Stress, serotonin, and hippocampal neurogenesis
... (Akiskal et al., 1983). More recent theoretical focus has largely been on biological factors, including a wealth of information supporting stress as a causal factor in depression, largely concerning chronic stress-related HPA dysregulation and toxicity from excessive glucocorticoid release (Lupien e ...
... (Akiskal et al., 1983). More recent theoretical focus has largely been on biological factors, including a wealth of information supporting stress as a causal factor in depression, largely concerning chronic stress-related HPA dysregulation and toxicity from excessive glucocorticoid release (Lupien e ...
Dimensions of integration in embedded and extended cognitive
... this framework. These dimensions are all matters of degree and jointly they constitute a multidimensional space in which situated cognitive systems can be located and have certain dimensional configurations. The higher a particular system scores on these dimensions, the more deeply the functional in ...
... this framework. These dimensions are all matters of degree and jointly they constitute a multidimensional space in which situated cognitive systems can be located and have certain dimensional configurations. The higher a particular system scores on these dimensions, the more deeply the functional in ...
Is anterior cingulate cortex necessary for cognitive control?Brain, 128
... Functional neuroimaging studies in normal humans suggest that dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) plays an important role in cognitive control. This brain area is reliably activated when tasks require the ongoing adjustment of the allocation of attention. The dACC has come to occupy a central ro ...
... Functional neuroimaging studies in normal humans suggest that dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) plays an important role in cognitive control. This brain area is reliably activated when tasks require the ongoing adjustment of the allocation of attention. The dACC has come to occupy a central ro ...
Effects of lithium and valproate on amphetamine
... oxidation. 12 More recently, King and Jope 13 showed that lithium protects against caspase activation that is induced by intrinsic and extrinsic sources of oxidative stress in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Together, these findings strongly suggest that the modulation of ROS generation may be re ...
... oxidation. 12 More recently, King and Jope 13 showed that lithium protects against caspase activation that is induced by intrinsic and extrinsic sources of oxidative stress in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Together, these findings strongly suggest that the modulation of ROS generation may be re ...
Document
... Exercise performed using a specialized apparatus here we used cybex isokinetic dynamometer that provides variable resistance to a movement, so that no matter how much effort is exerted, the movement takes place at a constant speed and for ankle strength training was given on dorsi flexion. So, there ...
... Exercise performed using a specialized apparatus here we used cybex isokinetic dynamometer that provides variable resistance to a movement, so that no matter how much effort is exerted, the movement takes place at a constant speed and for ankle strength training was given on dorsi flexion. So, there ...
Gut Microbiota: A Modulator of Brain Plasticity and Cognitive
... (CNS) through metabolic, neuroendocrine and immune pathways [1]. In particular, studies have illustrated an association between gut flora composition and cognitive processes such as learning and memory. Intestinal microbiota additionally contribute to the early development of normal social and cogni ...
... (CNS) through metabolic, neuroendocrine and immune pathways [1]. In particular, studies have illustrated an association between gut flora composition and cognitive processes such as learning and memory. Intestinal microbiota additionally contribute to the early development of normal social and cogni ...
CONTENT
... individual’s location to rivals or predators and impair the ability to detect their approach. Although these types of cost may be important, discussions of the cost of singing have generally focused on energy costs. Overall the evidence is equivocal: for instance, while Eberhardt found increases in ...
... individual’s location to rivals or predators and impair the ability to detect their approach. Although these types of cost may be important, discussions of the cost of singing have generally focused on energy costs. Overall the evidence is equivocal: for instance, while Eberhardt found increases in ...
Characterizing cognition in ADHD: beyond executive dysfunction
... whereas hyperactivity/impulsivity symptoms will be found to reflect ‘hot’ EF deficits. This gives rise to the possibility that some individuals with ADHD will manifest primarily ‘hot’ EF dysfunction, whereas others will show mainly ‘cool’ EF deficits and others will have both types. For example, ris ...
... whereas hyperactivity/impulsivity symptoms will be found to reflect ‘hot’ EF deficits. This gives rise to the possibility that some individuals with ADHD will manifest primarily ‘hot’ EF dysfunction, whereas others will show mainly ‘cool’ EF deficits and others will have both types. For example, ris ...
Implications of two conflicting views
... These functions, which do not operate perfectly at all times for anyone, are critically important for multiple aspects of daily life in all individuals. ADHD is not an all-or-nothing syndrome like pregnancy, where one either is pregnant or is not. It is more like depression. That is, all individuals ...
... These functions, which do not operate perfectly at all times for anyone, are critically important for multiple aspects of daily life in all individuals. ADHD is not an all-or-nothing syndrome like pregnancy, where one either is pregnant or is not. It is more like depression. That is, all individuals ...
Aerobic Glycolysis in the Frontal Cortex Correlates with Memory
... enzymes correlated with improved memory in control mice. Interestingly, in APP/PS1 mice the opposite effect was detected. In these mice, increased expression of lactate producing enzymes correlated with poorer memory performance. Immunofluorescent staining revealed localization of the aerobic glycol ...
