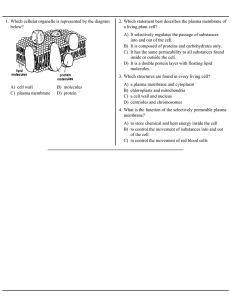
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
I1-3 Cell organelle notes
... B. Cell Theory – took 150 yrs 1. All living things composed of one or more cells 2. Cells – Basic unit of structure and function in organisms 3. Cells reproduce II. ...
... B. Cell Theory – took 150 yrs 1. All living things composed of one or more cells 2. Cells – Basic unit of structure and function in organisms 3. Cells reproduce II. ...
cells - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
... • Observes cork (plant) under microscope; – looked like thousands of tiny, empty chambers = “cells” ...
... • Observes cork (plant) under microscope; – looked like thousands of tiny, empty chambers = “cells” ...
Review Game Questions
... 5. What happens when an animal cell is dropped into a fresh water solution? _____________________________________________________________ 6. What happens when an animal cell is dropped into a salt water solution? 7. This type of particle transport requires energy from the cell and is called ________ ...
... 5. What happens when an animal cell is dropped into a fresh water solution? _____________________________________________________________ 6. What happens when an animal cell is dropped into a salt water solution? 7. This type of particle transport requires energy from the cell and is called ________ ...
Organelle Function Matching
... 3. A cell structure that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instructions that direct all the cell’s functions 4. A small grain-like structure in the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made. 5. A small-round cell structure containing chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller o ...
... 3. A cell structure that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instructions that direct all the cell’s functions 4. A small grain-like structure in the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made. 5. A small-round cell structure containing chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller o ...
Mor-ganelles - JhaveriChemBioWiki
... Cell Wall The cell wall is only found in plant cells. It is on the outside of the cell, outside the cell membrane. It gives support and structure to plant cells. *Notice- plant cells are usually rectangular because of the cell wall ...
... Cell Wall The cell wall is only found in plant cells. It is on the outside of the cell, outside the cell membrane. It gives support and structure to plant cells. *Notice- plant cells are usually rectangular because of the cell wall ...
The Organelles of Cells
... d) What would you consider to be the “POWER PLANT” of the cell? _______________________ e) What would you consider to be the “STORAGE BIN” of the cell? _______________________ f) What would you consider to be the “SOLAR PANNEL” of the cell? ______________________ ...
... d) What would you consider to be the “POWER PLANT” of the cell? _______________________ e) What would you consider to be the “STORAGE BIN” of the cell? _______________________ f) What would you consider to be the “SOLAR PANNEL” of the cell? ______________________ ...
Unit 4: Cells and Transport Short Answer Five of
... Five of the following will be chosen for the Short Answer portion of the exam. 1. What do all cells have in common? 2. How can you tell the difference between a plant and an animal cell? List at least 3 differences. ...
... Five of the following will be chosen for the Short Answer portion of the exam. 1. What do all cells have in common? 2. How can you tell the difference between a plant and an animal cell? List at least 3 differences. ...
RESPONSE OF HUMAN CANCER CELLS TO IONIZING RADIATION
... Chorna I.V., Shkandala A.Yu., second-year student Sumy State University, department of biochemistry and pharmacology Ionizing radiation remains an effective tool in cancer therapy, but considerable differences exist in the outcomes of the radiotherapeutic treatment of tumors of different histologica ...
... Chorna I.V., Shkandala A.Yu., second-year student Sumy State University, department of biochemistry and pharmacology Ionizing radiation remains an effective tool in cancer therapy, but considerable differences exist in the outcomes of the radiotherapeutic treatment of tumors of different histologica ...
Cell division is part of the cell cycle
... organisms produces one or more new organisms that are identical to itself and that live independently of it ...
... organisms produces one or more new organisms that are identical to itself and that live independently of it ...
Ch. 3 Review - Cobb Learning
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs ______ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size ...
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs ______ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size ...
Goal 2 Cells as Living Systems-- Concept 2 Types of Cells
... Goal 2 Cells as Living Systems-- Concept 2 Types of Cells Essential Questions 8. What is the proper order of steps when using a light microscope? 9. What are the two general types of cells? Describe each. 10. How are cells organized? 11. What are the differences in plant and animal cells? 12. Identi ...
... Goal 2 Cells as Living Systems-- Concept 2 Types of Cells Essential Questions 8. What is the proper order of steps when using a light microscope? 9. What are the two general types of cells? Describe each. 10. How are cells organized? 11. What are the differences in plant and animal cells? 12. Identi ...
LT2a, 1b size.
... LT2a, 1b Using scaling theory, explain why cells have an upper limit on their size. (Hint: “Surface area increases by the ______ of length while volume increases by the _____ of length.”) Equate the appropriate parts of the cell with surface area and volume to explain. ...
... LT2a, 1b Using scaling theory, explain why cells have an upper limit on their size. (Hint: “Surface area increases by the ______ of length while volume increases by the _____ of length.”) Equate the appropriate parts of the cell with surface area and volume to explain. ...
Topic 1 and 2 vocab practice - wths
... __ Macromolecule E. This is a molecule that contains both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. They are the building blocks of protein. __ Nitrogenous ...
... __ Macromolecule E. This is a molecule that contains both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. They are the building blocks of protein. __ Nitrogenous ...
Cytotoxicity tests MEDETOX EN
... The dye exclusion test is used to determine the number of viable cells present in a cell suspension. It is based on the principle that live cells possess intact cell membranes that exclude certain dyes, such as trypan blue, Eosin, or propidium, whereas dead cells do not. In this test, a cell suspens ...
... The dye exclusion test is used to determine the number of viable cells present in a cell suspension. It is based on the principle that live cells possess intact cell membranes that exclude certain dyes, such as trypan blue, Eosin, or propidium, whereas dead cells do not. In this test, a cell suspens ...
Chapter Review Part A. Vocabulary Review Assessm ent
... 4. A group of similar cells that work together to do one job ...
... 4. A group of similar cells that work together to do one job ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.