Transport thru the Cell Membrane
... accept only specific molecules, like a lock accepts a particular key. ...
... accept only specific molecules, like a lock accepts a particular key. ...
5.5 Multicellular Life TEKS 5B, 5C, 10C
... among the specialized cells of many organs and tissues. 2. Embryonic stem cells; taken from clusters of undifferentiated cells in a 3-to-5-day-old embryo; pluripotent; can be grown indefinitely in culture. ...
... among the specialized cells of many organs and tissues. 2. Embryonic stem cells; taken from clusters of undifferentiated cells in a 3-to-5-day-old embryo; pluripotent; can be grown indefinitely in culture. ...
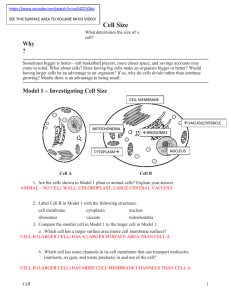
Model 1 – Investigating Cell Size
... a. Which cell has more mitochondria? CELL B (LARGER CELL) HAS MORE MITOCHONDRIA THAN CELL A. b. Propose an explanation for why the cell in part a would need more mitochondria for proper functioning of the cell. SINCE THE CELL IS LARGER, IT WILL NEED MORE ATP TO RUN CELL PROCESSES. 5. What would be t ...
... a. Which cell has more mitochondria? CELL B (LARGER CELL) HAS MORE MITOCHONDRIA THAN CELL A. b. Propose an explanation for why the cell in part a would need more mitochondria for proper functioning of the cell. SINCE THE CELL IS LARGER, IT WILL NEED MORE ATP TO RUN CELL PROCESSES. 5. What would be t ...
Membranes of Living Organisms Outline
... Active transport - movement from low to high concentration ¾Movement through proteins ¾Pumps Æ Require ATP (energy source) ...
... Active transport - movement from low to high concentration ¾Movement through proteins ¾Pumps Æ Require ATP (energy source) ...
Body Organization
... Body Organization BEGINNING OF CLASS: In the flow chart below, list the five levels of organization in the human body in order from simplest to most complex: Organism, Tissue, Organ, Cell, and Organ System. Cell ...
... Body Organization BEGINNING OF CLASS: In the flow chart below, list the five levels of organization in the human body in order from simplest to most complex: Organism, Tissue, Organ, Cell, and Organ System. Cell ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Two lipid bilayers pressed together as a single membrane surrounding the nucleus • Outer bilayer is continuous with the ER • Nuclear pores allow certain substances to pass through the membrane ...
... • Two lipid bilayers pressed together as a single membrane surrounding the nucleus • Outer bilayer is continuous with the ER • Nuclear pores allow certain substances to pass through the membrane ...
Biosensors as alarm systems for drinking and
... such as the protein structure of mammalian and bacterial cell systems change in a substance-specific way. Both measuring meth- ...
... such as the protein structure of mammalian and bacterial cell systems change in a substance-specific way. Both measuring meth- ...
Chapter 17: The History and Diversity of Life
... Called “true” bacteria because they have a thick, rigid cell wall made of the carbohydrate peptidoglycan Very diverse, some photosynthetic ...
... Called “true” bacteria because they have a thick, rigid cell wall made of the carbohydrate peptidoglycan Very diverse, some photosynthetic ...
Lecture 4 - TeachLine
... essential for deriving mechanisms. Division into neuron classes basic for • visual system, differentiating processing pathways, using one, the other, or a combination of streams. Analysis of response types may aid in • understanding neuron role/function. ...
... essential for deriving mechanisms. Division into neuron classes basic for • visual system, differentiating processing pathways, using one, the other, or a combination of streams. Analysis of response types may aid in • understanding neuron role/function. ...
Moving Cellular Material Chapter 2 Lesson 3
... concentration to high solute concentration The cell uses energy (ATP) to actively transport Na+ out of the cell and K+ into the cell against the concentration gradient ...
... concentration to high solute concentration The cell uses energy (ATP) to actively transport Na+ out of the cell and K+ into the cell against the concentration gradient ...
Cell Membranes
... Why would the cell “waste” energy on a proton pump? *Because the cell needs isolated areas of the cell with different pH for particular functions; ex) lysosomes – have proton pumps to maintain a pH=5 *Because the cell only uses one ATP to pump a proton out, and that proton can be used in co-transpor ...
... Why would the cell “waste” energy on a proton pump? *Because the cell needs isolated areas of the cell with different pH for particular functions; ex) lysosomes – have proton pumps to maintain a pH=5 *Because the cell only uses one ATP to pump a proton out, and that proton can be used in co-transpor ...
