• The Golgi apparatus Functions of the Golgi apparatus Lysosomes
... – Extracellular structures of plant cells that distinguish them from animal cells – Are made of cellulose fibers embedded in other polysaccharides and protein – May have multiple layers Central vacuole of cell ...
... – Extracellular structures of plant cells that distinguish them from animal cells – Are made of cellulose fibers embedded in other polysaccharides and protein – May have multiple layers Central vacuole of cell ...
Ch 4 A Tour of the Cell 2016
... 2. Nucleoid Region or Nucleus-the brain of the cell 3. Cytoplasm: region within the plasma membrane that is fluid based ...
... 2. Nucleoid Region or Nucleus-the brain of the cell 3. Cytoplasm: region within the plasma membrane that is fluid based ...
Embryology • Important as a process, the way the organism
... open up within the mesoderm in which we call a coelom. Chordamesoderm will form the notochord. Dorsal ventral sections of the mesoderm –epimere, mesomere, hypomere. Neural crest cells now become detached and begin to migrate, the neural tube is isolated. The lateral mesoderm, there is an expansion o ...
... open up within the mesoderm in which we call a coelom. Chordamesoderm will form the notochord. Dorsal ventral sections of the mesoderm –epimere, mesomere, hypomere. Neural crest cells now become detached and begin to migrate, the neural tube is isolated. The lateral mesoderm, there is an expansion o ...
Unit 3 part 1 PPT
... transport materials to all body cells. This is the link between the cells and their environment. Plasma is the liquid portion of the blood and transports ...
... transport materials to all body cells. This is the link between the cells and their environment. Plasma is the liquid portion of the blood and transports ...
www.theallpapers.com
... 33 Some foods contain ‘hydrogenated vegetable oils’. These are unsaturated fats that have been converted to saturated fats. Which property of the fats will have changed? A ...
... 33 Some foods contain ‘hydrogenated vegetable oils’. These are unsaturated fats that have been converted to saturated fats. Which property of the fats will have changed? A ...
Unit 2 Lesson 5
... • Plants and animals use oxygen during cellular respiration to produce energy from food. • Sugars and oxygen are converted to water, carbon dioxide, and energy during respiration. • Photosynthesis and respiration are linked because each one depends on the products of the other. ...
... • Plants and animals use oxygen during cellular respiration to produce energy from food. • Sugars and oxygen are converted to water, carbon dioxide, and energy during respiration. • Photosynthesis and respiration are linked because each one depends on the products of the other. ...
video slide
... – Extracellular structures of plant cells that distinguish them from animal cells ...
... – Extracellular structures of plant cells that distinguish them from animal cells ...
Document
... act as channels & pumps that move different molecules into & out of the cell. • Receptor proteins in cell membrane allow cells to detect external signaling molecules such as hormones ...
... act as channels & pumps that move different molecules into & out of the cell. • Receptor proteins in cell membrane allow cells to detect external signaling molecules such as hormones ...
Document
... Apoptosis (programmed cell death) is a cell fate that is essential in some developmental programs. Apoptosis is highly regulated. It can be induced by withdrawal of trophic factors, which signal cells to stay alive. Alternatively, signals (e.g., death signals like tumor necrosis factor) trigger apop ...
... Apoptosis (programmed cell death) is a cell fate that is essential in some developmental programs. Apoptosis is highly regulated. It can be induced by withdrawal of trophic factors, which signal cells to stay alive. Alternatively, signals (e.g., death signals like tumor necrosis factor) trigger apop ...
mitosis web activity_biology
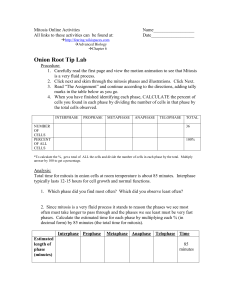
... *To calculate the %, get a total of ALL the cells and divide the number of cells in each phase by the total. Multiply answer by 100 to get a percentage. ...
... *To calculate the %, get a total of ALL the cells and divide the number of cells in each phase by the total. Multiply answer by 100 to get a percentage. ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE MIDTERM REVIEW Units 1
... 56. Some scientists believe that RNA is essential to the evolution of life on Earth. Which of the following is not one of the capabilities of RNA that supports this theory? a. Catalyzation b. Metabolism c. Immune defense d. Replication 57. Gel electrophoresis is a technique that loads a digest into ...
