In Vitro Metabolism of Haloperidol and Sila-Haloperidol
... metabolites formed were tentatively assigned as two separate hydroxylated products (OH1 and OH2), two diasteromeric N-oxides (N-oxide1 and N-oxide2), reduced haloperidol (red), and an N-dealkylated metabolite (N-dealk). The pyridinium ion metabolite, reduced haloperidol, and the first eluting N-oxid ...
... metabolites formed were tentatively assigned as two separate hydroxylated products (OH1 and OH2), two diasteromeric N-oxides (N-oxide1 and N-oxide2), reduced haloperidol (red), and an N-dealkylated metabolite (N-dealk). The pyridinium ion metabolite, reduced haloperidol, and the first eluting N-oxid ...
Cubic SiC Nanowires: Growth, Characterization and
... in contact with the metal droplets, the precursor deposits on the liquid surface and forms an alloy. A continuous incorporation of the precursor leads to a supersaturation of the desired compounds and as a consequence to the NW growth at the solid-liquid interface. With other growth techniques it is ...
... in contact with the metal droplets, the precursor deposits on the liquid surface and forms an alloy. A continuous incorporation of the precursor leads to a supersaturation of the desired compounds and as a consequence to the NW growth at the solid-liquid interface. With other growth techniques it is ...
Electronics
... First there is applying heat on a semiconductor. At very low temperatures semiconductors happen to be good electrical insulators but as their temperature increases they become increasingly better electrical conductors. This means at every day temperatures they allow some current to pass through them ...
... First there is applying heat on a semiconductor. At very low temperatures semiconductors happen to be good electrical insulators but as their temperature increases they become increasingly better electrical conductors. This means at every day temperatures they allow some current to pass through them ...
A family of diatom-like silicon transporters in the siliceous loricate
... dioxide into the physical macrostructure of an organism. In eukaryotes, biosilica formation occurs within a silicon deposition vesicle (SDV) to isolate the polymerizing silica from the general cell metabolism [1]. Silicon is present in the environment primarily as silicic acid (Si(OH)4). Silicic aci ...
... dioxide into the physical macrostructure of an organism. In eukaryotes, biosilica formation occurs within a silicon deposition vesicle (SDV) to isolate the polymerizing silica from the general cell metabolism [1]. Silicon is present in the environment primarily as silicic acid (Si(OH)4). Silicic aci ...
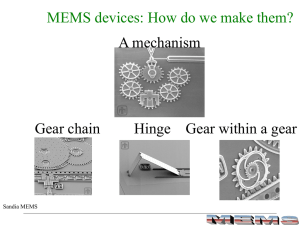
Bulk and Surface Micromachining
... for the Miller Indices <110>:<100>:<111>, planar selectivity can be as high as 600:400:1. However, KOH is not used in micromachining because its potassium ion content bans it from clean room operations. Also, it is highly corrosive and attacks aluminum, which makes it undesirable for CMOS fabricatio ...
... for the Miller Indices <110>:<100>:<111>, planar selectivity can be as high as 600:400:1. However, KOH is not used in micromachining because its potassium ion content bans it from clean room operations. Also, it is highly corrosive and attacks aluminum, which makes it undesirable for CMOS fabricatio ...
Silicon as an intermediary between renewable
... , Global reserves of coal, oil and natural gas are diminishing; global energy requirements however are dramatically increasing. Renewable energy sources lower the threat to the earth’s climate but are not able to meet the energy consumption in major urban areas. The opinion of many experts is that t ...
... , Global reserves of coal, oil and natural gas are diminishing; global energy requirements however are dramatically increasing. Renewable energy sources lower the threat to the earth’s climate but are not able to meet the energy consumption in major urban areas. The opinion of many experts is that t ...
On the Origin of the Second-Order Nonlinearity in Strained Si
... compounds, such as nitrides and oxides, is expected to dramatically enhance silicon photonics by eliminating the need for non-CMOS-compatible materials. While bulk Si is centrosymmetric and thus displays no second-order (χ(2)) effects, a body of experimental evidence accumulated in the last decade d ...
... compounds, such as nitrides and oxides, is expected to dramatically enhance silicon photonics by eliminating the need for non-CMOS-compatible materials. While bulk Si is centrosymmetric and thus displays no second-order (χ(2)) effects, a body of experimental evidence accumulated in the last decade d ...
INTEGRATED CIRCUIT FABRICATION
... SiO2 has the property of preventing the diffusion of almost all impurities through it. It serves two very important purposes. 1. SiO2 is an extremely hard protective coating and is unaffected by almost all reagents except hydrofluoric acid. Thus, it stands against any contamination. 2. By selective ...
... SiO2 has the property of preventing the diffusion of almost all impurities through it. It serves two very important purposes. 1. SiO2 is an extremely hard protective coating and is unaffected by almost all reagents except hydrofluoric acid. Thus, it stands against any contamination. 2. By selective ...
