Chapter 8 cell-structure and function.pmd
... 11. The unit of measurement used for expressing dimension (size) of cells is: (a) centimeter (c) micrometer (b) millimeter (d) metre 12. The most important function of cell membrane is that it: (a) controls the entry and exit of materials from cells. (b) controls only the entry of materials into cel ...
... 11. The unit of measurement used for expressing dimension (size) of cells is: (a) centimeter (c) micrometer (b) millimeter (d) metre 12. The most important function of cell membrane is that it: (a) controls the entry and exit of materials from cells. (b) controls only the entry of materials into cel ...
Biology 101 Chapter 1
... All cells are placed in one of 2 classes: Prokaryotic = lack a nucleus (bacteria) Eukaryotic = have a nucleus (protists, fungi, plants, and animals) PROKARYOTIC CELLS very, very small very simple structure Parts: A) Plasma (cell) membrane = encloses cytoplasm of cell B) Nucleoid Region = where D ...
... All cells are placed in one of 2 classes: Prokaryotic = lack a nucleus (bacteria) Eukaryotic = have a nucleus (protists, fungi, plants, and animals) PROKARYOTIC CELLS very, very small very simple structure Parts: A) Plasma (cell) membrane = encloses cytoplasm of cell B) Nucleoid Region = where D ...
Anticancer activity of red pigment from Serratia marcescens in
... in which mono-and bipyrrole precursors are obtained separately and then coupled to for the production of linear tripyrrole red pigment during the stationary phase of bacterial growth.4 The production of prodigiosin has been shown to be influenced by numerous environmental factors including inorganic ...
... in which mono-and bipyrrole precursors are obtained separately and then coupled to for the production of linear tripyrrole red pigment during the stationary phase of bacterial growth.4 The production of prodigiosin has been shown to be influenced by numerous environmental factors including inorganic ...
Prokaryotic Profiles: Bacteria and Archaea
... D. Structure of Cell Wall 1.Determines shape, provides support 2.Peptidoglycan a. Unique macromolecule composed of a repeating framework of long glycan chains cross-linked by short peptides b. Provides strong, flexible support to keep bacteria from bursting or collapsing because of changes in osmot ...
... D. Structure of Cell Wall 1.Determines shape, provides support 2.Peptidoglycan a. Unique macromolecule composed of a repeating framework of long glycan chains cross-linked by short peptides b. Provides strong, flexible support to keep bacteria from bursting or collapsing because of changes in osmot ...
Protected Cell Companies
... No audit is performed for the Cell itself, the PCC structure as a whole will be subject to audit. However, the following also needs to be considered: Since the establishment of the PCC concept, there has not been a case of a Cell bankruptcy; hence the legal framework has not been tested in pract ...
... No audit is performed for the Cell itself, the PCC structure as a whole will be subject to audit. However, the following also needs to be considered: Since the establishment of the PCC concept, there has not been a case of a Cell bankruptcy; hence the legal framework has not been tested in pract ...
T-cell Maturation T cell maturation
... - IP3 triggers the release of calcium from intracellular storage vesicles into the cytosol, thus raising cytoplasmic calcium ...
... - IP3 triggers the release of calcium from intracellular storage vesicles into the cytosol, thus raising cytoplasmic calcium ...
Cells – The Basic Unit of Life - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Microtubules – hollow structure made of protein sub-unit. (large) 1. Cell division ...
... Microtubules – hollow structure made of protein sub-unit. (large) 1. Cell division ...
: Name: Cell Biology Basics http://www.biology4kids.com/files
... 1. Return to Biology4Kids and click the link for Endoplasmic Reticulum. Complete the following chart. ...
... 1. Return to Biology4Kids and click the link for Endoplasmic Reticulum. Complete the following chart. ...
