The integer quantum Hall effect II
... In the last lecture we have seen that for spinless fermions and for a time-reversal invariant system all states are localized in two spatial dimensions. How can we reconcile this with the above argument for the quantization of xy . The answer is, that for the case of a magnetic field, where time rev ...
... In the last lecture we have seen that for spinless fermions and for a time-reversal invariant system all states are localized in two spatial dimensions. How can we reconcile this with the above argument for the quantization of xy . The answer is, that for the case of a magnetic field, where time rev ...
berezinskii-kosterlitz-thouless transition and the haldane conjecture
... There are classes of systems, which may look quite different, In the limit ξ → ∞, the spacing between the lattice points but which share the same critical behavior, so we say that they becomes insignificant (it is negligible compared to ξ), so this belong to the same universality class. This means i ...
... There are classes of systems, which may look quite different, In the limit ξ → ∞, the spacing between the lattice points but which share the same critical behavior, so we say that they becomes insignificant (it is negligible compared to ξ), so this belong to the same universality class. This means i ...
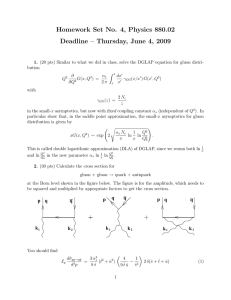
Homework Set No. 4, Physics 880.02
... with the Mandelstam variables ŝ = (k1 + k2 )2 , t̂ = (k1 − p)2 , û = (k2 − p)2 . The factor of 2 in front of the δ-function in Eq. (1) comes from the fact that either the quark or the antiquark can carry momentum p. (q and q̄ in the figure denote the quark and the antiquark. Time flows upward.) A ...
... with the Mandelstam variables ŝ = (k1 + k2 )2 , t̂ = (k1 − p)2 , û = (k2 − p)2 . The factor of 2 in front of the δ-function in Eq. (1) comes from the fact that either the quark or the antiquark can carry momentum p. (q and q̄ in the figure denote the quark and the antiquark. Time flows upward.) A ...
1. Which of the following is closest to your mass? A.0.06 kg B.0.6 kg
... up as heat by the gas equals the work done on the gas. As a result, the volume is: A.doubled B.halved C.unchanged D.need more information to answer E.nonsense; the process is impossible 61.An ideal gas expands into a vacuum in a rigid vessel. As a result there is: A.a change in entropy B.an increase ...
... up as heat by the gas equals the work done on the gas. As a result, the volume is: A.doubled B.halved C.unchanged D.need more information to answer E.nonsense; the process is impossible 61.An ideal gas expands into a vacuum in a rigid vessel. As a result there is: A.a change in entropy B.an increase ...
Elementary Particle Physics
... this way: 1 - There are conserved quantities, that is entities which have to have the same value after the interaction as before. We will later see that the different types of interactions in some cases have different conservation rules. There are however some universal conserved quantities like ene ...
... this way: 1 - There are conserved quantities, that is entities which have to have the same value after the interaction as before. We will later see that the different types of interactions in some cases have different conservation rules. There are however some universal conserved quantities like ene ...
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.286: The Early Universe
... We understand that Eeff is conserved because it is the energy in an analogue problem in which the test particle moves in the gravitational field of a point particle of mass M (ri ), located at the origin, with potential energy function Veff (r). In this analogue problem the force on the test particl ...
... We understand that Eeff is conserved because it is the energy in an analogue problem in which the test particle moves in the gravitational field of a point particle of mass M (ri ), located at the origin, with potential energy function Veff (r). In this analogue problem the force on the test particl ...
Last Time… - UW-Madison Department of Physics
... Particle in box question A particle in a box has a mass m. Its energy is all kinetic = p2/2m. Just saw that momentum in state n is npo. It’s energy levels A. are equally spaced everywhere B. get farther apart at higher energy C. get closer together at higher energy. ...
... Particle in box question A particle in a box has a mass m. Its energy is all kinetic = p2/2m. Just saw that momentum in state n is npo. It’s energy levels A. are equally spaced everywhere B. get farther apart at higher energy C. get closer together at higher energy. ...