CimeXa Insecticide Dust and Silica Gel
... silica is SiO2 – silicon dioxide. Silicon dioxide and numerous silicate minerals are ubiquitous in nature. The most prevalent mineral component of common sand is silicon dioxide, in the form of ground quartz. Sand, however, won’t kill bugs! Silica gel is made by a controlled mixture of sodium silica ...
... silica is SiO2 – silicon dioxide. Silicon dioxide and numerous silicate minerals are ubiquitous in nature. The most prevalent mineral component of common sand is silicon dioxide, in the form of ground quartz. Sand, however, won’t kill bugs! Silica gel is made by a controlled mixture of sodium silica ...
pulsed laser atom probe characterization of silicon carbide
... processes.'4"*' In addition, /9-SiC has applications for use in semiconductor device applications because of its unique combination of physical and electronic properties. Single crystal thin films of /3-SiC are currently grown by chemical vapor deposition onto (100) silicon substrates.'7' Several pr ...
... processes.'4"*' In addition, /9-SiC has applications for use in semiconductor device applications because of its unique combination of physical and electronic properties. Single crystal thin films of /3-SiC are currently grown by chemical vapor deposition onto (100) silicon substrates.'7' Several pr ...
Silicon Carbide Coating for Carbon Materials Produced by a
... This value is to compare with those of 466 kJ mol-I [13]and 472 W mol-l [ l o ] obtained for the C (s) + sjO (g) reaction. As usual, this high value of Ea should indicate that the S i c formation is monitored by the surface chemical kinetics. In this case, this interpretation seems to be very hazar ...
... This value is to compare with those of 466 kJ mol-I [13]and 472 W mol-l [ l o ] obtained for the C (s) + sjO (g) reaction. As usual, this high value of Ea should indicate that the S i c formation is monitored by the surface chemical kinetics. In this case, this interpretation seems to be very hazar ...
Cluster Assembled Metal Encapsulated Thin Nanotubes of Silicon
... reflection passing through its center. This is composed of Si24Be2 structure. • In the second diagram the Be atom is placed between successive hexagons and the doped portion is symmetric while the remaining nanotube becomes ...
... reflection passing through its center. This is composed of Si24Be2 structure. • In the second diagram the Be atom is placed between successive hexagons and the doped portion is symmetric while the remaining nanotube becomes ...
Crystallize Your Visions
... to form carbon dioxide at very high temperatures (approx.1,800°C). The carbon dioxide is drained off and silicon is left behind. This process is highly energyintensive, requiring approx. 14 kWh per kg of raw silicon. Raw silicon extracted in this way still contains approx. 1% impurities. However, a ...
... to form carbon dioxide at very high temperatures (approx.1,800°C). The carbon dioxide is drained off and silicon is left behind. This process is highly energyintensive, requiring approx. 14 kWh per kg of raw silicon. Raw silicon extracted in this way still contains approx. 1% impurities. However, a ...
Chemical Glossary - Wacker Chemie AG
... Cellulose acetate is one of the oldest thermoplastic polymers. The acetate and triacetate fibers made from it are derivatives of cellulose, a natural substance. Wacker Chemie produced one such synthetic fiber under the brand name Drawinella. Cellulose acetate is mostly converted into textile fibers ...
... Cellulose acetate is one of the oldest thermoplastic polymers. The acetate and triacetate fibers made from it are derivatives of cellulose, a natural substance. Wacker Chemie produced one such synthetic fiber under the brand name Drawinella. Cellulose acetate is mostly converted into textile fibers ...
Coupling of Silicon, Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolisms in Marine
... the basic pH and because of low concentrations, dissolved silicon is mainly in the form of monomeric orthosilicic acid. The leve\s vary from 0 to 180 IlM, with a mean value of 70 IlM for the World Ocean. Thus, diatoms have developed specific mechanisms to take up silicon from very diluted solutions. ...
... the basic pH and because of low concentrations, dissolved silicon is mainly in the form of monomeric orthosilicic acid. The leve\s vary from 0 to 180 IlM, with a mean value of 70 IlM for the World Ocean. Thus, diatoms have developed specific mechanisms to take up silicon from very diluted solutions. ...
What is a mineral? "A mineral is a naturally occurring, homogeneous
... are smaller than their neutral state, ions that have gained electrons (anions) are larger. ...
... are smaller than their neutral state, ions that have gained electrons (anions) are larger. ...
No Slide Title
... capacitor. Every time we go to row 3, column 5, we will access or address the same capacitor and obtain the same result (1) until the capacitive charge is changed by a write process. ...
... capacitor. Every time we go to row 3, column 5, we will access or address the same capacitor and obtain the same result (1) until the capacitive charge is changed by a write process. ...
13.IVA group. Carbon and Silicon and their compounds.
