Unit 1: Cells - Loudoun County Public Schools
... 1. Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane, and explain how substances get into and out of cells. a) The cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the environment. b) The cell membrane controls what enters and leaves the cell in order to maintain HOMEOSTASIS. c) Homeostasi ...
... 1. Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane, and explain how substances get into and out of cells. a) The cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the environment. b) The cell membrane controls what enters and leaves the cell in order to maintain HOMEOSTASIS. c) Homeostasi ...
The Bethesda System for Reporting Cytologic Diagnoses
... The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical/Vaginal Cytologic Diagnoses Format of the Report: a. A statement on Adequacy of the Specimen For evaluation b. A General categorization which may be used to assist with clerical triage (optional) c. The Descriptive Diagnosis ...
... The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical/Vaginal Cytologic Diagnoses Format of the Report: a. A statement on Adequacy of the Specimen For evaluation b. A General categorization which may be used to assist with clerical triage (optional) c. The Descriptive Diagnosis ...
Nature Rev.Mol.Cell Biol. 6
... Deletion of the CNS1 sequence in the Th2 cluster do not initiate within the IL13 gene from Aladjem, Nature Rev.Genet. 8, 588 (2007) ...
... Deletion of the CNS1 sequence in the Th2 cluster do not initiate within the IL13 gene from Aladjem, Nature Rev.Genet. 8, 588 (2007) ...
Sharply discordant biological properties of synthetic noncoding
... capable to induce cell death in certain types of cells by engaging various signal transduction pathways through TLRs, MDA5 and RIG-I. Depending on the chemical structure and molecular weight, synthetic RNAs could differentially trigger these and additional pathways yet to be characterized, providing ...
... capable to induce cell death in certain types of cells by engaging various signal transduction pathways through TLRs, MDA5 and RIG-I. Depending on the chemical structure and molecular weight, synthetic RNAs could differentially trigger these and additional pathways yet to be characterized, providing ...
Mitochondria Coloring
... the sun and was stored in chemical bonds by plants during photosynthesis. Glucose and other carbohydrates made by plants during photosynthesis are broken down by the process of aerobic cellular respiration (requires oxygen) in the mitochondria of the cell. This releases energy (ATP) for the cell. Th ...
... the sun and was stored in chemical bonds by plants during photosynthesis. Glucose and other carbohydrates made by plants during photosynthesis are broken down by the process of aerobic cellular respiration (requires oxygen) in the mitochondria of the cell. This releases energy (ATP) for the cell. Th ...
The Fungi The yeasts, molds and mushrooms: Eukaryotic
... I. Haploid Phase Start with haploid spores formed by meiosis Spores released by fruiting body Spores germinate and grow into haploid mycelia Cells haploid, undergo mitosis to form fungal body Mating types? II. The Dikaryotic (binucleate) Phase Fusion of two mating types, exchange of nucl ...
... I. Haploid Phase Start with haploid spores formed by meiosis Spores released by fruiting body Spores germinate and grow into haploid mycelia Cells haploid, undergo mitosis to form fungal body Mating types? II. The Dikaryotic (binucleate) Phase Fusion of two mating types, exchange of nucl ...
Cell Transport Homeostasis PPT
... concentration of solute relative to the cell. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water diffuses out of the cell attempting to match the solute concentration outside of it, causing the cell to shrivel. The fluid surrounding the body cell is said to be ...
... concentration of solute relative to the cell. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water diffuses out of the cell attempting to match the solute concentration outside of it, causing the cell to shrivel. The fluid surrounding the body cell is said to be ...
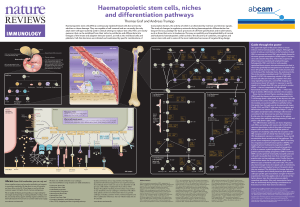
Haematopoietic stem cells, niches and differentiation
... T-cell lineage (lower right panel). In the thymus, the cells travel from the cortex through the subcapsular zone to the medulla, encountering different epithelial niches that guide them through several developmental stages. Finally, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells enter the circulation and differentiate into ...
... T-cell lineage (lower right panel). In the thymus, the cells travel from the cortex through the subcapsular zone to the medulla, encountering different epithelial niches that guide them through several developmental stages. Finally, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells enter the circulation and differentiate into ...
Ch 3 Biogeochemical powerpoint
... Why do we need: building block of amino acids, builds proteins, part of DNA and RNA Where stored: mostly in the atmosphere, not usable until the N has been fixed Human impact: burning fossil fuels and adds NOx to our atmosphere, used as fertilizers, **we are adding N to nature at rate of 1.5 times f ...
... Why do we need: building block of amino acids, builds proteins, part of DNA and RNA Where stored: mostly in the atmosphere, not usable until the N has been fixed Human impact: burning fossil fuels and adds NOx to our atmosphere, used as fertilizers, **we are adding N to nature at rate of 1.5 times f ...
Ch 3 Biogeochemical Cycle ppt
... Why do we need: building block of amino acids, builds proteins, part of DNA and RNA Where stored: mostly in the atmosphere, not usable until the N has been fixed Human impact: burning fossil fuels and adds NOx to our atmosphere, used as fertilizers, **we are adding N to nature at rate of 1.5 times f ...
... Why do we need: building block of amino acids, builds proteins, part of DNA and RNA Where stored: mostly in the atmosphere, not usable until the N has been fixed Human impact: burning fossil fuels and adds NOx to our atmosphere, used as fertilizers, **we are adding N to nature at rate of 1.5 times f ...
Bio10lab1 0710
... Adjust the amount of light coming through the slide. You’ll find that dim lighting is often better than bright lighting. Switch to the 10X objective; use the fine focus knob to focus. Switch to the 40X objective; use the fine focus knob to focus. ...
