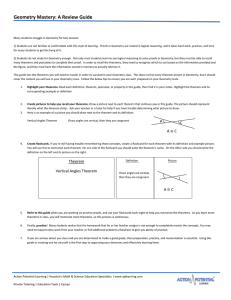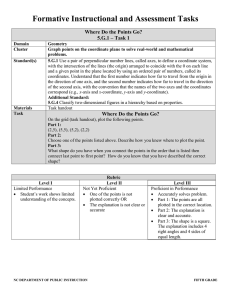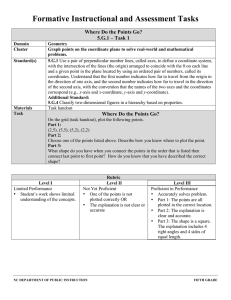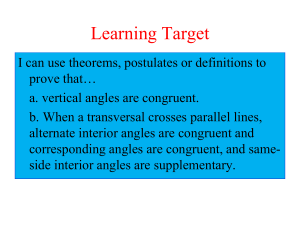
Geometry Vertical Angles and Transversal powerpoint
... Over 2000 years ago Eratosthenes estimated Earth’s circumference by using the fact that the Sun’s rays are parallel. When the Sun shone exactly down a vertical well in Syene, he measured the angle the Sun’s rays made with a vertical stick in Alexandria. He discovered that ...
... Over 2000 years ago Eratosthenes estimated Earth’s circumference by using the fact that the Sun’s rays are parallel. When the Sun shone exactly down a vertical well in Syene, he measured the angle the Sun’s rays made with a vertical stick in Alexandria. He discovered that ...
Use Oppesite Sides
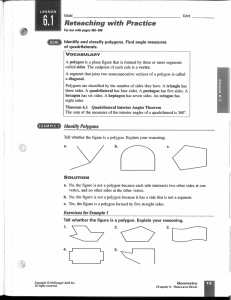
... called sides. The endpoint of each side is a vertex. A segment that joins two nonconsecutive vertices of a polygon is called a diagonal. Polygons are classified by the number of sides they have. A triangle has three sides. A quadrilateral has four sides. A pentagon has five sides. A hexagon has six ...
... called sides. The endpoint of each side is a vertex. A segment that joins two nonconsecutive vertices of a polygon is called a diagonal. Polygons are classified by the number of sides they have. A triangle has three sides. A quadrilateral has four sides. A pentagon has five sides. A hexagon has six ...
Doc
... Definition of Congruence: Having the exact same size and shape and there by having the exact same measures. Definition of Midpoint: The point that divides a segment into two congruent segments. Definition of Angle Bisector: The ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles. Definition of Perpe ...
... Definition of Congruence: Having the exact same size and shape and there by having the exact same measures. Definition of Midpoint: The point that divides a segment into two congruent segments. Definition of Angle Bisector: The ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles. Definition of Perpe ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)