Scientific explanation
... organelles – mitochondria - most probably originating from symbiotic bacteria and generating energy by using oxygen for aerobic oxidation. They have their own DNA and genes and reproduce only through division of existing mitochondria because the mitochondrion cannot be formed from the information co ...
... organelles – mitochondria - most probably originating from symbiotic bacteria and generating energy by using oxygen for aerobic oxidation. They have their own DNA and genes and reproduce only through division of existing mitochondria because the mitochondrion cannot be formed from the information co ...
Exam 1 Review - Iowa State University
... d) synthesize proteins e) form cell walls 11. The oldest group of organisms on earth are: a) plants b) prokayotes c) protists d) Euglenazoa e) dinosaurs 12. An “endosymbiont” is ___________________. a) a chimera b) a eukaryote cell c) an organism that lives inside another organism d) a plant and its ...
... d) synthesize proteins e) form cell walls 11. The oldest group of organisms on earth are: a) plants b) prokayotes c) protists d) Euglenazoa e) dinosaurs 12. An “endosymbiont” is ___________________. a) a chimera b) a eukaryote cell c) an organism that lives inside another organism d) a plant and its ...
Tissue Engineering
... cells know what to become, how do they know to stay that way? – What about you, how did you know where to fit in in high school, did you stay fitting in there? ...
... cells know what to become, how do they know to stay that way? – What about you, how did you know where to fit in in high school, did you stay fitting in there? ...
File
... of solutes and a higher concentration of water than inside the cell. (Low solute = High water) ...
... of solutes and a higher concentration of water than inside the cell. (Low solute = High water) ...
Long Version
... Explain the rule of 10% in regards to trophic levels. What are there not unlimited steps in the energy pyramid? What is primary productivity? What is Gross primary productivity? How is it idifferent than net primary productivity? Know the details of the following cycles: Nitrogen (nitrogen fixation, ...
... Explain the rule of 10% in regards to trophic levels. What are there not unlimited steps in the energy pyramid? What is primary productivity? What is Gross primary productivity? How is it idifferent than net primary productivity? Know the details of the following cycles: Nitrogen (nitrogen fixation, ...
Cells Alive - White Plains Public Schools
... Part C; Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there ...
... Part C; Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there ...
Biology 101 Chapter 1
... All cells are placed in one of 2 classes: Prokaryotic = lack a nucleus (bacteria) Eukaryotic = have a nucleus (protists, fungi, plants, and animals) PROKARYOTIC CELLS very, very small very simple structure Parts: A) Plasma (cell) membrane = encloses cytoplasm of cell B) Nucleoid Region = where D ...
... All cells are placed in one of 2 classes: Prokaryotic = lack a nucleus (bacteria) Eukaryotic = have a nucleus (protists, fungi, plants, and animals) PROKARYOTIC CELLS very, very small very simple structure Parts: A) Plasma (cell) membrane = encloses cytoplasm of cell B) Nucleoid Region = where D ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Consistent from Bacteria to Mammals 1) Forms a protective outer barrier for the cell 2) Helps maintain a constant internal ...
... Consistent from Bacteria to Mammals 1) Forms a protective outer barrier for the cell 2) Helps maintain a constant internal ...
Cell Organelles - Shelton School District
... Cell Introduction • Prokaryotic Cell: A cell that is lacking a nucleus and most organelles • Eukaryotic Cell: A cell that contains a membrane bound nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. • Organelles: “mini-organ” part of the cell with a specific job. ...
... Cell Introduction • Prokaryotic Cell: A cell that is lacking a nucleus and most organelles • Eukaryotic Cell: A cell that contains a membrane bound nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. • Organelles: “mini-organ” part of the cell with a specific job. ...
Cell Transport Review Worksheet
... B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving – FLUID MOSAIC D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids an ...
... B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving – FLUID MOSAIC D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids an ...
Cell Structure
... • Cell Structure: have cell walls that contain lipids found in no other organism; have genetic material but lack nuclear membrane or other membrane-bound organelles. • Nutrition: autotrophs or heterotrophs • Habitat: extreme environments such as d ...
... • Cell Structure: have cell walls that contain lipids found in no other organism; have genetic material but lack nuclear membrane or other membrane-bound organelles. • Nutrition: autotrophs or heterotrophs • Habitat: extreme environments such as d ...
