Synaptic function: Dendritic democracy
... a somato-dendritic gradient, in a manner that has important functional consequences. This indicates that there must be general mechanisms by which protein density, and possibly also dendritic structure, may be regulated depending on dendritic distance. A particularly interesting question is how dend ...
... a somato-dendritic gradient, in a manner that has important functional consequences. This indicates that there must be general mechanisms by which protein density, and possibly also dendritic structure, may be regulated depending on dendritic distance. A particularly interesting question is how dend ...
dendritic integration
... models in large-scale networks. Another strategy is to develop abstractions of neurons that capture the essential processing power of the real thing. A paper by Polsky and colleagues1 in this issue represents a large step in this direction by providing experimental insight into what kinds of computa ...
... models in large-scale networks. Another strategy is to develop abstractions of neurons that capture the essential processing power of the real thing. A paper by Polsky and colleagues1 in this issue represents a large step in this direction by providing experimental insight into what kinds of computa ...
KKDP 3: The role of the neuron (dendrites, axon, myelin and
... Dendrites ‘outgrowths’, called dendritic spines. A neuron may have from one to 20 dendrites, each dendrite may have from one to many branches, and the total numbers of spines on the branches may be in the hundreds or thousands. This means that a single neuron can have many thousands of connectio ...
... Dendrites ‘outgrowths’, called dendritic spines. A neuron may have from one to 20 dendrites, each dendrite may have from one to many branches, and the total numbers of spines on the branches may be in the hundreds or thousands. This means that a single neuron can have many thousands of connectio ...
A first-principle for the nervous system
... directs the search towards a mechanism at the presynaptic terminals at the ends of converging axons and naturally towards their respective synapses. Between what locations of the synapses of the converging inputs do learning-induced changes occur from which the cue stimulus can induce internal sensa ...
... directs the search towards a mechanism at the presynaptic terminals at the ends of converging axons and naturally towards their respective synapses. Between what locations of the synapses of the converging inputs do learning-induced changes occur from which the cue stimulus can induce internal sensa ...
Opposite Effects of Amphetamine Self
... in particular, in orbital frontal cortex (OFC). For example, imaging studies in human stimulant users have found persistent basal and drug-induced changes in metabolic activity (Volkow et al., 1992; Paulus et al., 2002; Adinoff et al., 2003; Bolla et al., 2003), DA receptor levels (Volkow et al., 19 ...
... in particular, in orbital frontal cortex (OFC). For example, imaging studies in human stimulant users have found persistent basal and drug-induced changes in metabolic activity (Volkow et al., 1992; Paulus et al., 2002; Adinoff et al., 2003; Bolla et al., 2003), DA receptor levels (Volkow et al., 19 ...
Opposite Effects of Amphetamine Self
... in particular, in orbital frontal cortex (OFC). For example, imaging studies in human stimulant users have found persistent basal and drug-induced changes in metabolic activity (Volkow et al., 1992; Paulus et al., 2002; Adinoff et al., 2003; Bolla et al., 2003), DA receptor levels (Volkow et al., 19 ...
... in particular, in orbital frontal cortex (OFC). For example, imaging studies in human stimulant users have found persistent basal and drug-induced changes in metabolic activity (Volkow et al., 1992; Paulus et al., 2002; Adinoff et al., 2003; Bolla et al., 2003), DA receptor levels (Volkow et al., 19 ...
LTP
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
Fast Readout of Object Identity from Macaque Inferior Temporal Cortex
... from the retina to anterior IT cortex, it has been proposed that the computations at each stage are based on just one or very few spikes per neuron (6, 7). At the end of the ventral stream, single cells in IT cortex show selectivity for complex objects with some tolerance to changes in object scale ...
... from the retina to anterior IT cortex, it has been proposed that the computations at each stage are based on just one or very few spikes per neuron (6, 7). At the end of the ventral stream, single cells in IT cortex show selectivity for complex objects with some tolerance to changes in object scale ...
Netter`s Atlas of Neuroscience - 9780323265119 | US Elsevier
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...
Channelrhodopsin as a tool to study synaptic
... to study activity-related processes at the level of individual neurons (Matsuo et al. 2008) and allows identification of stimulated cells without the need to monitor electrical activity during stimulation. Local ChR2 activation. Most studies employing ChR2 have used wide-field illumination for chann ...
... to study activity-related processes at the level of individual neurons (Matsuo et al. 2008) and allows identification of stimulated cells without the need to monitor electrical activity during stimulation. Local ChR2 activation. Most studies employing ChR2 have used wide-field illumination for chann ...
Adult Cortical Plasticity
... Use-dependent changes in synaptic functions Long-term potentiation (LTP) and Long-term depression (LTD) -- Persistent increase or decrease in synaptic response due to repetitive activity, found in hippocampus and cortex -- Brief high-frequency stimulation – LTP Prolonged low-frequency stimulation – ...
