View a sample here
... make it a much better conductor.) Thus, if water gets into insulation, the insulating value of the insulation is greatly reduced. On average, for every 1% increase (by volume) in the moisture content of an insulation material, its thermal conductivity (rate of heat transfer) increases by 7.5%. It is ...
... make it a much better conductor.) Thus, if water gets into insulation, the insulating value of the insulation is greatly reduced. On average, for every 1% increase (by volume) in the moisture content of an insulation material, its thermal conductivity (rate of heat transfer) increases by 7.5%. It is ...
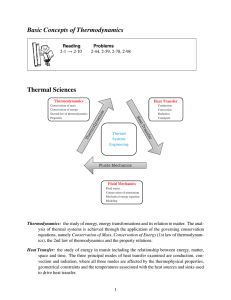
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Thermal Sciences
... Thermodynamics: the study of energy, energy transformations and its relation to matter. The analysis of thermal systems is achieved through the application of the governing conservation equations, namely Conservation of Mass, Conservation of Energy (1st law of thermodynamics), the 2nd law of thermod ...
... Thermodynamics: the study of energy, energy transformations and its relation to matter. The analysis of thermal systems is achieved through the application of the governing conservation equations, namely Conservation of Mass, Conservation of Energy (1st law of thermodynamics), the 2nd law of thermod ...
convective heat transfer coefficients: experimental
... 0° (only -1 to -1.5 W/m2K), 45° (7 to 16 W/m2K) and 90° (-8 to -9 W/m2K) on side walls (Chowdhury and Suksawang, 2012). In Latin-American context, experimental studies about convection heat transfer properties of building materials have not been carried out, except for only a few exceptions consisti ...
... 0° (only -1 to -1.5 W/m2K), 45° (7 to 16 W/m2K) and 90° (-8 to -9 W/m2K) on side walls (Chowdhury and Suksawang, 2012). In Latin-American context, experimental studies about convection heat transfer properties of building materials have not been carried out, except for only a few exceptions consisti ...
Global convection electric field and current : Comparisons
... Sd curve givesthe magneticvariation that would be observed by a station if it were rotating under a systemof two convection current cells of fixed intensity and location. Hence the ...
... Sd curve givesthe magneticvariation that would be observed by a station if it were rotating under a systemof two convection current cells of fixed intensity and location. Hence the ...
Influence of the ambient temperature during heat pipe
... during filling and exhausting heat pipes. This assumption is confirmed by experimental measurements which were used in three different working materials at three different operating temperatures. As working materials were used water, ethanol and Fluorinert FC72. As the most widely used working fluid ...
... during filling and exhausting heat pipes. This assumption is confirmed by experimental measurements which were used in three different working materials at three different operating temperatures. As working materials were used water, ethanol and Fluorinert FC72. As the most widely used working fluid ...
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM)
... A nanofluid is a dilute suspension of nanometer-sized particles and fibres dispersed in a liquid. Accordingly, their physical properties such as; velocity, density, thermal and electrical conductivities are superior as compared with those of the base fluids. The most important of the physical proper ...
... A nanofluid is a dilute suspension of nanometer-sized particles and fibres dispersed in a liquid. Accordingly, their physical properties such as; velocity, density, thermal and electrical conductivities are superior as compared with those of the base fluids. The most important of the physical proper ...
heat transfer (for d..
... liquid or gas.. By convection is meant the process of heat transport occurring through the movement of the macroparticles of the liquid or gas in space from a region of one atmosphere to that of another. Convection is possible only in a fluid medium. When the motion of the fluid arises only from the ...
... liquid or gas.. By convection is meant the process of heat transport occurring through the movement of the macroparticles of the liquid or gas in space from a region of one atmosphere to that of another. Convection is possible only in a fluid medium. When the motion of the fluid arises only from the ...
6S.1 Derivation of the Convection Transfer Equations
... conduction and developed means for determining the temperature distribution within the substance. We did so by applying conservation of energy to a differential control volume (Figure 2.11) and deriving a differential equation that was termed the heat equation. For a prescribed geometry and boundary ...
... conduction and developed means for determining the temperature distribution within the substance. We did so by applying conservation of energy to a differential control volume (Figure 2.11) and deriving a differential equation that was termed the heat equation. For a prescribed geometry and boundary ...
Convection

Convection is the concerted, collective movement of groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. Diffusion of heat can take place in solids, but that is called heat conduction. Convection cannot be demonstrated by placing a heat source (e.g. a Bunsen burner) at the side of a glass full of a liquid, and observing the changes in temperature in the glass caused by the warmer ghost fluid moving into cooler areas.Convective heat transfer is one of the major types of heat transfer, and convection is also a major mode of mass transfer in fluids. Convective heat and mass transfer take place both by diffusion – the random Brownian motion of individual particles in the fluid – and by advection, in which matter or heat is transported by the larger-scale motion of currents in the fluid. In the context of heat and mass transfer, the term ""convection"" is used to refer to the sum of advective and diffusive transfer. In common use the term ""convection"" may refer loosely to heat transfer by convection, as opposed to mass transfer by convection, or the convection process in general. Sometimes ""convection"" is even used to refer specifically to ""free heat convection"" (natural heat convection) as opposed to forced heat convection. However, in mechanics the correct use of the word is the general sense, and different types of convection should be qualified for clarity.Convection can be qualified in terms of being natural, forced, gravitational, granular, or thermomagnetic. It may also be said to be due to combustion, capillary action, or Marangoni and Weissenberg effects. Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be seen as clouds, with stronger convection resulting in thunderstorms. Natural convection also plays a role in stellar physics.