Pre-Lesson3: Growth (fill in the blanks)
... or hair of cells chained together. Some of the photosynthetic bacteria have this shape, but we will not study them. ...
... or hair of cells chained together. Some of the photosynthetic bacteria have this shape, but we will not study them. ...
Geminian Proteins Dual Nature Plays Key Role in
... therapies,” said Dr. Yu. “We have developed a model that proposes that TGF-β’s complicated nature may be governed by the cellular effects of SMAD’s partner proteins.” Their model was developed by using premalignant mammary epithelial cells in an experimental protocol to study the effects of differen ...
... therapies,” said Dr. Yu. “We have developed a model that proposes that TGF-β’s complicated nature may be governed by the cellular effects of SMAD’s partner proteins.” Their model was developed by using premalignant mammary epithelial cells in an experimental protocol to study the effects of differen ...
Hormones in intermediary metabolism
... Thyroid hormones actions • ↑ protein synthesis, but ↑↑ protein catabolism – result is proteocatabolic • Increased breakdown of muscle proteins • Stimulation of synthesis: Na+/K+ pump, respiratory chain enzymes, ... • The pro-growth importance: T3 and T4 support metabolism, which is necessary for pr ...
... Thyroid hormones actions • ↑ protein synthesis, but ↑↑ protein catabolism – result is proteocatabolic • Increased breakdown of muscle proteins • Stimulation of synthesis: Na+/K+ pump, respiratory chain enzymes, ... • The pro-growth importance: T3 and T4 support metabolism, which is necessary for pr ...
Sample
... adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (23) nucleus (23) chromosome (23) deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) (24) gene (24) cytoskeleton (24) enzyme (24) axoplasmic transport (24) microtubule (24) glia (24) astrocyte (24) phagocytosis (25) oligodendrocyte (25) myelin sheath (25) node of Ranvier (25) microglia (27) Sc ...
... adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (23) nucleus (23) chromosome (23) deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) (24) gene (24) cytoskeleton (24) enzyme (24) axoplasmic transport (24) microtubule (24) glia (24) astrocyte (24) phagocytosis (25) oligodendrocyte (25) myelin sheath (25) node of Ranvier (25) microglia (27) Sc ...
Gene Section GCNT3 (glucosaminyl (N-acetyl) transferase 3, mucin type)
... survival rate of colorectal cancer is not much higher than 50% even if the disease is diagnosed at an early stage. Colorectal cancer is mostly formed from adenomatous polyps. These polyps can be detected and removed during colonoscopy, which would decrease cancer death by greater than 80%. Metastasi ...
... survival rate of colorectal cancer is not much higher than 50% even if the disease is diagnosed at an early stage. Colorectal cancer is mostly formed from adenomatous polyps. These polyps can be detected and removed during colonoscopy, which would decrease cancer death by greater than 80%. Metastasi ...
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #1 KEY February 28, 2006
... (iii) How does the magnitude of the membrane potential across the lipid bilayer change over time? It doesn’t. It remains at zero the whole time. Ions cannot pass through the membrane unless there is a channel, pump, or transporter that allows movement of the ion. Ions traveling through channels is w ...
... (iii) How does the magnitude of the membrane potential across the lipid bilayer change over time? It doesn’t. It remains at zero the whole time. Ions cannot pass through the membrane unless there is a channel, pump, or transporter that allows movement of the ion. Ions traveling through channels is w ...
Tns (H-300): sc-28542 - Santa Cruz Biotechnology
... Tensin (Tns) is an actin filament capping protein localized to various types of adherens junctions in muscle and non-muscle cells. Tensin is involved in the maintenance of cellular structure by anchoring actin filaments at the focal adhesion via F-Actin binding and capping activities. However, tensi ...
... Tensin (Tns) is an actin filament capping protein localized to various types of adherens junctions in muscle and non-muscle cells. Tensin is involved in the maintenance of cellular structure by anchoring actin filaments at the focal adhesion via F-Actin binding and capping activities. However, tensi ...
Chapter 44
... Nerve Impulse Transmission • Propagation of action potentials – Each action potential, in its rising phase, reflects a reversal in membrane polarity – Positive charges due to influx of Na+ can depolarize the adjacent region to threshold – And so the next region produces its own action potential – M ...