Document
... The ECM can regulate a cell’s behavior by communicating with a cell through integrins. The ECM around a cell can influence the activity of gene in the nucleus. Mechanical signaling may occur through cytoskeletal changes, that trigger chemical signals in the cell. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... The ECM can regulate a cell’s behavior by communicating with a cell through integrins. The ECM around a cell can influence the activity of gene in the nucleus. Mechanical signaling may occur through cytoskeletal changes, that trigger chemical signals in the cell. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Cell Structures – Part 3 - Glasgow Independent Schools
... Mitochondria (Nicknamed the “Power House”) A. This organelle is involved in making energy by performing the process of cellular respiration inside it. B. This organelle has it’s own DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes inside it. C. It has a “Room within a Room” appearance. 1. Cristae – the folded inner memb ...
... Mitochondria (Nicknamed the “Power House”) A. This organelle is involved in making energy by performing the process of cellular respiration inside it. B. This organelle has it’s own DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes inside it. C. It has a “Room within a Room” appearance. 1. Cristae – the folded inner memb ...
File - Science with Mrs. Schulte
... cells and gives support for the cells, allowing plants to __________ ________________. ...
... cells and gives support for the cells, allowing plants to __________ ________________. ...
Pacemaking cells
... • Action potentials in the heart differ considerably from action potentials found in neural and skeletal muscle cells. • One major difference is in the duration of the action potentials. • In a typical nerve, the action potential duration is about 1 ms. In skeletal muscle cells, the action potential ...
... • Action potentials in the heart differ considerably from action potentials found in neural and skeletal muscle cells. • One major difference is in the duration of the action potentials. • In a typical nerve, the action potential duration is about 1 ms. In skeletal muscle cells, the action potential ...
let`s talk about cells
... Before cooking aubergines, it is usual to plunge them, in slices or in small cubes, into salt water. Why? Students carry out a research to find information about solanine and its effects on the human body. ...
... Before cooking aubergines, it is usual to plunge them, in slices or in small cubes, into salt water. Why? Students carry out a research to find information about solanine and its effects on the human body. ...
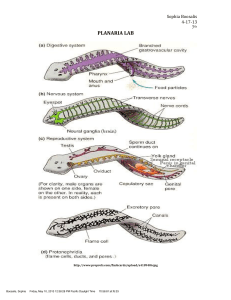
planaria lab report
... dropping. Tail dropping is when they separate into two different parts, to create a whole new copy. Another way to reproduce is called fragmentation. Fragmentation is like tail dropping, but split into ...
... dropping. Tail dropping is when they separate into two different parts, to create a whole new copy. Another way to reproduce is called fragmentation. Fragmentation is like tail dropping, but split into ...
nucleus - cloudfront.net
... 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
... 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
Name: Date - cloudfront.net
... 16. Why does the cell membrane arrange into a BILAYER (double layer) of phospholipids, with the heads facing the outside and inside of the cell and the tails facing each other? [HINT: Think about which parts are “water-loving” and which parts are “water-hating?”] ____________________________________ ...
... 16. Why does the cell membrane arrange into a BILAYER (double layer) of phospholipids, with the heads facing the outside and inside of the cell and the tails facing each other? [HINT: Think about which parts are “water-loving” and which parts are “water-hating?”] ____________________________________ ...
IV th Azospirillum Workshop
... wheat roots as well as another phenomenon of non-specific migration of bcteria ín soil were detected. Bacterial migration was signíficantly stimulated by various wheat cultivara and by synthetic attractants. After reaching the target plant, bacterial multiplication took place and two modes of bacter ...
... wheat roots as well as another phenomenon of non-specific migration of bcteria ín soil were detected. Bacterial migration was signíficantly stimulated by various wheat cultivara and by synthetic attractants. After reaching the target plant, bacterial multiplication took place and two modes of bacter ...
BIOFE (Biology OFE)
... 2) What is the job of 4? _____________________________ 3) What is transcribed at 5 that travels through 3?_____________ 4) What is the job of 3? ________________________________ 5) Why is 7 shaped the way it is?__________________________ 6) What happens at 7?__________________________________ 7) Wha ...
... 2) What is the job of 4? _____________________________ 3) What is transcribed at 5 that travels through 3?_____________ 4) What is the job of 3? ________________________________ 5) Why is 7 shaped the way it is?__________________________ 6) What happens at 7?__________________________________ 7) Wha ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.