Euclid`s Five Postulates Some of Euclid`s Book 1 Definitions
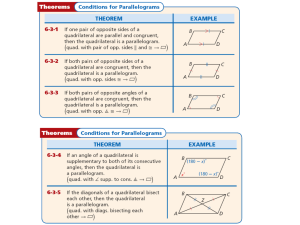
... Since F is the center of the circle with radius FD, it follows from Book I Definition 15: Circle that DF = KF, so a = KF by Euclid's first common notion. Since G is the center of the circle with radius GH, it follows from Book I Definition 15: Circle that GH = GK, so c = GK by Euclid's first common ...
... Since F is the center of the circle with radius FD, it follows from Book I Definition 15: Circle that DF = KF, so a = KF by Euclid's first common notion. Since G is the center of the circle with radius GH, it follows from Book I Definition 15: Circle that GH = GK, so c = GK by Euclid's first common ...
8th grade Mathematics Curriculum Guide – Unit 3 Geometry
... worked with triangles and classifying triangles. In previous grades, students made scale drawings of geometric figures and solved problems involving angle measure, surface area, and volume. In Grade 7, students found the volume of prisms and pyramids. In Grade 8, students expand on the general conce ...
... worked with triangles and classifying triangles. In previous grades, students made scale drawings of geometric figures and solved problems involving angle measure, surface area, and volume. In Grade 7, students found the volume of prisms and pyramids. In Grade 8, students expand on the general conce ...
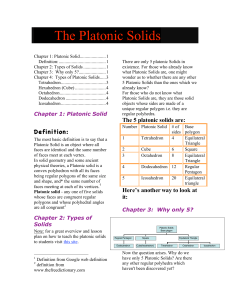
The Platonic Solids
... at the available data and build a formula to verify the existence of a given regular polyhedra with a given number of sides with a given regular polygon. The data available is that for a given polyhedra there is only one regular polygon which makes up its sides. The other data which is required to f ...
... at the available data and build a formula to verify the existence of a given regular polyhedra with a given number of sides with a given regular polygon. The data available is that for a given polyhedra there is only one regular polygon which makes up its sides. The other data which is required to f ...