Quadratic Functions
... 7) Nucleolus is another organelle located in the nucleus along with the DNA. It produces ribosomal subunits, which will leave the nucleus and combine to form ribosomes. 8) Ribosomes assemble proteins (enzymes) from amino acids according to the direction of the DNA. Note: These are not bound by membr ...
... 7) Nucleolus is another organelle located in the nucleus along with the DNA. It produces ribosomal subunits, which will leave the nucleus and combine to form ribosomes. 8) Ribosomes assemble proteins (enzymes) from amino acids according to the direction of the DNA. Note: These are not bound by membr ...
Cell Organelles and Functions
... hair-like organelles, identical in structure to flagella, that line the surfaces of certain cells and beat in rhythmic waves, providing locomotion to ciliate protozoans and moving liquids along internal epithelial tissue in humans and animals. ...
... hair-like organelles, identical in structure to flagella, that line the surfaces of certain cells and beat in rhythmic waves, providing locomotion to ciliate protozoans and moving liquids along internal epithelial tissue in humans and animals. ...
Cell-Structure-and
... 1. All living organisms are made of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism 3. Cell come only from the reproduction of existing cells ...
... 1. All living organisms are made of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism 3. Cell come only from the reproduction of existing cells ...
Explore HW
... Scientists discover Critter X. They know it is an aquatic animal and can live in water but they are not sure if it lives in salt water or fresh water. When they place Critter X in distilled water the cells and tissues swell up and begin to rupture. What is happening and what does it tell scientists ...
... Scientists discover Critter X. They know it is an aquatic animal and can live in water but they are not sure if it lives in salt water or fresh water. When they place Critter X in distilled water the cells and tissues swell up and begin to rupture. What is happening and what does it tell scientists ...
Week 9 CELL WALLS are found in plant cells. They are made up of
... A collection of cells that perform the same function and that work together is called a TISSUE. Examples of tissues include nervous tissues, muscle tissue, and blood tissue. ...
... A collection of cells that perform the same function and that work together is called a TISSUE. Examples of tissues include nervous tissues, muscle tissue, and blood tissue. ...
Cells are organized into.
... 52 Compared to annual rings of trees that have experienced years of sufficient rainfall, the annual rings of trees that have experienced a dry period will — ...
... 52 Compared to annual rings of trees that have experienced years of sufficient rainfall, the annual rings of trees that have experienced a dry period will — ...
Cells - cloudfront.net
... Made of microfilaments & microtubules Help support cell Maintains its shape Helps materials move within the cell ...
... Made of microfilaments & microtubules Help support cell Maintains its shape Helps materials move within the cell ...
AP Biology - San Marcos Middle School
... 3. What are the most important plastids? Why are they so important? 4. What is the function of the central vacuole (use the phrase “turgor pressure” in your answer)? Page 3 of 4 ...
... 3. What are the most important plastids? Why are they so important? 4. What is the function of the central vacuole (use the phrase “turgor pressure” in your answer)? Page 3 of 4 ...
Case#1 Erythocytes (red blood cells), are much smaller than most
... The following are REAL conditions affecting plant animal and bacterial cells. Try and figure what is going on!! (these are difficult, but give them a try) Case#1 Erythocytes (red blood cells), are much smaller than most human cells, and contain about 270 million hemoglobin molecules, the molecule re ...
... The following are REAL conditions affecting plant animal and bacterial cells. Try and figure what is going on!! (these are difficult, but give them a try) Case#1 Erythocytes (red blood cells), are much smaller than most human cells, and contain about 270 million hemoglobin molecules, the molecule re ...
Cells Alive- Internet Lesson
... 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Rough ER 9. What is the function of the cytosol? ...
... 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Rough ER 9. What is the function of the cytosol? ...
Notes for Cell Transport
... Some simple, single-celled organisms have contractile vacuoles which store excess water and then squirt it out. (c) Most cells pump ions out of the cell. This increases the solute concentration outside the cell and water follows by osmosis. (d) In complex organisms such as humans, the blood is isoto ...
