ACCIRC
... When the above circuit is supplied with an alternating voltage as shown, a voltage is developed across each component. vs = vR + vL The voltages in this equation are the instantaneous values. You could draw the sine waves and add them instant by instant. In a previous section you have seen that the ...
... When the above circuit is supplied with an alternating voltage as shown, a voltage is developed across each component. vs = vR + vL The voltages in this equation are the instantaneous values. You could draw the sine waves and add them instant by instant. In a previous section you have seen that the ...
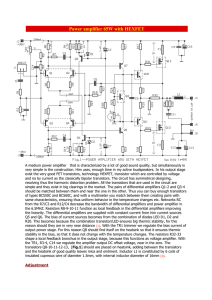
Power amplifier 65W with HEXFET
... and no by current as the classically bipolar transistors. The circuit has symmetrical designing, resolving thus the harmonic distortion problem. All the transistors that are used in the circuit are simple and they exist in big clearings in the market. The pairs of differential amplifiers Q1-2 and Q3 ...
... and no by current as the classically bipolar transistors. The circuit has symmetrical designing, resolving thus the harmonic distortion problem. All the transistors that are used in the circuit are simple and they exist in big clearings in the market. The pairs of differential amplifiers Q1-2 and Q3 ...
Stereo Phono/Line Preamplifier Ultra 4B SE Special Edition User’s Manual
... roll-off frequency of the RIAA curve at 2130 Hz. The selector switch is used to steer either the amplified phono signal or one of two line input signals (jacks J2 and J3) to the third stage, which utilizes the first section of the 12SN7GT in a common-cathode voltage amplifier configuration giving a ...
... roll-off frequency of the RIAA curve at 2130 Hz. The selector switch is used to steer either the amplified phono signal or one of two line input signals (jacks J2 and J3) to the third stage, which utilizes the first section of the 12SN7GT in a common-cathode voltage amplifier configuration giving a ...
Document
... Space vector modulation is a well-established theory. Generally, a three-phase voltage source inverter generates eight switching states, including six active and two zero states, by the bipolar method. This study proposes a novel way to synthesise the output voltage vector by turning off both switch ...
... Space vector modulation is a well-established theory. Generally, a three-phase voltage source inverter generates eight switching states, including six active and two zero states, by the bipolar method. This study proposes a novel way to synthesise the output voltage vector by turning off both switch ...
Experiment EM-4S for Physics 105
... 1b). The wire can be wound on a small cylinder of insulating material. The ends of the resistance wire are attached to terminals or heavy wires anchored to the ends of the insulating cylinder. Various alloys are used for the resistance wire, all of them being poorer conductors than copper. Typically ...
... 1b). The wire can be wound on a small cylinder of insulating material. The ends of the resistance wire are attached to terminals or heavy wires anchored to the ends of the insulating cylinder. Various alloys are used for the resistance wire, all of them being poorer conductors than copper. Typically ...
Linear Systems Offers Direct Alternative for Analog Devices MAT01
... IC = 100µA, VCE = 5V, BW=200Hz, RG= 10KΩ, f = 1KHz ...
... IC = 100µA, VCE = 5V, BW=200Hz, RG= 10KΩ, f = 1KHz ...
physics 212 chapter 17 current and resistance
... B____ 8. The unit of electric current, the ampere, is equivalent to which of the following? A. V×W D. V/s B. V/W E. W/V C. W×m A____ 9. The unit of electric resistance, the ohm, is equivalent to which of the following? A. V/A D. A/m B. V×m E. A/V C. A/s E___ 10. If a certain resistor obeys Ohm's la ...
... B____ 8. The unit of electric current, the ampere, is equivalent to which of the following? A. V×W D. V/s B. V/W E. W/V C. W×m A____ 9. The unit of electric resistance, the ohm, is equivalent to which of the following? A. V/A D. A/m B. V×m E. A/V C. A/s E___ 10. If a certain resistor obeys Ohm's la ...
FIRST ORDER CIRCUITS Introduction
... that gives sufficient time to the capacitors to fully charge and discharge. For 15 Vp-p square wave, draw the current and voltage of the resistor for two periods. 7. For the same values given in step 6, calculate the time constant of the circuit given in Figure 7. Compare your result with the time ...
... that gives sufficient time to the capacitors to fully charge and discharge. For 15 Vp-p square wave, draw the current and voltage of the resistor for two periods. 7. For the same values given in step 6, calculate the time constant of the circuit given in Figure 7. Compare your result with the time ...