2006-11-14-RAL-Wang - Indico
... conformal gravitational field is responsible for cosmic acceleration linked to inflation and the problem of the cosmological constant. The formula for relating the measured decoherence of matter waves to spacetime fluctuations, is “minimum” in the sense that ground-state matter fields have not bee ...
... conformal gravitational field is responsible for cosmic acceleration linked to inflation and the problem of the cosmological constant. The formula for relating the measured decoherence of matter waves to spacetime fluctuations, is “minimum” in the sense that ground-state matter fields have not bee ...
and n
... Are all transitions possible? – Selection rules Must always obey Pauli exclusion principle. Transitions are electric dipole transitions – the oscillating electric field component of the radiation interacts with electrical charges, i.e. the positive nuclei and negative electrons that comprise an ato ...
... Are all transitions possible? – Selection rules Must always obey Pauli exclusion principle. Transitions are electric dipole transitions – the oscillating electric field component of the radiation interacts with electrical charges, i.e. the positive nuclei and negative electrons that comprise an ato ...
Two types of potential functions and their use in the
... written in Lux’s model), as a result of having it embedded in our quantum/real potential model (thus now without expectation operator) then this would imply that dW dt = 0. If we now go back to the importance of expectation operators in Nelson’s theory we can say the following. Imagine we were to no ...
... written in Lux’s model), as a result of having it embedded in our quantum/real potential model (thus now without expectation operator) then this would imply that dW dt = 0. If we now go back to the importance of expectation operators in Nelson’s theory we can say the following. Imagine we were to no ...
Relations between Massive and Massless one
... A massive particle with spin j has 2j+1 one-particle states, such as the spin 3/2 9Be’s nuclei, whose magnetic quantum numbers are 3/2, 1/2, -1/2, -3/2. However, it is different about a particle with mass zero (for example photon). Photons’ helicity has only two values: 1,-1. Helicity zero is forbid ...
... A massive particle with spin j has 2j+1 one-particle states, such as the spin 3/2 9Be’s nuclei, whose magnetic quantum numbers are 3/2, 1/2, -1/2, -3/2. However, it is different about a particle with mass zero (for example photon). Photons’ helicity has only two values: 1,-1. Helicity zero is forbid ...
Physics 102: Lecture 24 Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Physics
... Note: This is LOWER energy since negative! Physics 102: Lecture 24, Slide 19 ...
... Note: This is LOWER energy since negative! Physics 102: Lecture 24, Slide 19 ...
APCTP-WCU APR 16 - Y.
... • We computed the EDM of triton and helion from TVPV potential. Matching between Nuclear EDM and effective ...
... • We computed the EDM of triton and helion from TVPV potential. Matching between Nuclear EDM and effective ...
Quantum Computation with Neutral Atoms
... Real world strategy “…If X is very hard it can be substituted with more of Y. Of course, in many cases both X and Y are beyond the present experimental state of the art …” ...
... Real world strategy “…If X is very hard it can be substituted with more of Y. Of course, in many cases both X and Y are beyond the present experimental state of the art …” ...
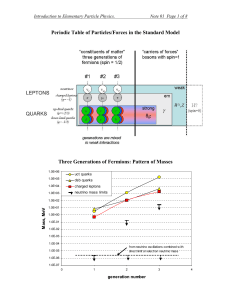
Periodic Table of Particles/Forces in the Standard Model
... quantum numbers like charge (electric, color, etc.), magnetic moment, etc. For photon , Z, and H, an anti-particle is the same as a particle. Same can be true for neutrinos, but we do not yet know this… In general, fermions—particles with half-integral spin: ½ , 3/2, …. Bosons—particles with integra ...
... quantum numbers like charge (electric, color, etc.), magnetic moment, etc. For photon , Z, and H, an anti-particle is the same as a particle. Same can be true for neutrinos, but we do not yet know this… In general, fermions—particles with half-integral spin: ½ , 3/2, …. Bosons—particles with integra ...