Chapter 3 Cells The Basic Units of Life
... nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) core surrounded by protein sheath. They are inert, except, when present in a living cell of some organism where they multiply by using cell’s mateials and ...
... nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) core surrounded by protein sheath. They are inert, except, when present in a living cell of some organism where they multiply by using cell’s mateials and ...
AP Biology - Review Sheet for TEST #1 - Chapters 02
... c. Triglyceride B is probably derived from a plant. Its fatty acid chains are unsaturated (double bonds) and relatively short, both characteristics of liquid, plant-derived triglycerides. d. Three water molecules will result. A water molecule results for each of the three fatty acids added to glycer ...
... c. Triglyceride B is probably derived from a plant. Its fatty acid chains are unsaturated (double bonds) and relatively short, both characteristics of liquid, plant-derived triglycerides. d. Three water molecules will result. A water molecule results for each of the three fatty acids added to glycer ...
File - Introduction
... Students will take a journey into a cell by watching a video clip in this link: http://ruorozk254.weebly.com/process.html and respond to the questions found in the webpage. The students will then engage in the next activity which will involve either designing an interactive poster or a brochure, or ...
... Students will take a journey into a cell by watching a video clip in this link: http://ruorozk254.weebly.com/process.html and respond to the questions found in the webpage. The students will then engage in the next activity which will involve either designing an interactive poster or a brochure, or ...
Back to the question I
... A vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane protein ...
... A vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm (the ER is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane). Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane protein ...
Bio10lab1 0710
... size, cells are amazingly complex and often very beautiful. There are two general types of cells: • Prokaryotic cells o Lack a nucleus, but they do contain DNA o Also lack other organelles, such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, etc. o Simple unicellular organisms like bacteria and cyanobacteria (blueg ...
... size, cells are amazingly complex and often very beautiful. There are two general types of cells: • Prokaryotic cells o Lack a nucleus, but they do contain DNA o Also lack other organelles, such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, etc. o Simple unicellular organisms like bacteria and cyanobacteria (blueg ...
HW2
... story about diffusion in neurons and how diffusion will take prohibitively long times. See Figure 1 for their depiction of the comparison between passive diffusion and active transport. Using what we have learned about diffusion, work out the time for diffusion of a protein over the 10 cm length of ...
... story about diffusion in neurons and how diffusion will take prohibitively long times. See Figure 1 for their depiction of the comparison between passive diffusion and active transport. Using what we have learned about diffusion, work out the time for diffusion of a protein over the 10 cm length of ...
Unit 2
... The nucleus contains most of the genes that control the cell. The nuclear envelope encloses the nucleus, separating its contents from the cytoplasm. ...
... The nucleus contains most of the genes that control the cell. The nuclear envelope encloses the nucleus, separating its contents from the cytoplasm. ...
Advanced Biology - Dwight Public Schools
... Multinucleated: have at least one macronucleus and one micronucleus. ...
... Multinucleated: have at least one macronucleus and one micronucleus. ...
unit 3. living things
... • All living things have three things in common. • These three things are called life processes: – Nutrition. – Reproduction. – Interaction with the enviroment. ...
... • All living things have three things in common. • These three things are called life processes: – Nutrition. – Reproduction. – Interaction with the enviroment. ...
Sample APBio Exam1 - Bruce Rife`s Web Page
... 3. solubility of the protein in water 4. the number of amino acids in the protein a. 1 d. 4 b. 2 e. 1, 2, and 3 c. 3 25. Which of the following factors can result in the denaturation of a protein? a. heat d. changes in salt concentration b. changes in pH e. all of these c. chemicals that destroy hyd ...
... 3. solubility of the protein in water 4. the number of amino acids in the protein a. 1 d. 4 b. 2 e. 1, 2, and 3 c. 3 25. Which of the following factors can result in the denaturation of a protein? a. heat d. changes in salt concentration b. changes in pH e. all of these c. chemicals that destroy hyd ...
Do Now - Typepad
... Think and answer on your notes 1. In your own words, explain how a pasta strainer shows “selective permeability.” How is this similar to cell membranes? ...
... Think and answer on your notes 1. In your own words, explain how a pasta strainer shows “selective permeability.” How is this similar to cell membranes? ...
The Cell
... Particles “push” against the outside of the cell membrane causing a pocket to form. This pocket breaks loose on the inside of the cell forming an individual vacuole, or storage structure. Large molecules, clumps of food and other cells can be taken into the cytoplasm this way. ...
... Particles “push” against the outside of the cell membrane causing a pocket to form. This pocket breaks loose on the inside of the cell forming an individual vacuole, or storage structure. Large molecules, clumps of food and other cells can be taken into the cytoplasm this way. ...