
What should I know for the TEST
... Which kind of cells have cell walls? PLANTS and BACTERIA How are the cell walls in Plant cells and Bacterial cells different? Plant cell walls contain CELLULOSE = makes plants STURDY Bacterial cell walls contain PEPTIDOGLYCAN What is the function of cell walls? SUPPORT, PROTECTION WHICH CELL PARTS H ...
... Which kind of cells have cell walls? PLANTS and BACTERIA How are the cell walls in Plant cells and Bacterial cells different? Plant cell walls contain CELLULOSE = makes plants STURDY Bacterial cell walls contain PEPTIDOGLYCAN What is the function of cell walls? SUPPORT, PROTECTION WHICH CELL PARTS H ...
Fall 2009 Lecture 1 - Department of Chemistry -
... Know chemical structures and reactivities of molecules that participate in cellular reactions Know biological function of cellular molecules Know how all of the pieces and different pathways fit together *Use knowledge from general chemistry, organic chemistry, and biology and apply it to biological ...
... Know chemical structures and reactivities of molecules that participate in cellular reactions Know biological function of cellular molecules Know how all of the pieces and different pathways fit together *Use knowledge from general chemistry, organic chemistry, and biology and apply it to biological ...
Osmosis in Plants
... Turgor (the state a plant is in when the cells are ____________) is very important to plants. The ____________ inside cells pushes neighbouring cells against each other. This supports the non-___________ parts of the plant like young __________ and leaves, and holds the stems _____________ so the le ...
... Turgor (the state a plant is in when the cells are ____________) is very important to plants. The ____________ inside cells pushes neighbouring cells against each other. This supports the non-___________ parts of the plant like young __________ and leaves, and holds the stems _____________ so the le ...
Cell Division (Mitosis) and Death
... - Replicates DNA and subcellular structures - Composed of G1, S, and G2 - Cells may exit the cell cycle at G1 or enter G0, a quiescent phase ...
... - Replicates DNA and subcellular structures - Composed of G1, S, and G2 - Cells may exit the cell cycle at G1 or enter G0, a quiescent phase ...
The Cell Study Guide
... 1. able to describe the internal structure of eukaryotic cells. 2. Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. 3. Know how organelles can work together as a system. For example, ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, they exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the ...
... 1. able to describe the internal structure of eukaryotic cells. 2. Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. 3. Know how organelles can work together as a system. For example, ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, they exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the ...
Unit 1 Test Review Guide
... 6. What organelle or cell part is described? Oval, produces ATP (energy), site of cellular respiration - __________________________ Oval, green, makes glucose, site of photosynthesis- _______________________________ Large, round, contains DNA, controls the cell, found in all eukaryotic cells- ______ ...
... 6. What organelle or cell part is described? Oval, produces ATP (energy), site of cellular respiration - __________________________ Oval, green, makes glucose, site of photosynthesis- _______________________________ Large, round, contains DNA, controls the cell, found in all eukaryotic cells- ______ ...
Grade 10 Science: Biology Unit Test
... 10. What vessels carry the oxygenated blood away from the heart? a) arteries b) veins c) capillaries d) ventricles 11. Which system transports oxygen and nutrients to where they are needed by the body? a) digestive b) respiratory c) excretory d) circulatory 12. We breathe because we need oxygen. We ...
... 10. What vessels carry the oxygenated blood away from the heart? a) arteries b) veins c) capillaries d) ventricles 11. Which system transports oxygen and nutrients to where they are needed by the body? a) digestive b) respiratory c) excretory d) circulatory 12. We breathe because we need oxygen. We ...
Function of Cell Organelles
... Organelles found only in plant cells that contain the green pigment chlorophyll They carry out the process of photosynthesis. ...
... Organelles found only in plant cells that contain the green pigment chlorophyll They carry out the process of photosynthesis. ...
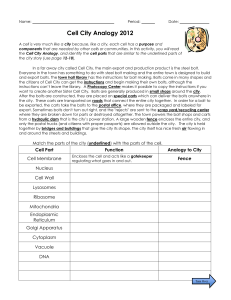
Cell City Analogy - Rochester Community Schools
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
Homework Exercise 4 The diagram below represents differences in
... The diagram below represents differences in the concentration of molecules inside and outside an animal cell, together with the direction of movement of the molecules. ...
