File
... Use the figure for Exercises 2 and 3. Given the information in each exercise, state the reason why lines b and c are parallel. ...
... Use the figure for Exercises 2 and 3. Given the information in each exercise, state the reason why lines b and c are parallel. ...
MATH 5: ASSIGNMENT 12 Today we are starting a
... [Hint: find the angle which each of these lines form with the horizontal] This property – or rather, similar property of corners in three dimensions — is widely used: reflecting road signs, tail lights of a car, reflecting strips on clothing are all constructed out of many small reflecting corners s ...
... [Hint: find the angle which each of these lines form with the horizontal] This property – or rather, similar property of corners in three dimensions — is widely used: reflecting road signs, tail lights of a car, reflecting strips on clothing are all constructed out of many small reflecting corners s ...
Lesson 4.2: Angles In a Polygon
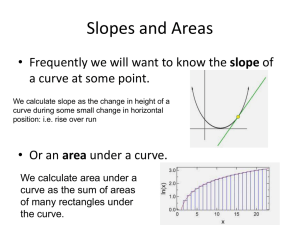
... Area: The amount of surface the 2D shape covers. It’s measured in square units. Some of these units are: squared centimeters (cm2), squared meters (m2) and squared kilometers (km2). The general way to calculate the area of a rectangle is by multiplying base by height (altitude). However, to calculat ...
... Area: The amount of surface the 2D shape covers. It’s measured in square units. Some of these units are: squared centimeters (cm2), squared meters (m2) and squared kilometers (km2). The general way to calculate the area of a rectangle is by multiplying base by height (altitude). However, to calculat ...