All forces arise from the interactions between different objects
... gravitational force, there exists a duality between strong and weak coupling. A coupling constant describes how strong an interaction is. A larger coupling constant means a stronger force; hence, the coupling constant is of the order of 10 -41 and it is derived from the masses of the proton and elec ...
... gravitational force, there exists a duality between strong and weak coupling. A coupling constant describes how strong an interaction is. A larger coupling constant means a stronger force; hence, the coupling constant is of the order of 10 -41 and it is derived from the masses of the proton and elec ...
In order to integrate general relativity with quantum
... representation and thus where the four states of |b0 , b1 , s, can be abbreviated as |(b1), =± ½These four (spinor) states support the definition of the matrices which result from the requirement that both representation and conjugate representation be used in order for the state to be ...
... representation and thus where the four states of |b0 , b1 , s, can be abbreviated as |(b1), =± ½These four (spinor) states support the definition of the matrices which result from the requirement that both representation and conjugate representation be used in order for the state to be ...
Untitled - College of William and Mary
... ties. Superconductors are grouped into two types: Type-I and Type-II. (The distinction between these two types is related to the ratio between the London penetration depth and the superconducting coherence length; this is discussed in more depth in Tinkham [1].) Type-I superconductors all have crit ...
... ties. Superconductors are grouped into two types: Type-I and Type-II. (The distinction between these two types is related to the ratio between the London penetration depth and the superconducting coherence length; this is discussed in more depth in Tinkham [1].) Type-I superconductors all have crit ...
Elements of a Physics Case for HE LHC
... C) Longitudinal W scattering unitarized for E>1 TeV by Higgs or some other non-perturbative dynamics (techni-r meson) ...
... C) Longitudinal W scattering unitarized for E>1 TeV by Higgs or some other non-perturbative dynamics (techni-r meson) ...
HillCTEQ2
... • A group G is a collection of elements { rj } • G has a “multiplication” operation: rj x rk = rk where rk is in G • There is a unique identity in G, 1, such that 1 x rk = r k x 1 = r k • Each element rk has a unique inverse rk-1 such that rk-1 x rk = rk x rk-1 = 1 • Group multiplication is associat ...
... • A group G is a collection of elements { rj } • G has a “multiplication” operation: rj x rk = rk where rk is in G • There is a unique identity in G, 1, such that 1 x rk = r k x 1 = r k • Each element rk has a unique inverse rk-1 such that rk-1 x rk = rk x rk-1 = 1 • Group multiplication is associat ...
Why 3+1 = 11 for small values of 7
... around the time of General Relativity by Kaluza and Klein. The concept worked with 5-dimensions and showed that if you curl the fifth dimension into a circle about the other 4 then you would only have 4 observable dimensions, and a fifth which interacted with the others. The physical representation ...
... around the time of General Relativity by Kaluza and Klein. The concept worked with 5-dimensions and showed that if you curl the fifth dimension into a circle about the other 4 then you would only have 4 observable dimensions, and a fifth which interacted with the others. The physical representation ...
General Relativity for Pedestrians-
... O as a real valued function φ(xα ) of space-time coordinates. Observer O’, however, will find the same physical variable to be represented by a different function φ′ (x′α ). The function φ is said to be a scalar field if everywhere on the space-time manifold, φ′ (x′α ) = φ(xα ) given that xα and x′α ...
... O as a real valued function φ(xα ) of space-time coordinates. Observer O’, however, will find the same physical variable to be represented by a different function φ′ (x′α ). The function φ is said to be a scalar field if everywhere on the space-time manifold, φ′ (x′α ) = φ(xα ) given that xα and x′α ...
THE FIELD OF A STEP–LIKE ACCELERATED POINT CHARGE
... pertaining expressions can be obtained also by direct application of the relativistic Lorentz transformation of the Coulomb potential of moving charge [4]. It is shown here that the respective results can by obtained by straightforward application of the formalism of symbolic functions (distribution ...
... pertaining expressions can be obtained also by direct application of the relativistic Lorentz transformation of the Coulomb potential of moving charge [4]. It is shown here that the respective results can by obtained by straightforward application of the formalism of symbolic functions (distribution ...
transparencies - Indico
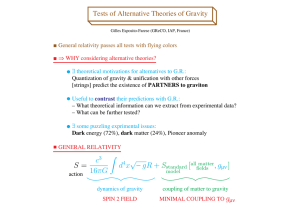
... illuminate connections among observable phenomena in new ways They are after all a possibility from perspective of general relativity Plus: Bonus: Even shed light on purely fourdimensional physics ...
... illuminate connections among observable phenomena in new ways They are after all a possibility from perspective of general relativity Plus: Bonus: Even shed light on purely fourdimensional physics ...