Operating System
... that manages the sharing of the resources of a computer. An operating system processes system data and user input, and responds by allocating and managing tasks and internal system resources as a service to users and programs of the system. ...
... that manages the sharing of the resources of a computer. An operating system processes system data and user input, and responds by allocating and managing tasks and internal system resources as a service to users and programs of the system. ...
7.2 Peripheral Supplementary
... The OS may support the interrupt requests to control the devices of the system ...
... The OS may support the interrupt requests to control the devices of the system ...
chp06
... of the central computer can be done by the desktop PC. In late 1980s and in the 1990s computing changed from centralized environment (batch, multi-programmed, TSS) to a distributed environment, where computing moved to the front-end (e.g. office, lab, classroom). OSs in PCs were initially single-use ...
... of the central computer can be done by the desktop PC. In late 1980s and in the 1990s computing changed from centralized environment (batch, multi-programmed, TSS) to a distributed environment, where computing moved to the front-end (e.g. office, lab, classroom). OSs in PCs were initially single-use ...
390aLecture01_12wi
... ability to execute programs (and multi-tasking) memory management (and virtual memory) file systems, disk and network access an interface to communicate with hardware a user interface (often graphical) ...
... ability to execute programs (and multi-tasking) memory management (and virtual memory) file systems, disk and network access an interface to communicate with hardware a user interface (often graphical) ...
390Lecture1
... Collection of tools and topics not specifically addressed in other courses that CSE majors should know • *nix command line interface (CLI), Shell scripting, compilation tools (makefiles), version control… ...
... Collection of tools and topics not specifically addressed in other courses that CSE majors should know • *nix command line interface (CLI), Shell scripting, compilation tools (makefiles), version control… ...
Design of OSes
... • How to make the pie go further? – Resource usage is bursty! So give to others when idle. – Eg. When waiting for a webpage! Give CPU to idle process. • 1000 years old idea: instead of one classroom per student, restaurant per customer, etc. ...
... • How to make the pie go further? – Resource usage is bursty! So give to others when idle. – Eg. When waiting for a webpage! Give CPU to idle process. • 1000 years old idea: instead of one classroom per student, restaurant per customer, etc. ...
CENG334 Introduction to Operating Systems
... The OS kernel is just a bunch of code that sits around in memory, waiting to be executed ...
... The OS kernel is just a bunch of code that sits around in memory, waiting to be executed ...
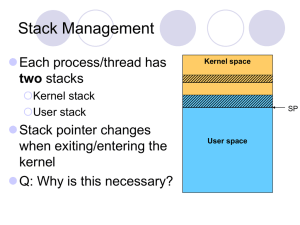
Page table
... ◦ Reliability requirement for Windows XP more stringent than Windows 2000 (which was the most reliable, stable system released by Microsoft) ◦ “extensive manual and automatic code review to identify over 63,000 lines in the source [code] that might contain issues not detected by testing” and then se ...
... ◦ Reliability requirement for Windows XP more stringent than Windows 2000 (which was the most reliable, stable system released by Microsoft) ◦ “extensive manual and automatic code review to identify over 63,000 lines in the source [code] that might contain issues not detected by testing” and then se ...
Computer Systems Overview
... Varies between systems (manufacturers) Let’s distinguish between : • Interrupts: independent of program that is executing. Examples: I/O, timer • Traps: caused by program execution. Examples: illegal access, divide by zero. also includes (deliberate) System Calls ...
... Varies between systems (manufacturers) Let’s distinguish between : • Interrupts: independent of program that is executing. Examples: I/O, timer • Traps: caused by program execution. Examples: illegal access, divide by zero. also includes (deliberate) System Calls ...
Chapter 6 An Introduction to System Software
... OS has the responsibilities of a security guard— controlling access to the computer and its resource. OS must prevent unauthorized users from accessing the system and prevent authorized users from doing unauthorized things. In most OS, access control is handled by requiring a user to enter a legal u ...
... OS has the responsibilities of a security guard— controlling access to the computer and its resource. OS must prevent unauthorized users from accessing the system and prevent authorized users from doing unauthorized things. In most OS, access control is handled by requiring a user to enter a legal u ...