... enzymes correlated with improved memory in control mice. Interestingly, in APP/PS1 mice the opposite effect was detected. In these mice, increased expression of lactate producing enzymes correlated with poorer memory performance. Immunofluorescent staining revealed localization of the aerobic glycol ...
A Global Model for the Cardiovascular and Respiratory System
... this type see, e.g., Noordergraaf [50] or Swan [66]. A comprehensive discussion of the control mechanisms in the human cardiovascular system is given in Guyton [17] or Rowell [60]. Models dealing with the regulation of breathing date back to the beginning of this century (Haldane and Priestley [18]) ...
... this type see, e.g., Noordergraaf [50] or Swan [66]. A comprehensive discussion of the control mechanisms in the human cardiovascular system is given in Guyton [17] or Rowell [60]. Models dealing with the regulation of breathing date back to the beginning of this century (Haldane and Priestley [18]) ...
Hemispheric Asymmetry Reduction in Older Adults
... semantic retrieval was absent for several years but was recently reported by Stebbins et al. (2002) and Logan and Buckner (2001). Stebbins et al. (2002) examined age-related differences in PFC activity during deep (concrete–abstract) and shallow (uppercase– lowercase) incidental encoding of words. I ...
... semantic retrieval was absent for several years but was recently reported by Stebbins et al. (2002) and Logan and Buckner (2001). Stebbins et al. (2002) examined age-related differences in PFC activity during deep (concrete–abstract) and shallow (uppercase– lowercase) incidental encoding of words. I ...
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Reduces Amyloidogenic
... patients with AD. Using screening approaches in primary neurons, we identified brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as a major inducer of Sorla that activates receptor gene transcription through the ERK (extracellular regulated kinase) pathway. In line with a physiological role as regulator of S ...
... patients with AD. Using screening approaches in primary neurons, we identified brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as a major inducer of Sorla that activates receptor gene transcription through the ERK (extracellular regulated kinase) pathway. In line with a physiological role as regulator of S ...
Vocal cord dysfunction: a functional cause of respiratory
... cord movement with adduction in inspiration and passive abduction on expiration (see video 1 in the supplementary material, with audio). This demonstrated that her dyspnoea was from VCD. The evaluation included a large positive skinprick test to corn pollen. That explained the initial episodes as be ...
... cord movement with adduction in inspiration and passive abduction on expiration (see video 1 in the supplementary material, with audio). This demonstrated that her dyspnoea was from VCD. The evaluation included a large positive skinprick test to corn pollen. That explained the initial episodes as be ...
Stress and Glucocorticoids Affect the Expression of Brain
... ticoids hasten the loss of hippocampal neurons that normally occurs during aging (Landfield, 1987). As the hippocampus is important in cognitive processes such as learning and memory, neuronal damage to this structure may be linked to the cognitive impairments that occur during aging and chronic str ...
... ticoids hasten the loss of hippocampal neurons that normally occurs during aging (Landfield, 1987). As the hippocampus is important in cognitive processes such as learning and memory, neuronal damage to this structure may be linked to the cognitive impairments that occur during aging and chronic str ...
What is the role of muscle receptors in proprioception?
... whereas the sensory map was distorted by it. The illusions seen in subjects after whole-body paralysis10 could be interpreted in terms of conflicting information reaching sensory and motor maps. Evidence that the effort and position control systems can be accessed facultatively has been demonstrated ...
... whereas the sensory map was distorted by it. The illusions seen in subjects after whole-body paralysis10 could be interpreted in terms of conflicting information reaching sensory and motor maps. Evidence that the effort and position control systems can be accessed facultatively has been demonstrated ...
Cerebral blood flow and gray matter volume covariance patterns of
... relationships and null results. Furthermore, this review found that relationships between structure and cognition remained stable across the lifespan, supporting the concept of neural reserve [Stern, 2009; Stern et al., 2005]. The purpose of this study was to examine the degree to which cognitive ch ...
... relationships and null results. Furthermore, this review found that relationships between structure and cognition remained stable across the lifespan, supporting the concept of neural reserve [Stern, 2009; Stern et al., 2005]. The purpose of this study was to examine the degree to which cognitive ch ...
AP Biology Lab 8/pdf
... form a tube is due to a dominant allele (Figure 2). Nonrollers are homozygous recessive for the trait. Widow’s Peak: The widow’s peak is a distinct downward point of the frontal hairline and is due to a dominant allele. Homozygous recessive individuals have a straight hairline. Of course, male patte ...
... form a tube is due to a dominant allele (Figure 2). Nonrollers are homozygous recessive for the trait. Widow’s Peak: The widow’s peak is a distinct downward point of the frontal hairline and is due to a dominant allele. Homozygous recessive individuals have a straight hairline. Of course, male patte ...
Chemotherapy and Cognitive Impairment
... the potential underlying neurobiological mechanisms linking chemotherapy with cognitive impairment (Figure 1; for reviews, see refs. 18,19). Healthy rodents that are given chemotherapy show increase in cell death in the central nervous system,20 increase in oxidative stress,20,21 increase in microgl ...
