Deterministic Controlled-NOT Gate For Single-Photon Two
... frequency-degenerate parametric down-conversion [12]. We have previously obtained a signal-idler quantum interference visibility of 99% for this source. The idlertriggered signal beam was used as a single-photon source for the input to the CNOT gate. The orthogonally polarized signal and idler photo ...
... frequency-degenerate parametric down-conversion [12]. We have previously obtained a signal-idler quantum interference visibility of 99% for this source. The idlertriggered signal beam was used as a single-photon source for the input to the CNOT gate. The orthogonally polarized signal and idler photo ...
Chapter 3: Relativistic dynamics
... So a four-velocity vector always squares to −c2 , regardless of the value of the 3-velocity. Let’s summarize what we’ve learned a bit more geometrically. The worldline x(τ ) describes some trajectory through spacetime. At every event along this worldline, the four-velocity u = dx/dτ is a 4-vector wh ...
... So a four-velocity vector always squares to −c2 , regardless of the value of the 3-velocity. Let’s summarize what we’ve learned a bit more geometrically. The worldline x(τ ) describes some trajectory through spacetime. At every event along this worldline, the four-velocity u = dx/dτ is a 4-vector wh ...
State of Equilibrium
... the amount of substance of the constituents does not change then this term is zero. However, if there is a reaction between the components of a mixture then this term will be non-zero and must be taken into account. Chemical potential is introduced in Chapter 12 when dissociation is discussed; it is ...
... the amount of substance of the constituents does not change then this term is zero. However, if there is a reaction between the components of a mixture then this term will be non-zero and must be taken into account. Chemical potential is introduced in Chapter 12 when dissociation is discussed; it is ...
homework assignment
... Problem set 4 1. Jackson 4.1. 2. Show that a charged particle in a good quantum state of angular momentum l, m has no permanent electric dipole moment. 3. An infinitely long copper cylinder of radius a is surrounded by a cylindrical shell of inner radius a, outer radius b. The dielectric has a diele ...
... Problem set 4 1. Jackson 4.1. 2. Show that a charged particle in a good quantum state of angular momentum l, m has no permanent electric dipole moment. 3. An infinitely long copper cylinder of radius a is surrounded by a cylindrical shell of inner radius a, outer radius b. The dielectric has a diele ...
Chapter 7 - TESD home
... Unless a system is acted on by a NET external force the initial momentum of a system must equal the final momentum of a system. However, two or more systems may exchange momentum. We will study how these changes occur. ...
... Unless a system is acted on by a NET external force the initial momentum of a system must equal the final momentum of a system. However, two or more systems may exchange momentum. We will study how these changes occur. ...
Erwin Schroedinger gained inspiration
... For a given element, the emission lines and the absorption lines occur at the same frequency. This is where quantum mechanics comes in. Here’s the basic idea (which was the product of Niels Bohr, Erwin Schroedinger, and Verner Heisenberg). The atom has a minimum energy state which is called its gro ...
... For a given element, the emission lines and the absorption lines occur at the same frequency. This is where quantum mechanics comes in. Here’s the basic idea (which was the product of Niels Bohr, Erwin Schroedinger, and Verner Heisenberg). The atom has a minimum energy state which is called its gro ...
Chapter 7 - TESD home
... Unless a system is acted on by a NET external force the initial momentum of a system must equal the final momentum of a system. However, two or more systems may exchange momentum. We will study how these changes occur. ...
... Unless a system is acted on by a NET external force the initial momentum of a system must equal the final momentum of a system. However, two or more systems may exchange momentum. We will study how these changes occur. ...
AP Physics Review Sheet 1
... or is capable of moving. Thus, for an object on a level surface, N and W are equal in size but opposite in direction. However, for an object on a ramp, this statement is not true because N is perpendicular to the surface of the ramp. Tension, T , is the force transmitted through a string. The tensio ...
... or is capable of moving. Thus, for an object on a level surface, N and W are equal in size but opposite in direction. However, for an object on a ramp, this statement is not true because N is perpendicular to the surface of the ramp. Tension, T , is the force transmitted through a string. The tensio ...
chapter 2
... energy/matter to another energy/matter as ‘interactions’ • Physics attempts to elucidate the interactions between them • But before we can study the basic physics of the matter-energy interactions, we must first have some general idea to differentiate between the two different modes of physical exis ...
... energy/matter to another energy/matter as ‘interactions’ • Physics attempts to elucidate the interactions between them • But before we can study the basic physics of the matter-energy interactions, we must first have some general idea to differentiate between the two different modes of physical exis ...
Theory of fluctuations in a network of parallel superconducting wires
... together by the proximity effect, subjected to a vector potential along the wires, can be mapped onto N-distinguishable two dimensional quantum-mechanics problem with a perpendicular imaginary magnetic field. Then, we show, using a mean field approximation, that, for a given coupling, there is a criti ...
... together by the proximity effect, subjected to a vector potential along the wires, can be mapped onto N-distinguishable two dimensional quantum-mechanics problem with a perpendicular imaginary magnetic field. Then, we show, using a mean field approximation, that, for a given coupling, there is a criti ...
E n - USM
... • But how do we ‘locate’ a wave? • Wave spreads out in a region of space and is not located in any specific point in space like the case of a particle • To be more precise we says that a plain wave exists within some region in space, Dx • For a particle, Dx is just the ‘size’ of its dimension, e.g. ...
... • But how do we ‘locate’ a wave? • Wave spreads out in a region of space and is not located in any specific point in space like the case of a particle • To be more precise we says that a plain wave exists within some region in space, Dx • For a particle, Dx is just the ‘size’ of its dimension, e.g. ...
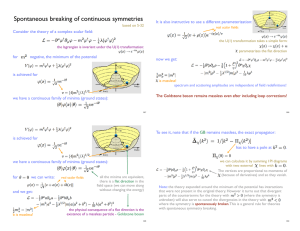
Spontaneous breaking of continuous symmetries
... to the path integral. Changing integration variables from and we must include the functional determinant: ...
... to the path integral. Changing integration variables from and we must include the functional determinant: ...