Detailed Notes with Basic Practice 1
... An animal cell and a plant cell were both placed in distilled water. After one hour, they were examined again under an optical microscope. Only fragments of cell membrane were observed in animal cell while the plant cell has increased in size. ...
... An animal cell and a plant cell were both placed in distilled water. After one hour, they were examined again under an optical microscope. Only fragments of cell membrane were observed in animal cell while the plant cell has increased in size. ...
GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours
... Set up activities that allow students to demonstrate what they have learned in this unit. The activities can be provided informally or formally during and at the end of the unit, or for homework. They can be selected from the teaching activities or can be new experiences. Choose tasks and questions ...
... Set up activities that allow students to demonstrate what they have learned in this unit. The activities can be provided informally or formally during and at the end of the unit, or for homework. They can be selected from the teaching activities or can be new experiences. Choose tasks and questions ...
Human Cell-Expressed Proteins
... human-specific glycosylation. These benefits are often not available from the non-human expression systems currently used to produce therapeutic proteins, such as bacteria, yeast, insect, mouse or hamster cells. The treatment of several diseases, particularly cancer, now routinely includes cell-base ...
... human-specific glycosylation. These benefits are often not available from the non-human expression systems currently used to produce therapeutic proteins, such as bacteria, yeast, insect, mouse or hamster cells. The treatment of several diseases, particularly cancer, now routinely includes cell-base ...
[PLANT CELL WALL] Functions of Cell Wall Structure of Cell Wall
... o They do not aggregate with themselves, hence they don’t form microfibers. o They form H-bonds with cellulose hence they are called as ‘cross-linking glycans’. o Hemicellulose molecules are very hydrophilic and they are easily hydrated and forms gels. o Hemicellulose is abundant in primary walls bu ...
... o They do not aggregate with themselves, hence they don’t form microfibers. o They form H-bonds with cellulose hence they are called as ‘cross-linking glycans’. o Hemicellulose molecules are very hydrophilic and they are easily hydrated and forms gels. o Hemicellulose is abundant in primary walls bu ...
An Introduction to Cells
... and explain their role in physiological systems. • 3-6 Describe carrier-mediated transport and vesicular transport mechanisms used by cells to facilitate the absorption or removal of specific substances. • 3-7 Explain the origin and significance of the transmembrane potential. ...
... and explain their role in physiological systems. • 3-6 Describe carrier-mediated transport and vesicular transport mechanisms used by cells to facilitate the absorption or removal of specific substances. • 3-7 Explain the origin and significance of the transmembrane potential. ...
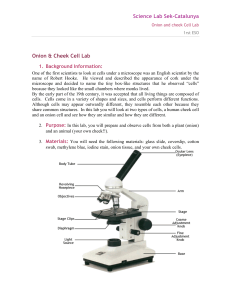
Onion and cheek Cell Lab
... but it will stain both your skin and your clothes. c. Place a coverslip over the newly stained tissue. d. Place the slide on the stage and view the slide under the low power. Once you have found an area with several good cells, switch to medium power and then to high power. Remember to only use the ...
... but it will stain both your skin and your clothes. c. Place a coverslip over the newly stained tissue. d. Place the slide on the stage and view the slide under the low power. Once you have found an area with several good cells, switch to medium power and then to high power. Remember to only use the ...
Title - Iowa State University
... decrease the protein’s activity by this binding. A competitive inhibitor will bind to the active site of an enzyme (where the substrate or reactant would usually bind) and prevent the substrate from being able to bind and thus decrease the activity of the enzyme. 12. According to Professor Powell-Co ...
... decrease the protein’s activity by this binding. A competitive inhibitor will bind to the active site of an enzyme (where the substrate or reactant would usually bind) and prevent the substrate from being able to bind and thus decrease the activity of the enzyme. 12. According to Professor Powell-Co ...
Icd 10 code for metastatic renal cell carcinoma
... Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common form of TEENney cancer, accounting for 90% of all TEENney cancers. RCC usually begins as a tumor growing in one TEENney. Learn About Renal Cell Carcinoma Symptoms, Remedies, Health Risks And More. Definition. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) accounts for 90% t ...
... Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common form of TEENney cancer, accounting for 90% of all TEENney cancers. RCC usually begins as a tumor growing in one TEENney. Learn About Renal Cell Carcinoma Symptoms, Remedies, Health Risks And More. Definition. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) accounts for 90% t ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... provided evidence that some organelles within cells were at one time free living cells themselves • Supporting evidence included organelles with their own DNA • Chloroplast and Mitochondria ...
... provided evidence that some organelles within cells were at one time free living cells themselves • Supporting evidence included organelles with their own DNA • Chloroplast and Mitochondria ...
cell division - El Paso High School
... enzymes for part of photosynthesis. – The thylakoids, flattened sacs, are stacked into grana and are critical for converting light to chemical energy. ...
... enzymes for part of photosynthesis. – The thylakoids, flattened sacs, are stacked into grana and are critical for converting light to chemical energy. ...
CELLS - Peoria Public Schools
... provided evidence that some organelles within cells were at one time free living cells themselves • Supporting evidence included organelles with their own DNA • Chloroplast and Mitochondria ...
... provided evidence that some organelles within cells were at one time free living cells themselves • Supporting evidence included organelles with their own DNA • Chloroplast and Mitochondria ...
Primary 6 Science Term One The Cell
... performs all life function. But most of us are multicellular organisms made up of lots of cells all working together. Some of these cells are all of the same type, collectively they are called a tissue. They all do the same job, for example connective tissue, which is used in animals to connect othe ...