... the potential underlying neurobiological mechanisms linking chemotherapy with cognitive impairment (Figure 1; for reviews, see refs. 18,19). Healthy rodents that are given chemotherapy show increase in cell death in the central nervous system,20 increase in oxidative stress,20,21 increase in microgl ...
Impact of diet on adult hippocampal neurogenesis
... correlation; therefore, it is possible that other factors such as structural plasticity, neurotrophin or hormone levels also contribute to genetically and environmentally induced changes in hippocampus-dependent learning and memory. Newborn neurons represent only a small cell population within the a ...
... correlation; therefore, it is possible that other factors such as structural plasticity, neurotrophin or hormone levels also contribute to genetically and environmentally induced changes in hippocampus-dependent learning and memory. Newborn neurons represent only a small cell population within the a ...
- Journal of Adolescent Health
... the hippocampus in the pathophysiology of PTSS, specifically as they relate to learning from previous experience. Animal research has shown that one potential mechanism of damage to the hippocampus is through corticosterone, the animal analog to cortisol in humans, which can be neurotoxic if secreted ...
... the hippocampus in the pathophysiology of PTSS, specifically as they relate to learning from previous experience. Animal research has shown that one potential mechanism of damage to the hippocampus is through corticosterone, the animal analog to cortisol in humans, which can be neurotoxic if secreted ...
Cognitive neuroscience of self-regulation failure
... Although the notion that glucose metabolism affects self-regulation is recent, the impact of glucose on cognitive performance has been known for some time. For example, studies conducted in the 1990 s showed that administering glucose improves performance on memory tasks and on tasks requiring respo ...
... Although the notion that glucose metabolism affects self-regulation is recent, the impact of glucose on cognitive performance has been known for some time. For example, studies conducted in the 1990 s showed that administering glucose improves performance on memory tasks and on tasks requiring respo ...
AQAAS_ch2 Resp.system
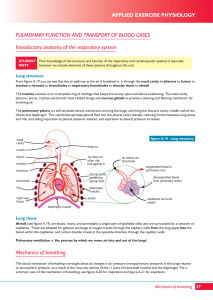
... One of the short-term effects of physical activity is to cause a small increase in pulmonary blood pressure, which distorts red blood corpuscles within the alveolar capillary system, and this enables 10 times as much oxygen to be picked up as at rest. ...
... One of the short-term effects of physical activity is to cause a small increase in pulmonary blood pressure, which distorts red blood corpuscles within the alveolar capillary system, and this enables 10 times as much oxygen to be picked up as at rest. ...
Neural mechanisms of the cognitive model of depression
... brain structure that is involved in detecting emotion (possibly linked to its proposed role in salience detection38,39), interprets and perpetuates the emotional quality of the stimulus and seems to be regulated in part by indirect inhibitory input from the left DLPFC40,41. Amygdala activity increas ...
... brain structure that is involved in detecting emotion (possibly linked to its proposed role in salience detection38,39), interprets and perpetuates the emotional quality of the stimulus and seems to be regulated in part by indirect inhibitory input from the left DLPFC40,41. Amygdala activity increas ...
Central neural control of the cardiovascular system
... curve to the right) (49) as well as central regulatory mechanisms that maintain the arterial blood PO2 (PaO2) despite large changes in metabolic activity (1). Apart from physical exercise, coordinated cardiovascular and respiratory mechanisms regulate the O2 supply to all tissue during other behavio ...
... curve to the right) (49) as well as central regulatory mechanisms that maintain the arterial blood PO2 (PaO2) despite large changes in metabolic activity (1). Apart from physical exercise, coordinated cardiovascular and respiratory mechanisms regulate the O2 supply to all tissue during other behavio ...
Neurobiological effects of physical exercise

The neurobiological effects of physical exercise are numerous and involve a wide range of interrelated neuropsychological changes. A large body of research in humans has demonstrated that consistent aerobic exercise (e.g., 30 minutes every day) induces persistent beneficial behavioral and neural plasticity as well as healthy alterations in gene expression in the brain; some of these long-term effects include: increased neuron growth, increased neurological activity (c-Fos and BDNF signaling), improved stress coping, enhanced cognitive control over behavior, improved declarative and working memory, and structural and functional improvements in brain structures and pathways associated with cognitive control and memory. The effects of exercise on cognition have important implications for improving academic performance in children and college students, improving adult productivity, preserving cognitive function in old age, preventing or treating certain neurological disorders, and improving overall quality of life.People who regularly participate in aerobic exercise have greater scores on neuropsychological function and performance tests. Examples of aerobic exercise that produce these changes are running, jogging, brisk walking, swimming, and cycling. Exercise intensity and duration are positively correlated with the release of neurotrophic factors and the magnitude of nearly all forms of exercise-induced behavioral and neural plasticity; consequently, more pronounced improvements in measures of neuropsychological performance are observed in endurance athletes as compared with recreational athletes or sedentary individuals. Aerobic exercise is also a potent long-term antidepressant and a short-term euphoriant; consequently, consistent exercise has also been shown to produce general improvements in mood and self-esteem in all individuals.