... Adjust the amount of light coming through the slide. You’ll find that dim lighting is often better than bright lighting. Switch to the 10X objective; use the fine focus knob to focus. Switch to the 40X objective; use the fine focus knob to focus. ...
Bio sample items goal 1 - Charles D Owen High School
... natural environment and placed into a body of water that contains more salt than the inside of each plant cell. This situation is most similar to which of the following events? A ...
... natural environment and placed into a body of water that contains more salt than the inside of each plant cell. This situation is most similar to which of the following events? A ...
The Cell - Haiku Learning for FSD
... together form and organ system. An organism may only have a few organ systems while others have many. Humans have about 10 organ systems. The nervous system for examples includes: brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors in organs such as the eyes and ears. ...
... together form and organ system. An organism may only have a few organ systems while others have many. Humans have about 10 organ systems. The nervous system for examples includes: brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors in organs such as the eyes and ears. ...
Standard Biology Test Cell Unit
... Cell A is a eukaryotic cell. We know this because the cell contains a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. 2. Is cell B a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell? HOW DO YOU KNOW? Cell A is a eukaryotic cell. We know this because the cell contains a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. 3. Is ...
... Cell A is a eukaryotic cell. We know this because the cell contains a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. 2. Is cell B a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell? HOW DO YOU KNOW? Cell A is a eukaryotic cell. We know this because the cell contains a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. 3. Is ...
P T ASSIVE RANSPORT
... linked such that the product of one reaction is consumed in the next reaction. 2. Chloroplasts have an inner membrane system consisting of thylakoids. The pumping of protons into the thylakoids builds up a proton concentration gradient across the thylakoid membrane. 3. The energy-carrying products a ...
... linked such that the product of one reaction is consumed in the next reaction. 2. Chloroplasts have an inner membrane system consisting of thylakoids. The pumping of protons into the thylakoids builds up a proton concentration gradient across the thylakoid membrane. 3. The energy-carrying products a ...
Monday - Houston ISD
... 1. How do organelles function in cells? 2. Why is energy needed to sustain cell interactions and how do cells acquire this energy? 3. What would make a cell need more or less energy? ...
... 1. How do organelles function in cells? 2. Why is energy needed to sustain cell interactions and how do cells acquire this energy? 3. What would make a cell need more or less energy? ...
The lung and the Upper Respiratory Tract
... previous scar (scar carcinoma). Not clearly linked to smoking. – Bronchoalveolar Ca: Not related to smoking. Multiple tumor, present as pneumonia. ...
... previous scar (scar carcinoma). Not clearly linked to smoking. – Bronchoalveolar Ca: Not related to smoking. Multiple tumor, present as pneumonia. ...
Protocols for next session
... minimize the time the incubator is open to keep the cultures at precisely 37C. Don’t forget to note the absolute time of day in your notebook (to compare to the time of the inoculation) as well as the time on the class stopwatch. 2. Carefully insert the cuvette into the spec in the correct orientat ...
... minimize the time the incubator is open to keep the cultures at precisely 37C. Don’t forget to note the absolute time of day in your notebook (to compare to the time of the inoculation) as well as the time on the class stopwatch. 2. Carefully insert the cuvette into the spec in the correct orientat ...
M1 Chapter 2
... Mitochondria are membraneenclosed organelles distributed through the cytosol of most eukaryotic cells. Their main function is the conversion of the potential energy of food molecules into ATP Every type of cell has a different amount of mitochondria.. There are more mitochondria in cells that have t ...
... Mitochondria are membraneenclosed organelles distributed through the cytosol of most eukaryotic cells. Their main function is the conversion of the potential energy of food molecules into ATP Every type of cell has a different amount of mitochondria.. There are more mitochondria in cells that have t ...
CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL
... • The subunits pass from the nuclear pores to the cytoplasm where they combine to form ribosomes. • Cell types active in proteins synthesis (e.g., pancreas) have large numbers of ribosomes and prominent ...
... • The subunits pass from the nuclear pores to the cytoplasm where they combine to form ribosomes. • Cell types active in proteins synthesis (e.g., pancreas) have large numbers of ribosomes and prominent ...
Unit 5(The Fundamental Unit Of Life)
... 32. Why does the skin of your finger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time? 33. Why is endocytosis found in animals only? 34. A person takes concentrated solution of salt, after sometime, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation? Explain. 35. Name any cell org ...
... 32. Why does the skin of your finger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time? 33. Why is endocytosis found in animals only? 34. A person takes concentrated solution of salt, after sometime, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation? Explain. 35. Name any cell org ...
Gastrulation, Vertebrates
... Figure 11. Rho mediates actin remodeling during gastrulation in zebrafish. Rho acts through its downstream effector, Rho associated kinase (ROCK), which presumably phosphorylates regulatory myosin light chains (MRLCs) and enforces actomyosin contractility. In conjunction, zDia2 or other formins may ...
... Figure 11. Rho mediates actin remodeling during gastrulation in zebrafish. Rho acts through its downstream effector, Rho associated kinase (ROCK), which presumably phosphorylates regulatory myosin light chains (MRLCs) and enforces actomyosin contractility. In conjunction, zDia2 or other formins may ...
Chapter 5 - Tiwariacademy.net
... 32. Why does the skin of your finger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time? 33. Why is endocytosis found in animals only? 34. A person takes concentrated solution of salt, after sometime, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation? Explain. 35. Name any cell org ...
... 32. Why does the skin of your finger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time? 33. Why is endocytosis found in animals only? 34. A person takes concentrated solution of salt, after sometime, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation? Explain. 35. Name any cell org ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.