... performs all life function. But most of us are multicellular organisms made up of lots of cells all working together. Some of these cells are all of the same type, collectively they are called a tissue. They all do the same job, for example connective tissue, which is used in animals to connect othe ...
Profile
... Polymer (N-acetyl glucosamine, Nacetyl muramic acid, amino acids) FUNCTION: - Protects everything inside the cell - Provides rigidity to plants - Regulates growth of plants and protects it from disease -Provides a porous area for the distribution of water and other nutrients -Prevents cell from burs ...
... Polymer (N-acetyl glucosamine, Nacetyl muramic acid, amino acids) FUNCTION: - Protects everything inside the cell - Provides rigidity to plants - Regulates growth of plants and protects it from disease -Provides a porous area for the distribution of water and other nutrients -Prevents cell from burs ...
Cellular Transport Study Guide_PDF
... In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the italicized term to make the statement true. Write this answer in the blank provided. _______________ 7. A solution in which the concentration of dissolved substances is lower than the concentration i ...
... In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the italicized term to make the statement true. Write this answer in the blank provided. _______________ 7. A solution in which the concentration of dissolved substances is lower than the concentration i ...
Eukaryotic checkpoints are absent in the cell division cycle of
... nucleus in uni-nucleated and multi-nucleated trophozoites showed that the DNA content of each nucleus varied from 1n to 10n on an average (Das and Lohia 2002). Sporadically, nuclei with greater than 10n genome contents could also be detected. Similar results were also observed with trophozoites of t ...
... nucleus in uni-nucleated and multi-nucleated trophozoites showed that the DNA content of each nucleus varied from 1n to 10n on an average (Das and Lohia 2002). Sporadically, nuclei with greater than 10n genome contents could also be detected. Similar results were also observed with trophozoites of t ...
Diffusion - Net Texts
... The diffusion of water across a membrane because of a difference in concentration is called osmosis. Let’s explore three different situations and analyze the flow of water. 1. A hypotonic solution means the environment outside of the cell has a lower concentration of dissolved material than the insi ...
... The diffusion of water across a membrane because of a difference in concentration is called osmosis. Let’s explore three different situations and analyze the flow of water. 1. A hypotonic solution means the environment outside of the cell has a lower concentration of dissolved material than the insi ...
What does it do?
... bubble-like sac that envelopes the proteins and transports them to the golgi apparatus or plasma membrane) •smooth endoplasmic reticulum: lacking ribosomes, makes enzymes to make and break down lipids and other nutrients and protect the cell from toxins ...
... bubble-like sac that envelopes the proteins and transports them to the golgi apparatus or plasma membrane) •smooth endoplasmic reticulum: lacking ribosomes, makes enzymes to make and break down lipids and other nutrients and protect the cell from toxins ...
Transport Across Plasma Membrane
... NA or hydrogen ions to move other chemicals b. How does secondary active transport maintain low calcium concentrations in the cytosol and/or absorption of nutrients into cell? In many cells antiporters move calcium out of the cell while sodium flows in. This maintains the low calcium concentration i ...
... NA or hydrogen ions to move other chemicals b. How does secondary active transport maintain low calcium concentrations in the cytosol and/or absorption of nutrients into cell? In many cells antiporters move calcium out of the cell while sodium flows in. This maintains the low calcium concentration i ...
Cell Structure Section 2 The Framework of the Cell
... • The cytoskeleton helps the cell move, keep its shape, and organize its parts • DNA instructions are copied as RNA messages, which leave the nucleus. In the cytoplasm, ribosomes use the RNA messages to assemble proteins. • The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus are organelles involved in pre ...
... • The cytoskeleton helps the cell move, keep its shape, and organize its parts • DNA instructions are copied as RNA messages, which leave the nucleus. In the cytoplasm, ribosomes use the RNA messages to assemble proteins. • The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus are organelles involved in pre ...
Unravelling the molecular pathways of Plasmodium falciparum programmed cell death: identification of novel therapeutic targets.
... induce apoptosis-like features in P. falciparum erythrocytic stages, including early loss of mitochondrial outer membrane potential and caspase-like activity. Therefore, we proposed to initiate our study by PCD induction using a variety of drugs and assaying for typical apoptotic features including ...
... induce apoptosis-like features in P. falciparum erythrocytic stages, including early loss of mitochondrial outer membrane potential and caspase-like activity. Therefore, we proposed to initiate our study by PCD induction using a variety of drugs and assaying for typical apoptotic features including ...
Presentation - Cell analogies
... Cells are systems - their parts function together to promote an outcome. The the case of a cell, the outcome is the production of proteins. ...
... Cells are systems - their parts function together to promote an outcome. The the case of a cell, the outcome is the production of proteins. ...
Cell Transport
... hydrophobic interior of the lipid bi-layer 0 The molecule can then be delivered either into or out of the cell 0 Example- glucose is too large to diffuse across the membrane but ...
... hydrophobic interior of the lipid bi-layer 0 The molecule can then be delivered either into or out of the cell 0 Example- glucose is too large to diffuse across the membrane but ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.

![Prostista[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012483874_1-5710510f3d3c0b6a1f0d4f56d41850e6-300x300.png)

![[PLANT CELL WALL] Functions of Cell Wall Structure of Cell Wall](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014512284_1-fafd2bca61d6dff1e76fb2585a0a6724-300x300.png)