Layout
... In order to meet the Given Signal to interference ratio, We need to try N( Reuse factor) with different combination of Sectoring(60 120 180 360) and through this calculating Number of First level interfering channels n. The aim here is to minimize the Reuse factor N. ...
... In order to meet the Given Signal to interference ratio, We need to try N( Reuse factor) with different combination of Sectoring(60 120 180 360) and through this calculating Number of First level interfering channels n. The aim here is to minimize the Reuse factor N. ...
12-1 pm Location: Room HSW1057 UCSF
... Presented By: Antonia Livolsi, Ph.D, Research Application Scientist Traditional methods for examining gene expression involve lysed or fixed cell populations. The ability to do so in live cells would allow for more physiologically relevant information based on a cell’s response to given stimuli. Det ...
... Presented By: Antonia Livolsi, Ph.D, Research Application Scientist Traditional methods for examining gene expression involve lysed or fixed cell populations. The ability to do so in live cells would allow for more physiologically relevant information based on a cell’s response to given stimuli. Det ...
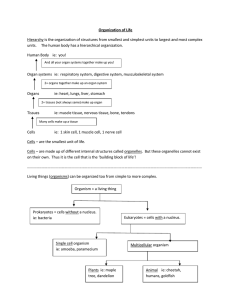
Organization of Life Hierarchy is the organization of structures from
... Organ systems ie: respiratory system, digestive system, musculoskeletal system 2+ organs together make up an organ system ...
... Organ systems ie: respiratory system, digestive system, musculoskeletal system 2+ organs together make up an organ system ...
11-14-02
... Discovery of the Cell Invention of the microscope seventeenth century Robert Hooke , Looked at cork Saw little boxes that reminded him of cells in a monastery; Coined the word cell Anton von Leeuwenhoek observed the first living cell ...
... Discovery of the Cell Invention of the microscope seventeenth century Robert Hooke , Looked at cork Saw little boxes that reminded him of cells in a monastery; Coined the word cell Anton von Leeuwenhoek observed the first living cell ...
Where do new cells come from?
... Life Span of Cells Skin cell-two weeks Red blood cell-4 months Liver cell-300-500 days Intestine-(muscle)-16 years ...
... Life Span of Cells Skin cell-two weeks Red blood cell-4 months Liver cell-300-500 days Intestine-(muscle)-16 years ...
Lecture Quiz 2, Biol-1, C. Briggs, ver 9.13 (1pt each, unless noted
... Lecture Quiz 2, Biol-1, C. Briggs, ver 9.13 (1pt each, unless noted) ...
... Lecture Quiz 2, Biol-1, C. Briggs, ver 9.13 (1pt each, unless noted) ...
Document
... Supplemental Methods Stimulation of Cell Lines The same concentrations of TLR agonists were used to stimulate reactivation of the J-Lat 10.6, ACH-2 and U1 HIV-1 latently cell lines, and in order to induce expression of IL-8 cytokine in THP-1 cells. Cells were maintained in culture medium made of RPM ...
... Supplemental Methods Stimulation of Cell Lines The same concentrations of TLR agonists were used to stimulate reactivation of the J-Lat 10.6, ACH-2 and U1 HIV-1 latently cell lines, and in order to induce expression of IL-8 cytokine in THP-1 cells. Cells were maintained in culture medium made of RPM ...
Chapter 3 Lesson 3.2
... Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Vesicle Lysosomes Vacuoles ...
... Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Vesicle Lysosomes Vacuoles ...
Cell Processes Unit Review Newsletter Questions
... Cell Processes Unit Review Newsletter Questions Directions: Read the newsletter provided and use it to answer the following questions. 1. Most animal cells are ________________________, meaning they have a ________________. 2. Fill in the chart below about the different organelles in a cell: ...
... Cell Processes Unit Review Newsletter Questions Directions: Read the newsletter provided and use it to answer the following questions. 1. Most animal cells are ________________________, meaning they have a ________________. 2. Fill in the chart below about the different organelles in a cell: ...
Vacuoles
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
Cell Review
... 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of function in all living things 3. All cells come from preexisting cells Exceptions 1. Virus- can not reproduce on their own 2. Mitochondria and Chloroplasts contain their own DNA Organelles ...
... 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of function in all living things 3. All cells come from preexisting cells Exceptions 1. Virus- can not reproduce on their own 2. Mitochondria and Chloroplasts contain their own DNA Organelles ...
CELL ORGANELLES 1. How does the structure of a cell suggest its
... 7. In which kinds of human cells would you expect to find the most mitochondria? The most lysosomes? The most ribosomes? Explain your answers. ...
... 7. In which kinds of human cells would you expect to find the most mitochondria? The most lysosomes? The most ribosomes? Explain your answers. ...
Debbie Spector
... Deborah Spector, Ph.D. Research Interests Association of cytomegalovirus with atherosclerosis Mechanisms governing hearing loss as a result of congenital cytomegalovirus infection Development of herpesvirus vaccines Exploiting autophagy as an antiviral ...
... Deborah Spector, Ph.D. Research Interests Association of cytomegalovirus with atherosclerosis Mechanisms governing hearing loss as a result of congenital cytomegalovirus infection Development of herpesvirus vaccines Exploiting autophagy as an antiviral ...
Cells and Microscope Test Study Guide
... Cells and Microscope Test Study Guide Use your notes and handouts to help you study! Know different parts of cell and function of each part (what it does) Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cell wall Understand that cells are the basic unit of structure and function ...
... Cells and Microscope Test Study Guide Use your notes and handouts to help you study! Know different parts of cell and function of each part (what it does) Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cell wall Understand that cells are the basic unit of structure and function ...
Cell Analogies Worksheet
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
Homework: Respiration - Fall River Public Schools
... Cell Biologist’s Name: _________________________________ Class: 8__ Date: ______________ Mrs. Bouchard– 8th Grade Science ...
... Cell Biologist’s Name: _________________________________ Class: 8__ Date: ______________ Mrs. Bouchard– 8th Grade Science ...
An Inside Look: Lysosome
... dense spherical vacuoles. (Approx. diameter ranging up to one micrometer) They can display considerable variation in size and shape as a result of differences in the materials that have been taken up for digestion. This organelle is mainly found in animal cells but are sometimes found in plant cells ...
... dense spherical vacuoles. (Approx. diameter ranging up to one micrometer) They can display considerable variation in size and shape as a result of differences in the materials that have been taken up for digestion. This organelle is mainly found in animal cells but are sometimes found in plant cells ...
Slide 1
... – To learn characteristics of all cells – To identify cell parts – To compare and contrast various cell types• Plant and animal cells ...
... – To learn characteristics of all cells – To identify cell parts – To compare and contrast various cell types• Plant and animal cells ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.