... Nerve Impulse Transmission • Propagation of action potentials – Each action potential, in its rising phase, reflects a reversal in membrane polarity – Positive charges due to influx of Na+ can depolarize the adjacent region to threshold – And so the next region produces its own action potential – M ...
Human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER-1:HER
... this family of receptors, only HER-1, HER-3, and HER-4 bind canonical growth factor ligands (1, 2, 4). HER-1, HER-2, and HER-4 are active as tyrosine kinases, whereas HER-3, despite having a kinase domain, is inactive as a kinase and signals via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway (1, 4 – 9). ...
... this family of receptors, only HER-1, HER-3, and HER-4 bind canonical growth factor ligands (1, 2, 4). HER-1, HER-2, and HER-4 are active as tyrosine kinases, whereas HER-3, despite having a kinase domain, is inactive as a kinase and signals via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway (1, 4 – 9). ...
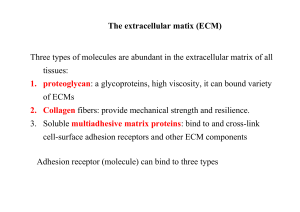
The extracellular matix (ECM) Three types of molecules are
... Three types of molecules are abundant in the extracellular matrix of all tissues: 1. proteoglycan: a glycoproteins, high viscosity, it can bound variety of ECMs 2. Collagen fibers: provide mechanical strength and resilience. 3. Soluble multiadhesive matrix proteins: bind to and cross-link cell-surfa ...
... Three types of molecules are abundant in the extracellular matrix of all tissues: 1. proteoglycan: a glycoproteins, high viscosity, it can bound variety of ECMs 2. Collagen fibers: provide mechanical strength and resilience. 3. Soluble multiadhesive matrix proteins: bind to and cross-link cell-surfa ...
Chapters 4 and 5 Cell Structures, Functions and Transport
... Function: packages and transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell Appearance: stack of pancakes ...
... Function: packages and transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell Appearance: stack of pancakes ...
Mitosis PPT
... The cell cycle is driven by specific chemical signals present in the cytoplasm Sequential events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct cell cycle control system - driven by a built in clock - the cell cycle is regulated at certain checkpoints by internal and external controls ...
... The cell cycle is driven by specific chemical signals present in the cytoplasm Sequential events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct cell cycle control system - driven by a built in clock - the cell cycle is regulated at certain checkpoints by internal and external controls ...
Fermentation
... • Biosynthesis helps organisms to grow and maintain their structure • Definition provided by definition bing.com • biological production of chemical substances: the synthesis of chemical substances as the result of biological activity ...
... • Biosynthesis helps organisms to grow and maintain their structure • Definition provided by definition bing.com • biological production of chemical substances: the synthesis of chemical substances as the result of biological activity ...
Science Vocabulary: Cells and Behavior Traits
... rigid (stiff) than the cell membrane. It provides the plant with its shape and stiffness. 8. Chloroplast: chloroplasts are found in the cytoplasm of a plant cell. Chloroplasts contain a green substance called chlorophyll. 9. Chlorophyll: Chlorophyll is the green pigment needed by plants to make food ...
... rigid (stiff) than the cell membrane. It provides the plant with its shape and stiffness. 8. Chloroplast: chloroplasts are found in the cytoplasm of a plant cell. Chloroplasts contain a green substance called chlorophyll. 9. Chlorophyll: Chlorophyll is the green pigment needed by plants to make food ...
Mammalian skin cell biology: At the interface between
... 500 knockout mouse mutants via confocal microscopy (39). Roughly 10% of mutants had an epidermal phenotype, several of which mapped to known human genetic conditions. Some mutant genes were expressed in the skin, whereas others were not, indicating systemic effects that could not have been found by ...
... 500 knockout mouse mutants via confocal microscopy (39). Roughly 10% of mutants had an epidermal phenotype, several of which mapped to known human genetic conditions. Some mutant genes were expressed in the skin, whereas others were not, indicating systemic effects that could not have been found by ...
protein metabolism - cmb
... phenomenon referred to as heat-shock response or stress response. Many of these proteins were found to be molecular chaperones. ...