... Some simple, single-celled organisms have contractile vacuoles which store excess water and then squirt it out. (c) Most cells pump ions out of the cell. This increases the solute concentration outside the cell and water follows by osmosis. (d) In complex organisms such as humans, the blood is isoto ...
Cells - Ms. Brandon`s Classroom
... Cell Wall – a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. Cell Membrane – All cells have cell membranes. The cell membrane controls what substances come into and out of a cell and provides a barrier and protects the cell and its environment. Nucleus ...
... Cell Wall – a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. Cell Membrane – All cells have cell membranes. The cell membrane controls what substances come into and out of a cell and provides a barrier and protects the cell and its environment. Nucleus ...
Cell Structure
... • Vesicles are sacs containing enzymes – Lysosomes • Intracellular digestion • Destroy bacteria in white blood cells • Breaks down damaged organelles ...
... • Vesicles are sacs containing enzymes – Lysosomes • Intracellular digestion • Destroy bacteria in white blood cells • Breaks down damaged organelles ...
No Slide Title
... a. He observed them closely to identify their traits. b. He determined the relative ages of pigeon fossils c. He allowed only birds with desirable traits to breed. d. He transferred genetic material from one bird to another ...
... a. He observed them closely to identify their traits. b. He determined the relative ages of pigeon fossils c. He allowed only birds with desirable traits to breed. d. He transferred genetic material from one bird to another ...
cell membrane
... lysosome will attach itself to it and break it down like food (kind of like a cannibal) • Lysosomes can also destroy the cell if it breaks ...
... lysosome will attach itself to it and break it down like food (kind of like a cannibal) • Lysosomes can also destroy the cell if it breaks ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
Class 3
... THAN OUR BODY; FREES UP WATER TO GO TO CELL; TOO MUCH = HEMOLYSIS (0.45% NaCl) HYPERTONIC – MORE SOLUTE THAN OUR BODY; PULLS WATER TOWARD IT; TOO MUCH DEHYDRATED CELL = CRENATION (3% NaCl) ...
... THAN OUR BODY; FREES UP WATER TO GO TO CELL; TOO MUCH = HEMOLYSIS (0.45% NaCl) HYPERTONIC – MORE SOLUTE THAN OUR BODY; PULLS WATER TOWARD IT; TOO MUCH DEHYDRATED CELL = CRENATION (3% NaCl) ...
Two Basic Cell Types: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... easily and quickly reach inner parts of the cell. – Eukaryotic cells are larger and can not pass nutrients as quickly. They require specialized organelles to: • carry out metabolism ...
... easily and quickly reach inner parts of the cell. – Eukaryotic cells are larger and can not pass nutrients as quickly. They require specialized organelles to: • carry out metabolism ...
Cells - Uplift Education
... Selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the environment. What does ‘selectively permeable’ mean? Only some materials can cross the membrane Selective permeability is necessary for the cell to maintain the correct internal environment for physiological functions. ...
... Selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the environment. What does ‘selectively permeable’ mean? Only some materials can cross the membrane Selective permeability is necessary for the cell to maintain the correct internal environment for physiological functions. ...
NAME DATE ______ PERIOD _____
... 11. NO other kind of atom can form the number and variety of molecules that ___________ can because it can bond to 4 other atoms at the same time to make carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. A. hydrogen B. oxygen C. carbon D. sodium ...
... 11. NO other kind of atom can form the number and variety of molecules that ___________ can because it can bond to 4 other atoms at the same time to make carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. A. hydrogen B. oxygen C. carbon D. sodium ...
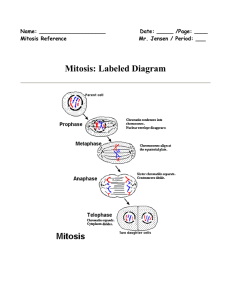
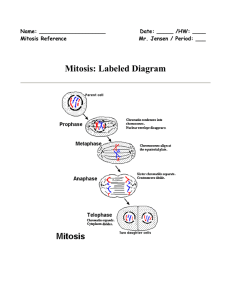
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.