Heat transfer and air flow in a domestic refrigerator
... safety-determining factor. It is therefore necessary to fully understand the mechanism of heat transfer and airflow. Three types of domestic refrigerators are available in the market: static, brewed, and no-frost. The static type (Figure 16.1a) is widely used in Europe. In this case, heat is transfe ...
... safety-determining factor. It is therefore necessary to fully understand the mechanism of heat transfer and airflow. Three types of domestic refrigerators are available in the market: static, brewed, and no-frost. The static type (Figure 16.1a) is widely used in Europe. In this case, heat is transfe ...
Study of a Transformer Thermal System
... transformer considering all the different temperatures. In order to be possible to establish a lumped model, it will be considered zones with material homogeneity, as well as zones where it can be found heat sources and using the Biot number [14] is possible to establish a criterion where we can say ...
... transformer considering all the different temperatures. In order to be possible to establish a lumped model, it will be considered zones with material homogeneity, as well as zones where it can be found heat sources and using the Biot number [14] is possible to establish a criterion where we can say ...
226_che.pdf
... Two experimental approaches are performed to characterize the thermal performance of the board-level packaging, the IR thermography-based technique and the thermal test die measurement. Both these two experiments apply the same measurement environment set up and the test specimen. According to EIA/J ...
... Two experimental approaches are performed to characterize the thermal performance of the board-level packaging, the IR thermography-based technique and the thermal test die measurement. Both these two experiments apply the same measurement environment set up and the test specimen. According to EIA/J ...
Macrosegregation
... impact on the subsequent processing behavior and properties of cast materials and can lead to rejection of cast components or processed products. Macrosegregation is present in virtually all casting processes, including continuous, ingot, and shape casting of steel and aluminum alloys, iron casting, ...
... impact on the subsequent processing behavior and properties of cast materials and can lead to rejection of cast components or processed products. Macrosegregation is present in virtually all casting processes, including continuous, ingot, and shape casting of steel and aluminum alloys, iron casting, ...
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM)
... electrically conducting fluid in presence of applied magnetic field in connection with the theories of fluid motion in the liquid core of the Earth and also meteorological and oceanographic applications. In recent years, the analysis of hydromagnetic flow involving heat and mass transfer in porous m ...
... electrically conducting fluid in presence of applied magnetic field in connection with the theories of fluid motion in the liquid core of the Earth and also meteorological and oceanographic applications. In recent years, the analysis of hydromagnetic flow involving heat and mass transfer in porous m ...
ch1010 heat transfer unit i heat conduction
... temperature varies on a regular basis, eg., the variation of temperature of the surface of the earth during a twenty four hour period.. In the non periodic type, the temperature at any point within the system varies non linearly with time. 1.10.1. Systems with negligible internal resistance – Lumped ...
... temperature varies on a regular basis, eg., the variation of temperature of the surface of the earth during a twenty four hour period.. In the non periodic type, the temperature at any point within the system varies non linearly with time. 1.10.1. Systems with negligible internal resistance – Lumped ...
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-ISSN: 2278-5728,p-ISSN: 2319-765X,
... the system which were non-existent in their absence. The case of overstability is discussed & sufficient conditions for non-existence of overstability are derived. For thermosolutal convection, buoyancy forces can arise not only from density differences due to variation in temperature gradient, but ...
... the system which were non-existent in their absence. The case of overstability is discussed & sufficient conditions for non-existence of overstability are derived. For thermosolutal convection, buoyancy forces can arise not only from density differences due to variation in temperature gradient, but ...
Advanced Cooling for Power Electronics
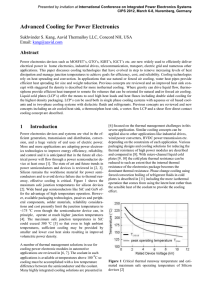
... The main limitation of the two-phase loop thermosiphon is that it is not suitable for moving platforms such as automobiles where external body forces other than gravity could potentially move the liquid out of the evaporator and cause dryout. Since the working fluid inside the thermosiphon is dielec ...
... The main limitation of the two-phase loop thermosiphon is that it is not suitable for moving platforms such as automobiles where external body forces other than gravity could potentially move the liquid out of the evaporator and cause dryout. Since the working fluid inside the thermosiphon is dielec ...
Common architectural implementations of thermal mass storage are
... can even be beneficial for external finishes to have low thermal mass, as well as low conductivity, to increase the effectiveness of insulation. Thermal lag from mass can greatly reduce the need for insulation in the building envelope, especially in climates with large temperature swings from day t ...
... can even be beneficial for external finishes to have low thermal mass, as well as low conductivity, to increase the effectiveness of insulation. Thermal lag from mass can greatly reduce the need for insulation in the building envelope, especially in climates with large temperature swings from day t ...
Chapter1_08-24-2015
... Fluid mechanics is the science and technology of fluids either at rest (fluid statics) or in motion (fluid dynamics) and their effects on boundaries such as solid surfaces or interfaces with other fluids. Definition of a fluid: A substance that deforms continuously when subjected to a shear stress C ...
... Fluid mechanics is the science and technology of fluids either at rest (fluid statics) or in motion (fluid dynamics) and their effects on boundaries such as solid surfaces or interfaces with other fluids. Definition of a fluid: A substance that deforms continuously when subjected to a shear stress C ...
Convection

Convection is the concerted, collective movement of groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. Diffusion of heat can take place in solids, but that is called heat conduction. Convection cannot be demonstrated by placing a heat source (e.g. a Bunsen burner) at the side of a glass full of a liquid, and observing the changes in temperature in the glass caused by the warmer ghost fluid moving into cooler areas.Convective heat transfer is one of the major types of heat transfer, and convection is also a major mode of mass transfer in fluids. Convective heat and mass transfer take place both by diffusion – the random Brownian motion of individual particles in the fluid – and by advection, in which matter or heat is transported by the larger-scale motion of currents in the fluid. In the context of heat and mass transfer, the term ""convection"" is used to refer to the sum of advective and diffusive transfer. In common use the term ""convection"" may refer loosely to heat transfer by convection, as opposed to mass transfer by convection, or the convection process in general. Sometimes ""convection"" is even used to refer specifically to ""free heat convection"" (natural heat convection) as opposed to forced heat convection. However, in mechanics the correct use of the word is the general sense, and different types of convection should be qualified for clarity.Convection can be qualified in terms of being natural, forced, gravitational, granular, or thermomagnetic. It may also be said to be due to combustion, capillary action, or Marangoni and Weissenberg effects. Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be seen as clouds, with stronger convection resulting in thunderstorms. Natural convection also plays a role in stellar physics.