Chapter 6 An Introduction to System Software and
... OS has the responsibilities of a security guard— controlling access to the computer and its resource. OS must prevent unauthorized users from accessing the system and prevent authorized users from doing unauthorized things. In most OS, access control is handled by requiring a user to enter a legal u ...
... OS has the responsibilities of a security guard— controlling access to the computer and its resource. OS must prevent unauthorized users from accessing the system and prevent authorized users from doing unauthorized things. In most OS, access control is handled by requiring a user to enter a legal u ...
OPERATING SYSTEMS: DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION
... Figure 1-15. (a) File system before the mount. (b) File system ...
... Figure 1-15. (a) File system before the mount. (b) File system ...
Basic Unix - University of Arizona
... Input and output • Data are read from and written to i/o streams • There are three predefined streams: stdin : “standard input” usually, keyboard input stdout : “standard output” usually, the screen stderr : “standard error” for error messages (usually, the screen) ...
... Input and output • Data are read from and written to i/o streams • There are three predefined streams: stdin : “standard input” usually, keyboard input stdout : “standard output” usually, the screen stderr : “standard error” for error messages (usually, the screen) ...
Introduction
... Types of Systems • Time-sharing Systems (multitasking) logical extension of multiprogramming in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing – Response time should be < 1 second – Each user has at least one program e ...
... Types of Systems • Time-sharing Systems (multitasking) logical extension of multiprogramming in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing – Response time should be < 1 second – Each user has at least one program e ...
Module 3: Operating
... I/O operations – since user programs cannot execute I/O operations directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O. File-system manipulation – program capability to read, write, create, and delete files. Communications – exchange of information between processes executing ...
... I/O operations – since user programs cannot execute I/O operations directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O. File-system manipulation – program capability to read, write, create, and delete files. Communications – exchange of information between processes executing ...
Operating System
... • A concept used to group files together. • System calls are needed – to create and remove directories. – to put an existing file in a directory, – to remove a file from the directory. ...
... • A concept used to group files together. • System calls are needed – to create and remove directories. – to put an existing file in a directory, – to remove a file from the directory. ...
CS4023_-_lecture_05_-_0910
... offers run-time adding and removal of services. The whole kernel runs in "kernel mode" in which the software has full control over the machine. The processes running on top of the kernel run in "user mode", in which programs have only access to the kernel services. ...
... offers run-time adding and removal of services. The whole kernel runs in "kernel mode" in which the software has full control over the machine. The processes running on top of the kernel run in "user mode", in which programs have only access to the kernel services. ...
Introduction - UW Courses Web Server
... Several jobs are kept in main memory at the same time. OS picks one of them to execute. The job may have to wait for a slow I/O operation to complete. OS switches to and executes another job. To facilitate multiprogramming, OS needs: Job scheduling Memory management CSS430 Introduction ...
... Several jobs are kept in main memory at the same time. OS picks one of them to execute. The job may have to wait for a slow I/O operation to complete. OS switches to and executes another job. To facilitate multiprogramming, OS needs: Job scheduling Memory management CSS430 Introduction ...
dsk-01-intro
... Another set of OS functions exists for ensuring the efficient operation of the system itself via resource sharing Resource allocation - When multiple users or multiple jobs running concurrently, resources must be allocated to each of them Many types of resources - Some (such as CPU cycles, main ...
... Another set of OS functions exists for ensuring the efficient operation of the system itself via resource sharing Resource allocation - When multiple users or multiple jobs running concurrently, resources must be allocated to each of them Many types of resources - Some (such as CPU cycles, main ...
Introduction to Linux/Unix
... • working on Linux/Unix system • logging in • managing passwords • navigating the Linux/Unix file system ...
... • working on Linux/Unix system • logging in • managing passwords • navigating the Linux/Unix file system ...
Operating-System Structures
... too small to accommodate all data and programs permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. ...
... too small to accommodate all data and programs permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. ...
Solaris System Management - Understanding System Concepts -
... – Bourne – located in /bin/sh, uses $ prompt – C – located in /bin/csh, uses a % prompt – Korn – best of both, located in /bin/ksh, uses $ prompt va-scan ...
... – Bourne – located in /bin/sh, uses $ prompt – C – located in /bin/csh, uses a % prompt – Korn – best of both, located in /bin/ksh, uses $ prompt va-scan ...