... phenomenon referred to as heat-shock response or stress response. Many of these proteins were found to be molecular chaperones. ...
animal_vs_plant_cell_cycle_comparison
... 2. Provide a summary for each of the phases in the spaces provided. ANIMAL CELL CYCLE STAGE NAME AND PICTORIAL REPRESENTATION SUMMARY -G1 phase: The cell increases in size (period of Interphase growth) and synthesizes new proteins and organelles. -S phase - As the cell prepares for mitosis, the chro ...
... 2. Provide a summary for each of the phases in the spaces provided. ANIMAL CELL CYCLE STAGE NAME AND PICTORIAL REPRESENTATION SUMMARY -G1 phase: The cell increases in size (period of Interphase growth) and synthesizes new proteins and organelles. -S phase - As the cell prepares for mitosis, the chro ...
CHAPTER 3: CELLS
... Nuclear Membrane (or nuclear envelope) is a double membrane that separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm; ...
... Nuclear Membrane (or nuclear envelope) is a double membrane that separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm; ...
Rotate into shape: MreB and bacterial
... MreB, the bacterial actin homologue, plays a vital role in determining cell shape, but the mechanisms by which it actually functions have remained largely mysterious. Recent studies now shed new light on MreB, demonstrating that it associates with many cell-wall synthesis enzymes, including a newly ...
... MreB, the bacterial actin homologue, plays a vital role in determining cell shape, but the mechanisms by which it actually functions have remained largely mysterious. Recent studies now shed new light on MreB, demonstrating that it associates with many cell-wall synthesis enzymes, including a newly ...
Ch 6-2 6-3 Notes Labeled
... 3. Second growth (G2) phase: In the G2 phase, preparations are made for the nucleus to divide. Microtubules are rearranged. 4. Mitosis: Mitosis is the process during cell division in which the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei, each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the ori ...
... 3. Second growth (G2) phase: In the G2 phase, preparations are made for the nucleus to divide. Microtubules are rearranged. 4. Mitosis: Mitosis is the process during cell division in which the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei, each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the ori ...
Chapter 4 Notes/Activities Package BLANK
... The DNA message (_________) for the protein is copied into a small molecule called _______. ...
... The DNA message (_________) for the protein is copied into a small molecule called _______. ...
two genes control a superoxide stress regulon
... entire sequence has been deposited in the EMBL Data Library (accession number X59593) and is identical to that just reported by Wu and Weiss (21). The first ORF encodes a predicted protein of 107 amino acids and molecular weight 12,902. The second ORF encodes a predicted protein of 154 amino acids a ...
... entire sequence has been deposited in the EMBL Data Library (accession number X59593) and is identical to that just reported by Wu and Weiss (21). The first ORF encodes a predicted protein of 107 amino acids and molecular weight 12,902. The second ORF encodes a predicted protein of 154 amino acids a ...
Chapter 3 Cells The Basic Units of Life
... - The surface of a cell is the area that interfaces with the cell’s environment. The volume of a cell is a measure of the space inside a cell. - Surface area-to-volume ratio is defined as the surface area divided by the volume. For any given shape, increasing volume decreases the surface area-to-vol ...
... - The surface of a cell is the area that interfaces with the cell’s environment. The volume of a cell is a measure of the space inside a cell. - Surface area-to-volume ratio is defined as the surface area divided by the volume. For any given shape, increasing volume decreases the surface area-to-vol ...
The fundamental units of life
... Ans) Lysosomes contains hydrolytic enzymes and these enzymes may digest their own content. And cell would die. Thus, they are called suicidal bag. Q10) which organelle is known as the power house of the cell? Why? Ans) ‘Mitochondria’ is known as the power house of the cell. They are site for synthes ...
... Ans) Lysosomes contains hydrolytic enzymes and these enzymes may digest their own content. And cell would die. Thus, they are called suicidal bag. Q10) which organelle is known as the power house of the cell? Why? Ans) ‘Mitochondria’ is known as the power house of the cell. They are site for synthes ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.