THE HISTORY OF CELL BIOLOGY
... SHORT ANSWER Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. What roles do membrane proteins play in transporting only certain substances into a cell? ...
... SHORT ANSWER Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. What roles do membrane proteins play in transporting only certain substances into a cell? ...
Photosynthesis Test
... a. organ systems, organism, organs, tissues, cells b. tissues, cells, organs, organ systems, organism c. cells, tissues, organ systems, organs, organism d. cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism ____ 18. The primary function of roots is a. to absorb sunlight b. to transport food up the stem ...
... a. organ systems, organism, organs, tissues, cells b. tissues, cells, organs, organ systems, organism c. cells, tissues, organ systems, organs, organism d. cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism ____ 18. The primary function of roots is a. to absorb sunlight b. to transport food up the stem ...
The Cell Cycle Control System
... Gametes (reproductive cells: sperm and eggs) have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells ...
... Gametes (reproductive cells: sperm and eggs) have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells ...
File
... The diagrams below represent two different cells and some of their parts. The diagrams are not drawn to scale. ...
... The diagrams below represent two different cells and some of their parts. The diagrams are not drawn to scale. ...
Midterm Review - Jupiter Files
... Sexual reproduction requires two parents and the off the offspring is genetically different from the parents. Each parent contributes half the genetic information in sex cells or gametes. *Examples of organisms that reproduce sexually: humans, plants, fish, insects If species stop reproducing they r ...
... Sexual reproduction requires two parents and the off the offspring is genetically different from the parents. Each parent contributes half the genetic information in sex cells or gametes. *Examples of organisms that reproduce sexually: humans, plants, fish, insects If species stop reproducing they r ...
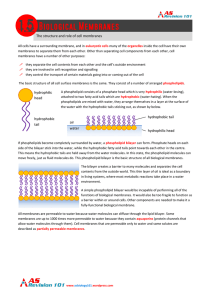
The structure and role of cell membranes hydrophilic head
... in living systems, where most metabolic reactions take place in a water environment. A simple phospholipid bilayer would be incapable of performing all of the functions of biological membranes. It would also be too fragile to function as a barrier within or around cells. Other components are needed ...
... in living systems, where most metabolic reactions take place in a water environment. A simple phospholipid bilayer would be incapable of performing all of the functions of biological membranes. It would also be too fragile to function as a barrier within or around cells. Other components are needed ...
Cell Structure and Function - Mount Mansfield Union High
... – Cytoplasmic oozing forces a “foot” out in a certain direction, the cell then drags itself ...
... – Cytoplasmic oozing forces a “foot” out in a certain direction, the cell then drags itself ...
HOXA9 regulates expression of cancer stem cell markers and
... of cancers and CD24, CD44, and CD133 are considered CSC markers. Therefore, we want to study whether the expression of HOXA9 gene can influence the expression of CSC markers, such as CD24, CD44, and CD133, and change the cancerization of gastric tumor. Method and Material: We selected a normal human ...
... of cancers and CD24, CD44, and CD133 are considered CSC markers. Therefore, we want to study whether the expression of HOXA9 gene can influence the expression of CSC markers, such as CD24, CD44, and CD133, and change the cancerization of gastric tumor. Method and Material: We selected a normal human ...
Name:
... 4. Flash Card Example: Each organelle flash card will have: Side 1: (1) What is the function of the nucleus? (2) Describe an interesting fact about this organelle. Side 2: (1) Answer: Controls activities of the cell. (2) Fact: Contains DNA (Genetic Information) (3) Draw a picture of the organelle. 5 ...
... 4. Flash Card Example: Each organelle flash card will have: Side 1: (1) What is the function of the nucleus? (2) Describe an interesting fact about this organelle. Side 2: (1) Answer: Controls activities of the cell. (2) Fact: Contains DNA (Genetic Information) (3) Draw a picture of the organelle. 5 ...
cell as a school powerpoint webquest
... The cell wall connects to Dr. Baugus because he provides shape and order for our school like a cell wall provides the shape of the cell. ...
... The cell wall connects to Dr. Baugus because he provides shape and order for our school like a cell wall provides the shape of the cell. ...