Chapter 32.
... (a) The current is constant and is directed from a to b (b) The current is constant and is directed from b to a. (c) The current is increasing and is directed from a to b. (d) The current is decreasing and is directed from a to b (e) The current is increasing and is directed from b to a (f) The curr ...
... (a) The current is constant and is directed from a to b (b) The current is constant and is directed from b to a. (c) The current is increasing and is directed from a to b. (d) The current is decreasing and is directed from a to b (e) The current is increasing and is directed from b to a (f) The curr ...
Solution - Bryn Mawr College
... a rough sketch of the voltage of the capacitor over time, VC (t), starting when switch 2 is opened. What is the characteristic time scale on which the capacitor changes? (You are not required to give a formula for VC (t). Just draw the sketch and calculate the characteristic time scale.) See the cir ...
... a rough sketch of the voltage of the capacitor over time, VC (t), starting when switch 2 is opened. What is the characteristic time scale on which the capacitor changes? (You are not required to give a formula for VC (t). Just draw the sketch and calculate the characteristic time scale.) See the cir ...
Em05: Series-Resonant LCR Circuit
... In this experiment my aim was to plot resonance curves and determine the circuit magnification factor for various resistances. To do this I set up a series circuit containing a capacitor, an inductor and a resistor. These instruments were connected to a signal generator and the circuit was used to p ...
... In this experiment my aim was to plot resonance curves and determine the circuit magnification factor for various resistances. To do this I set up a series circuit containing a capacitor, an inductor and a resistor. These instruments were connected to a signal generator and the circuit was used to p ...
03_EE394J_2_Spring11_HW1_Refresher_Problems
... b. Phase a-b-c wires connecting the motor to a power panel each have 0.1 resistive ohms per phase, and negligible inductance. If the electrician reads the line-to-neutral voltage at the power panel, what reading can the electrician expect to see? ...
... b. Phase a-b-c wires connecting the motor to a power panel each have 0.1 resistive ohms per phase, and negligible inductance. If the electrician reads the line-to-neutral voltage at the power panel, what reading can the electrician expect to see? ...
Battery, Light Bulbs, and Wires
... f. Add a third bulb to the circuit in series. What happened to the current and voltage as compared with before? _______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ g. Move your series circuit off to th ...
... f. Add a third bulb to the circuit in series. What happened to the current and voltage as compared with before? _______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ g. Move your series circuit off to th ...
VIR Lab Name:
... NOTE: RECORD , just below the resistor symbol above, all the numbers and symbols written on the resistor. You will need them later. Define: Current (I) in amperes or amps or milliamps = # of charges to pass a given point in one second. Define: Voltage (V) in volts = change in electric potential betw ...
... NOTE: RECORD , just below the resistor symbol above, all the numbers and symbols written on the resistor. You will need them later. Define: Current (I) in amperes or amps or milliamps = # of charges to pass a given point in one second. Define: Voltage (V) in volts = change in electric potential betw ...
ECE 6340 - Courses
... 1) Show that v = 0 for a time-harmonic (i.e., sinusoidal steady-state) field in a source-free homogeneous region of matter, having an arbitrary complex permittivity . Homogeneous means that the material properties do not vary with position inside the material. Source-free means that there are no c ...
... 1) Show that v = 0 for a time-harmonic (i.e., sinusoidal steady-state) field in a source-free homogeneous region of matter, having an arbitrary complex permittivity . Homogeneous means that the material properties do not vary with position inside the material. Source-free means that there are no c ...
Circuits-Ohm`s Law
... 1. decreases 2. increases 3. remains the same 47. The heating element in an automobile window has a resistance of 1.2 ohms when operated at 12 volts. Calculate the power dissipated in the heating element. [Show all work, including the equation and ...
... 1. decreases 2. increases 3. remains the same 47. The heating element in an automobile window has a resistance of 1.2 ohms when operated at 12 volts. Calculate the power dissipated in the heating element. [Show all work, including the equation and ...
Electrical ballast

An electrical ballast is a device intended to limit the amount of current in an electric circuit. A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps, to limit the current through the tube, which would otherwise rise to destructive levels due to the tube's negative resistance characteristic.Ballasts vary in design complexity. They can be as simple as a series resistor or inductor, capacitors, or a combination thereof or as complex as electronic ballasts used with fluorescent lamps and high-intensity discharge lamps.