Slides - MAGNETISM.eu
... • Correlation energy of e-e interaction is the same in initial and finite state -- center mass motion only affected by the probe (Kohn theorem) -- z-component of total spin affected (Yafet theorem) • Momentum and (for spherical Fermi surface) velocity is conserved in e-e collisions • Total Coulomb e ...
... • Correlation energy of e-e interaction is the same in initial and finite state -- center mass motion only affected by the probe (Kohn theorem) -- z-component of total spin affected (Yafet theorem) • Momentum and (for spherical Fermi surface) velocity is conserved in e-e collisions • Total Coulomb e ...
my Work 4 U
... These X-ray photons have discrete energies that are equal to the difference in energy between the valence and core energy levels. The characteristic lines are called K, L, M, ... and correspond to transitions from higher energy states to the n = 1, 2, 3, ... quantum levels, ...
... These X-ray photons have discrete energies that are equal to the difference in energy between the valence and core energy levels. The characteristic lines are called K, L, M, ... and correspond to transitions from higher energy states to the n = 1, 2, 3, ... quantum levels, ...
ch06C-2013
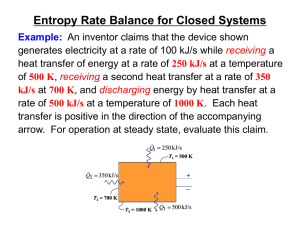
... The claim is in accord with the first law of thermodynamics. ► Applying an entropy rate balance dS 0 ...
... The claim is in accord with the first law of thermodynamics. ► Applying an entropy rate balance dS 0 ...
Techniques and Applications - Angelo Raymond Rossi
... The Classical Harmonic Oscillator To understand vibrations in molecules, it is important to understand the quantum mechanical treatment of a harmonic oscillator. As background, it is necessary to review the classical treatment of harmonic oscillator. The simplest example of a harmonic oscillator is ...
... The Classical Harmonic Oscillator To understand vibrations in molecules, it is important to understand the quantum mechanical treatment of a harmonic oscillator. As background, it is necessary to review the classical treatment of harmonic oscillator. The simplest example of a harmonic oscillator is ...
PHILOSOPHY OF QUANTUM INFORMATION
... out to be correlated (although this can be found out only later, when Alice and Bob are able to compare their results). The fact that the results are correlated is not a great surprise – after all, the particles came from a common source. What is astonishing, however, is that they are correlated in ...
... out to be correlated (although this can be found out only later, when Alice and Bob are able to compare their results). The fact that the results are correlated is not a great surprise – after all, the particles came from a common source. What is astonishing, however, is that they are correlated in ...
PROBABILITIES FOR SINGLE EVENTS
... for renormalizing the probabilities so that the rules are exactly obeyed without changing their values in any relevent sense. II.1.2. Probabilities in Quantum Mechanics The characteristic feature of a quantum mechanical theory is that not every history that can be described can be assigned a probabi ...
... for renormalizing the probabilities so that the rules are exactly obeyed without changing their values in any relevent sense. II.1.2. Probabilities in Quantum Mechanics The characteristic feature of a quantum mechanical theory is that not every history that can be described can be assigned a probabi ...
Ch 6 - Momentum
... In real life, forces during collisions are not constant In physics world, we will work as if we are using the “average force” in our calculations ...
... In real life, forces during collisions are not constant In physics world, we will work as if we are using the “average force” in our calculations ...
noise - Michael Nielsen
... X , to the actual output. A quantum operation The usual way two states a and b are compared is to compute the fidelity, or overlap: F (a , b ) a b . The fidelity measures how similar the states are, ranging from 0 (totally dissimilar), up to 1 (the same). ...
... X , to the actual output. A quantum operation The usual way two states a and b are compared is to compute the fidelity, or overlap: F (a , b ) a b . The fidelity measures how similar the states are, ranging from 0 (totally dissimilar), up to 1 (the same). ...
Euclidean Field Theory - Department of Mathematical Sciences
... describe both the set of momenta that appear, as well as the number of particles of each momentum. We will leave this expression for the time being, and instead ask the question whether we can write (1.10) back in a path integral language. It is not immediately clear how to do this, because the Gaus ...
... describe both the set of momenta that appear, as well as the number of particles of each momentum. We will leave this expression for the time being, and instead ask the question whether we can write (1.10) back in a path integral language. It is not immediately clear how to do this, because the Gaus ...
HW 2 solutions
... (a) The Hamiltonian for a particle with spin in a magnetic field is (ignoring the spatial part) H = −γB · S Our magnetic field is B = B0 k̂ + B î, so H = −γ(B0 Sz + BSx ) We can solve for the energy eigenvalues of this Hamiltonian in two different ways. The first is to use a brute-force approach: u ...
... (a) The Hamiltonian for a particle with spin in a magnetic field is (ignoring the spatial part) H = −γB · S Our magnetic field is B = B0 k̂ + B î, so H = −γ(B0 Sz + BSx ) We can solve for the energy eigenvalues of this Hamiltonian in two different ways. The first is to use a brute-force approach: u ...
Status Update: Search for Low Mass Strings at CMS
... Significance is evaluated based on the number of observed events compared to the number of expected background events in the region of the peak. Random fluctuations in the background can lead to “accidental” peak-like structures in the spectrum. Five sigma significance - the probability that a c ...
... Significance is evaluated based on the number of observed events compared to the number of expected background events in the region of the peak. Random fluctuations in the background can lead to “accidental” peak-like structures in the spectrum. Five sigma significance - the probability that a c ...
Comparison of entropy difference in the cooling process
... increase or decrease the temperature. That step always keeps a constant property, which is distinctive for each cooling technique. – Vapour-compression: after evaporation, the liquid increases its temperature in an adiabatic step. After condensing at high temperature, the liquid expands when passing ...
... increase or decrease the temperature. That step always keeps a constant property, which is distinctive for each cooling technique. – Vapour-compression: after evaporation, the liquid increases its temperature in an adiabatic step. After condensing at high temperature, the liquid expands when passing ...