... Use-dependent changes in synaptic functions Long-term potentiation (LTP) and Long-term depression (LTD) -- Persistent increase or decrease in synaptic response due to repetitive activity, found in hippocampus and cortex -- Brief high-frequency stimulation – LTP Prolonged low-frequency stimulation – ...
Slide 1
... the Mg2+ block in the presence of bound glutamate. Calcium may also enter through the ligand-gated AMPA receptor channel or voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC), which may be located on the spine head or dendritic shaft. Calcium pumps (P), located on the spine head, neck, and dendritic shaft, are h ...
... the Mg2+ block in the presence of bound glutamate. Calcium may also enter through the ligand-gated AMPA receptor channel or voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC), which may be located on the spine head or dendritic shaft. Calcium pumps (P), located on the spine head, neck, and dendritic shaft, are h ...
39_LectureSlides
... III. Topics/Controversies in recent research (not in the text book) A. Are cortical ocular dominance columns set up prenatally in absence of neural activity? Molecular matching? B. Dendritic Spines (sites of excitatory synaptic input on large neurons) are highly dynamic, changing shape and synaptic ...
... III. Topics/Controversies in recent research (not in the text book) A. Are cortical ocular dominance columns set up prenatally in absence of neural activity? Molecular matching? B. Dendritic Spines (sites of excitatory synaptic input on large neurons) are highly dynamic, changing shape and synaptic ...
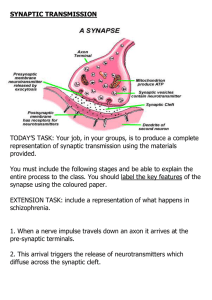
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... 3. When released, the neurotransmitter must be taken up immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic ...
... 3. When released, the neurotransmitter must be taken up immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic ...
Pull out the stops for plasticity
... Jonathan M. Levine is at the Institute of Integrative Biology, Department of ...
... Jonathan M. Levine is at the Institute of Integrative Biology, Department of ...
Long-term depression
... Purkinje cells only output from cerebellar cortex inhibit deep cerebellar nuclei Input to Purkinje cells Mossy fibers via parallel fibers ...
... Purkinje cells only output from cerebellar cortex inhibit deep cerebellar nuclei Input to Purkinje cells Mossy fibers via parallel fibers ...
presentation
... n Gaussian PSP generates spikes with more timing reliable n Ion-channel variability is included (Gaussian) ...
... n Gaussian PSP generates spikes with more timing reliable n Ion-channel variability is included (Gaussian) ...
Watching synapses during sensory information
... At present, due to the technical constraints, our knowledge about the dendritic organization of sensory inputs in cortical neurons is largely restricted to neurons that are located near the cortical surface, i.e. at a depth of 100-300 µm [14-16, 19]. Future development of two-photon microscopy may h ...
... At present, due to the technical constraints, our knowledge about the dendritic organization of sensory inputs in cortical neurons is largely restricted to neurons that are located near the cortical surface, i.e. at a depth of 100-300 µm [14-16, 19]. Future development of two-photon microscopy may h ...
Cellular Neuroanatomy II
... Dendritic trees have a large variety of shapes and sizes to enhance this functionality. In addition, the dendritic membrane has many specialized protein molecules called receptors that detect the chemicals released at the synapse. cell bodies: blue microtubules: green axon terminals: red ...
... Dendritic trees have a large variety of shapes and sizes to enhance this functionality. In addition, the dendritic membrane has many specialized protein molecules called receptors that detect the chemicals released at the synapse. cell bodies: blue microtubules: green axon terminals: red ...
research Nerve Cells, Axons, Dendrites, and Synapses: The
... Neuron system responds and Structure makes the synaptic Cell contact stronger. This Body response also causes the neuron to expand its receptive connections, the dendrites, and it Dendrite creates more axon contacts for association. These are real physical changes and they can be demonstrated in exp ...
... Neuron system responds and Structure makes the synaptic Cell contact stronger. This Body response also causes the neuron to expand its receptive connections, the dendrites, and it Dendrite creates more axon contacts for association. These are real physical changes and they can be demonstrated in exp ...
Dendritic spine

A dendritic spine (or spine) is a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite that typically receives input from a single synapse of an axon. Dendritic spines serve as a storage site for synaptic strength and help transmit electrical signals to the neuron's cell body. Most spines have a bulbous head (the spine head), and a thin neck that connects the head of the spine to the shaft of the dendrite. The dendrites of a single neuron can contain hundreds to thousands of spines. In addition to spines providing an anatomical substrate for memory storage and synaptic transmission, they may also serve to increase the number of possible contacts between neurons.