Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes - Duncanville Middle School
... Ribosomes are produced inside the nucleus at the nucleolus. ...
... Ribosomes are produced inside the nucleus at the nucleolus. ...
questions - Hatboro
... 10. What is the space between neurons called? 11. The sending cell converts the electrical signal to a chemical signal at the axon terminal. These chemical signals are called __________________________________ and are contained in bags called _____________________________. 12. What’s the neurotransm ...
... 10. What is the space between neurons called? 11. The sending cell converts the electrical signal to a chemical signal at the axon terminal. These chemical signals are called __________________________________ and are contained in bags called _____________________________. 12. What’s the neurotransm ...
Name: : :___ PLASMA MEMBRANE QUESTIONS 1. The cell
... D. are only found on the outer layer of the membrane. 9. Which molecules function as pores and carriers in a cell membrane? A. lipids B. proteins C. nucleotides D. carbohydrates Use the following diagram to answer question 10. 10. a) Identify molecule X. (1 mark) • phospholipid (1 mark) b) Give one ...
... D. are only found on the outer layer of the membrane. 9. Which molecules function as pores and carriers in a cell membrane? A. lipids B. proteins C. nucleotides D. carbohydrates Use the following diagram to answer question 10. 10. a) Identify molecule X. (1 mark) • phospholipid (1 mark) b) Give one ...
Cells
... boundary, allowing only certain substances to pass. They are mainly composed of proteins and lipids called phospholipids. Since lipids are hydrophobic, they create a boundary between the cell’s aqueous cytoplasm and the aqueous environment surrounding the cell. ...
... boundary, allowing only certain substances to pass. They are mainly composed of proteins and lipids called phospholipids. Since lipids are hydrophobic, they create a boundary between the cell’s aqueous cytoplasm and the aqueous environment surrounding the cell. ...
Slide 1
... The process by which water molecules defuse across a cell membrane from a area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. ...
... The process by which water molecules defuse across a cell membrane from a area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. ...
PowerPoint
... • Hypotonic: Low solute on the outside of cell causing the water to rush into the cells to reach an equilibrium….cell could lyse (explode) • Hypertonic: High solute on the outside causing water to leave cell and cell dehydrates (crenate) • Isotonic: Cell and solute are at an equilibrium. ...
... • Hypotonic: Low solute on the outside of cell causing the water to rush into the cells to reach an equilibrium….cell could lyse (explode) • Hypertonic: High solute on the outside causing water to leave cell and cell dehydrates (crenate) • Isotonic: Cell and solute are at an equilibrium. ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... b. ligands. c. G proteins. d. second messengers. e. transcription factors. Answer: d. Second messengers are small molecules that relay signals within the cell. 7. The benefit of second messengers in signal transduction pathways is a. an increase in the speed of a cellular response. b. duplication of ...
... b. ligands. c. G proteins. d. second messengers. e. transcription factors. Answer: d. Second messengers are small molecules that relay signals within the cell. 7. The benefit of second messengers in signal transduction pathways is a. an increase in the speed of a cellular response. b. duplication of ...
Structure and Function of Cells
... Strong, stiff, nonliving layer outside the cell membrane; can be made of cellulose Outermost living layer of the cell; elastic and flexible; contains pores Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane; consists of a jellylike substance that contains many organelles Large, oval structure in the c ...
... Strong, stiff, nonliving layer outside the cell membrane; can be made of cellulose Outermost living layer of the cell; elastic and flexible; contains pores Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane; consists of a jellylike substance that contains many organelles Large, oval structure in the c ...
Cells and Organelles Test Review C) recognize levels of
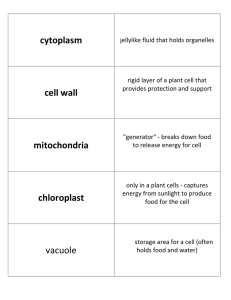
... C) recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms; (D) differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vac ...
... C) recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms; (D) differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vac ...
Learning Checkpoint ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS p. 16
... apparatus receives proteins from the ER and modifies, sorts, and packages these proteins for delivery throughout the cell or out of the cell. 4. The thylakoids act as solar collectors, collecting light energy from the Sun. This energy is used during photosynthesis to produce sugars. 5. Plant cells c ...
... apparatus receives proteins from the ER and modifies, sorts, and packages these proteins for delivery throughout the cell or out of the cell. 4. The thylakoids act as solar collectors, collecting light energy from the Sun. This energy is used during photosynthesis to produce sugars. 5. Plant cells c ...
Plasma Membranes1 Year 11 biology
... be different But the plasma membrane must be able to allow this exchange – HOW? ...
... be different But the plasma membrane must be able to allow this exchange – HOW? ...
cell membrane
... The protist Vorticelli feeding with cilia Movement of substances like mucus ...
... The protist Vorticelli feeding with cilia Movement of substances like mucus ...
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
... receiving end of the Golgi 4. They are modified and packaged by the Golgi. 5. They leave from the migrating end of the Golgi in vesicles. 6. The vesicles fuse with the cell membrane. 7. The contents are released externally by exocytosis. ...
... receiving end of the Golgi 4. They are modified and packaged by the Golgi. 5. They leave from the migrating end of the Golgi in vesicles. 6. The vesicles fuse with the cell membrane. 7. The contents are released externally by exocytosis. ...
TABLE 12–1 Relative Volumes Occupied by the Major Intracellular
... Nuclear proteins can be transported through a pore complex while they are in a fully folded conformation ...
... Nuclear proteins can be transported through a pore complex while they are in a fully folded conformation ...
Cell specialisation
... Not all the cells in our body are the same. There are many different types of cell. Each type of cell is adapted to carry out a particular job. ...
... Not all the cells in our body are the same. There are many different types of cell. Each type of cell is adapted to carry out a particular job. ...
Organelle Notes #2
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
Plasma Membrane
... • The polar (water soluble) heads face out • The non-polar (water insoluble) tails face in • This allows water soluble materials to move through membrane but molecules that are not soluble don’t pass through • This model of the plasma membrane if called the “Fluid Mosaic” model ...
... • The polar (water soluble) heads face out • The non-polar (water insoluble) tails face in • This allows water soluble materials to move through membrane but molecules that are not soluble don’t pass through • This model of the plasma membrane if called the “Fluid Mosaic” model ...
Organic Molecules - Riverdale Middle School
... – Cholesterol – found in your blood – Phosopholipids – make up cell membrane ...
... – Cholesterol – found in your blood – Phosopholipids – make up cell membrane ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.