map solutions ...