... Silicon is a solid at room temperature, with relatively high melting and boiling points of approximately 1,400 and 2,800 degrees Celsius respectively. With a relatively high thermal conductivity of 149 W·m−1·K−1, silicon conducts heat well and as a result is not often used to insulate hot objects. I ...
... Silicon is a solid at room temperature, with relatively high melting and boiling points of approximately 1,400 and 2,800 degrees Celsius respectively. With a relatively high thermal conductivity of 149 W·m−1·K−1, silicon conducts heat well and as a result is not often used to insulate hot objects. I ...
Class 3 updated Sep 30 2011
... Today, silicon is purified by converting it to a silicon compound that can be more easily purified than silicon itself, and then converting that silicon compound back into pure silicon. Trichlorosilane is the silicon compound most commonly used as the intermediate. In the Siemens process, high-purit ...
... Today, silicon is purified by converting it to a silicon compound that can be more easily purified than silicon itself, and then converting that silicon compound back into pure silicon. Trichlorosilane is the silicon compound most commonly used as the intermediate. In the Siemens process, high-purit ...
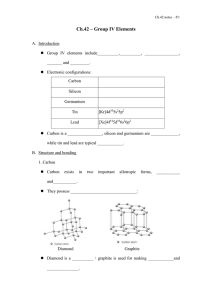
E. Oxides of Group IV elements
... The melting points show a general ______________ on going down the group. Diamond has giant covalent structure, it needs a great amount of energy to break the _________________________. From carbon to germanium, the bond lengths increases and the ____________________ decrease. Tin and lead h ...
... The melting points show a general ______________ on going down the group. Diamond has giant covalent structure, it needs a great amount of energy to break the _________________________. From carbon to germanium, the bond lengths increases and the ____________________ decrease. Tin and lead h ...
Health Benefits
... After oxygen, silicon is the second most abundant element on Earth. It is present especially in rocks and soil in the form of silica or silicic acid. Quartz is commonly recognised by most people and the Czech Republic is rich in quartz gemstones. Silicon is part of the same group of elements as carb ...
... After oxygen, silicon is the second most abundant element on Earth. It is present especially in rocks and soil in the form of silica or silicic acid. Quartz is commonly recognised by most people and the Czech Republic is rich in quartz gemstones. Silicon is part of the same group of elements as carb ...
in combination with other materials in glass, semi
... lung disease, silicosis Read more: http://scienceray.com/chemistry/simple-facts-about-silicon/#ixzz11UvkFMYh Silicon element facts: Silicon atoms contain 14 protons and a varying number of neutrons in their nuclei. In their neutral state they possess 14 electrons. Silicon is a very common element an ...
... lung disease, silicosis Read more: http://scienceray.com/chemistry/simple-facts-about-silicon/#ixzz11UvkFMYh Silicon element facts: Silicon atoms contain 14 protons and a varying number of neutrons in their nuclei. In their neutral state they possess 14 electrons. Silicon is a very common element an ...
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a tetravalent metalloid, more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table. Controversy about silicon's character dates to its discovery; it was first prepared and characterized in pure form in 1823. In 1808, it was given the name silicium (from Latin: silex, hard stone or flint), with an -ium word-ending to suggest a metal, a name which the element retains in several non-English languages. However, its final English name, first suggested in 1817, reflects the more physically similar elements carbon and boron.Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure free element in nature. It is most widely distributed in dusts, sands, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide (silica) or silicates. Over 90% of the Earth's crust is composed of silicate minerals, making silicon the second most abundant element in the Earth's crust (about 28% by mass) after oxygen.Most silicon is used commercially without being separated, and indeed often with little processing of compounds from nature. These include direct industrial building-use of clays, silica sand and stone. Silicate goes into Portland cement for mortar and stucco, and when combined with silica sand and gravel, to make concrete. Silicates are also in whiteware ceramics such as porcelain, and in traditional quartz-based soda-lime glass and many other specialty glasses. More modern silicon compounds such as silicon carbide form abrasives and high-strength ceramics. Silicon is the basis of the widely used synthetic polymers called silicones.Elemental silicon also has a large impact on the modern world economy. Although most free silicon is used in the steel refining, aluminium-casting, and fine chemical industries (often to make fumed silica), the relatively small portion of very highly purified silicon that is used in semiconductor electronics (< 10%) is perhaps even more critical. Because of wide use of silicon in integrated circuits, the basis of most computers, a great deal of modern technology depends on it.Silicon is an essential element in biology, although only tiny traces of it appear to be required by animals. However, various sea sponges as well as microorganisms like diatoms and radiolaria secrete skeletal structures made of silica. Silica is often deposited in plant tissues, such as in the bark and wood of Chrysobalanaceae and the silica cells and silicified trichomes of Cannabis sativa, horsetails and many grasses.