... The diagram below represents differences in the concentration of molecules inside and outside an animal cell, together with the direction of movement of the molecules. ...
Cell Organelle Powerpoint
... 1. What are the 2 main types of cells? Which Domains do they consist of? 2. List 3 ways that eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes. ...
... 1. What are the 2 main types of cells? Which Domains do they consist of? 2. List 3 ways that eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes. ...
Chapter 40
... homologous structures c. Sympatric and Allopatric isolation can create homologies ...
... homologous structures c. Sympatric and Allopatric isolation can create homologies ...
Chapter-5-worksheet
... ___________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. ...
... ___________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. ...
7-3_cell_boundaries
... a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmotic pressure? ___________ ...
... a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmotic pressure? ___________ ...
Cell Tutorial Internet Lesson
... 3. These little organelles follow instructions from the nucleus and create proteins that the cell needs. a. ________________________________ 4. This thin lining controls what molecules enter and leave the cell. a. ________________________________ 5. This fluid maintains the internal pressure of the ...
... 3. These little organelles follow instructions from the nucleus and create proteins that the cell needs. a. ________________________________ 4. This thin lining controls what molecules enter and leave the cell. a. ________________________________ 5. This fluid maintains the internal pressure of the ...
Cell Theory and Viruses - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... Does it maintain homeostasis? Does it carry out metabolism? Does it reproduce? ...
... Does it maintain homeostasis? Does it carry out metabolism? Does it reproduce? ...
Endocytosis 2 Types: 1. Phagocytosis 2. Pinocytosis
... materials or liquids into a cell. 2 Types: 1. Phagocytosis 2. Pinocytosis ...
... materials or liquids into a cell. 2 Types: 1. Phagocytosis 2. Pinocytosis ...
Lab-2- The Plant cell. (Prokaryote and Eukaryote cell)
... familiar with, such as animals, plants, fungi and protists (animal-like microbes). The organelles in Eukaryotic cell. ( figure -1-) Cell Wall. The cell wall encloses and protects the cell contents and plays a vital role in cell division and cell expansion. Composed of overlapping cellulose microfibr ...
... familiar with, such as animals, plants, fungi and protists (animal-like microbes). The organelles in Eukaryotic cell. ( figure -1-) Cell Wall. The cell wall encloses and protects the cell contents and plays a vital role in cell division and cell expansion. Composed of overlapping cellulose microfibr ...
Plant vs. Animal Cells - Fall River Public Schools
... BONUS OPTIONS: Either a) make your own analogy for a chloroplast (a chloroplast is like … because …) or b) write an acrostic poem for CHLOROPLAST. ...
... BONUS OPTIONS: Either a) make your own analogy for a chloroplast (a chloroplast is like … because …) or b) write an acrostic poem for CHLOROPLAST. ...
PowerPoint
... • Openings in the nuclear membrane that permit passage of substances into nucleus • City Hall gates/doors ...
... • Openings in the nuclear membrane that permit passage of substances into nucleus • City Hall gates/doors ...
[pdf]
... program highlighted both the physical forces exerted during migration and the signaling pathways involved in the process. Celeste Nelson (Princeton University) presented results suggesting that cells migrate collectively through fibrous extracellular matrix (ECM) by exerting tensile forces at the le ...
... program highlighted both the physical forces exerted during migration and the signaling pathways involved in the process. Celeste Nelson (Princeton University) presented results suggesting that cells migrate collectively through fibrous extracellular matrix (ECM) by exerting tensile forces at the le ...
The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life. Some organisms are made
... Although there are lots of different kinds of cells, they are often divided into two main categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. ...
... Although there are lots of different kinds of cells, they are often divided into two main categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. ...
Chapter 3 Cell Structure - Shelbyville Central Schools
... •Nucleus controls cell’s functions •Nuclear envelope is double membrane surrounding the nucleus •Nuclear pores are small openings scattered over surface of nuclear envelope ...
... •Nucleus controls cell’s functions •Nuclear envelope is double membrane surrounding the nucleus •Nuclear pores are small openings scattered over surface of nuclear envelope ...



















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008789103_1-746b7a86138a2a5bab5758b7de85a178-300x300.png)