... 56. Some scientists believe that RNA is essential to the evolution of life on Earth. Which of the following is not one of the capabilities of RNA that supports this theory? a. Catalyzation b. Metabolism c. Immune defense d. Replication 57. Gel electrophoresis is a technique that loads a digest into ...
Scenario 1
... high oxygen concentration is drawn into small sacs within your lungs, called alveoli. The air in the alveoli has a higher oxygen concentration than the blood in the tiny blood vessels surrounding the alveoli. Oxygen will diffuse out of the alveoli and into your blood. Show with a large diagram on po ...
... high oxygen concentration is drawn into small sacs within your lungs, called alveoli. The air in the alveoli has a higher oxygen concentration than the blood in the tiny blood vessels surrounding the alveoli. Oxygen will diffuse out of the alveoli and into your blood. Show with a large diagram on po ...
Module 9 - Moline High School
... • Fiber that communicates the signal down the neuron and away from the cell body ...
... • Fiber that communicates the signal down the neuron and away from the cell body ...
What is the structure of the spinal cord?
... Ribosomes: Located on rough endoplasmic reticulum. Cellular structures on which proteins are synthesized. Golgi complex: A system of membranes that packages molecules in vesicles. Microtubules: Tubules that allow for the rapid transport of material throughout neurons. ...
... Ribosomes: Located on rough endoplasmic reticulum. Cellular structures on which proteins are synthesized. Golgi complex: A system of membranes that packages molecules in vesicles. Microtubules: Tubules that allow for the rapid transport of material throughout neurons. ...
cytology - Citrus College
... • Membrane-enclosed bag of hydrolytic enzymes (digestive enzymes). • Functions: 1. intracellular digestion - phagocytosis. 2. Autophagy - engulfs other cellular organelles. ...
... • Membrane-enclosed bag of hydrolytic enzymes (digestive enzymes). • Functions: 1. intracellular digestion - phagocytosis. 2. Autophagy - engulfs other cellular organelles. ...
The Cell Membrane
... * semi-permeable/selective permeability: Some molecules can pass across the membrane while other molecules cannot ...
... * semi-permeable/selective permeability: Some molecules can pass across the membrane while other molecules cannot ...
Biology Unit 5: Cellular Structure and Function
... 10. The invention of the compound light microscope enabled scientists to observe cells, helping them to a. determine the number of atoms in a molecule b. discover a basic similarity among organisms c. study the behavior of chordates d. develop techniques for growing plants in a laboratory 3.1.C.a 11 ...
... 10. The invention of the compound light microscope enabled scientists to observe cells, helping them to a. determine the number of atoms in a molecule b. discover a basic similarity among organisms c. study the behavior of chordates d. develop techniques for growing plants in a laboratory 3.1.C.a 11 ...
Cells Structure and Function PRACTICE Test
... slide that you are viewing is not visible. Explain two things you might do to fix the problem. ...
... slide that you are viewing is not visible. Explain two things you might do to fix the problem. ...
Extracurricular Activities
... Microfilaments help the cell move with their versatile shape. This function is called amoeboid movement. ...
... Microfilaments help the cell move with their versatile shape. This function is called amoeboid movement. ...
Cell
... Let’s create the levels of organization for a frog. Each level must build upon the previous level. For example, if you draw a cardiac muscle cell, then you should draw cardiac muscle tissue, a heart, & the ...
... Let’s create the levels of organization for a frog. Each level must build upon the previous level. For example, if you draw a cardiac muscle cell, then you should draw cardiac muscle tissue, a heart, & the ...
Cookie Factory Equivalent?
... them down into energy • Can grow, move and combine with other mitochondria • Responsible for 90% of energy needed by the body ...
... them down into energy • Can grow, move and combine with other mitochondria • Responsible for 90% of energy needed by the body ...
Embryology Complete
... The endoderm forms the mucosa of the digestive system and respiratory system and associated glands The mesoderm forms virtually everything else lying between the two (skeleton, walls of digestive organs, urinary system, skeletal muscles, circulatory system and others) All ground work is completed by ...
... The endoderm forms the mucosa of the digestive system and respiratory system and associated glands The mesoderm forms virtually everything else lying between the two (skeleton, walls of digestive organs, urinary system, skeletal muscles, circulatory system and others) All ground work is completed by ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.