Chemicals: What`s in? What`s out?
... Mention the word chemistry in a middle level classroom and the first thing students want to know is, “Will we be blowing anything up?” Chemistry should be fun and exciting, but much preparation and skill are needed by the teacher and students in working with chemicals. Unfortunately, accidents do ha ...
... Mention the word chemistry in a middle level classroom and the first thing students want to know is, “Will we be blowing anything up?” Chemistry should be fun and exciting, but much preparation and skill are needed by the teacher and students in working with chemicals. Unfortunately, accidents do ha ...
Chemical Formulas
... that each element symbol starts with a capital letter. But be careful to not count an element twice if repeated in the formula. In HC 2 H 3 O 2 , there are only three elements, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, even though there are four capital letters. (The H symbol is repeated twice in the formula.) ...
... that each element symbol starts with a capital letter. But be careful to not count an element twice if repeated in the formula. In HC 2 H 3 O 2 , there are only three elements, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, even though there are four capital letters. (The H symbol is repeated twice in the formula.) ...
TEK 8.5D: Chemical Formulas
... that each element symbol starts with a capital letter. But be careful to not count an element twice if repeated in the formula. In HC 2 H 3 O 2 , there are only three elements, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, even though there are four capital letters. (The H symbol is repeated twice in the formula.) ...
... that each element symbol starts with a capital letter. But be careful to not count an element twice if repeated in the formula. In HC 2 H 3 O 2 , there are only three elements, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, even though there are four capital letters. (The H symbol is repeated twice in the formula.) ...
Balancing Chemical Equations Lab
... 1. Using your set of cards, replicate the chemical equation onto your desk. Record the following results into Table 1: 2. Identify the elements on the reactant side. 3. Count the number of atoms for each element. 4. Identify the elements on the product side. 5. Count the number of atoms on the produ ...
... 1. Using your set of cards, replicate the chemical equation onto your desk. Record the following results into Table 1: 2. Identify the elements on the reactant side. 3. Count the number of atoms for each element. 4. Identify the elements on the product side. 5. Count the number of atoms on the produ ...
Unit 3C Standards for Quiz
... It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structure 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements i ...
... It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structure 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements i ...
chemical reaction
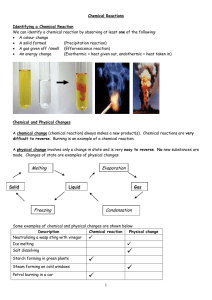
... does not change its chemical composition; ex: phase changes, size changes • Chemical change – a change in substance that results in entirely new substance with different chemical composition and properties; ex: burning, tarnishing, rusting, baking ...
... does not change its chemical composition; ex: phase changes, size changes • Chemical change – a change in substance that results in entirely new substance with different chemical composition and properties; ex: burning, tarnishing, rusting, baking ...
High School Chemistry Essential Questions
... 2. What observations about chemical systems and chemical interactions lead us to form the physical, graphical, and mathematical models that we use to represent, analyze, and communicate structure and relationships in chemical systems and chemical interactions? 3. How do we use the physical models, s ...
... 2. What observations about chemical systems and chemical interactions lead us to form the physical, graphical, and mathematical models that we use to represent, analyze, and communicate structure and relationships in chemical systems and chemical interactions? 3. How do we use the physical models, s ...
Chemistry Notes
... Separate the water in salt water from the salts Boil off the water and salts will remain Separate a mixture of gases Cool them – they will condense at different temperatures ...
... Separate the water in salt water from the salts Boil off the water and salts will remain Separate a mixture of gases Cool them – they will condense at different temperatures ...
Notes for Matter Packet- Balancing equations (PDF
... 2. Find the number of atoms for each element on the left side. Compare those against the number of the atoms of the same element on the right side. 3. Determine where to place coefficients in front of formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in o ...
... 2. Find the number of atoms for each element on the left side. Compare those against the number of the atoms of the same element on the right side. 3. Determine where to place coefficients in front of formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in o ...
Chemicals and Their Reactions
... Word vs Chemical Equations? chemical equations provide more detail such as: Chemical formulas of substances involved The ratio of substances involved State of substances involved ...
... Word vs Chemical Equations? chemical equations provide more detail such as: Chemical formulas of substances involved The ratio of substances involved State of substances involved ...
Chemical Reactions
... The reactants are separated from each other by a plus sign and the products are separated from each other by a plus sign. There should be an arrow in the middle. Examples: When sodium is mixed with water, a purple alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide is produced and hydrogen gas is evolved. Sodium ...
... The reactants are separated from each other by a plus sign and the products are separated from each other by a plus sign. There should be an arrow in the middle. Examples: When sodium is mixed with water, a purple alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide is produced and hydrogen gas is evolved. Sodium ...
Matter 1. ______ is anything that has ______ and takes up ______
... 7. Classification of Matter – matter can be classified by its physical and chemical properties. a _______________ _________________– a characteristic of a substance that can be observed without changing the substance into another substance. Examples: physical state (solid, liquid, gas) electrical an ...
... 7. Classification of Matter – matter can be classified by its physical and chemical properties. a _______________ _________________– a characteristic of a substance that can be observed without changing the substance into another substance. Examples: physical state (solid, liquid, gas) electrical an ...
Lead Compounds from Higher Plants
... Despite the fact that the PSE is basically a society of European scientists, the organizers ensured that researchers from other parts of the world, and notably from developing countries, participated at the meeting. For example, the African continent was well represented and participants were able t ...
... Despite the fact that the PSE is basically a society of European scientists, the organizers ensured that researchers from other parts of the world, and notably from developing countries, participated at the meeting. For example, the African continent was well represented and participants were able t ...
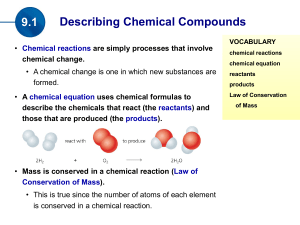
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... • Some chemical reactions are slow, some are fast. • For example a car rusting is slow; a matchstick burning is fast. • The reaction rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of reactant consumed per unit time or the amount of product formed per unit time. • It is the “speed” of the reaction. ...
... • Some chemical reactions are slow, some are fast. • For example a car rusting is slow; a matchstick burning is fast. • The reaction rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of reactant consumed per unit time or the amount of product formed per unit time. • It is the “speed” of the reaction. ...
Balancing Equations
... A. Classifying reactions • Reactions are classified into several general types B. Combination/Synthesis Reactions • Key Characteristic: 2 or more reactants 1 product • General Form: A + B AB ...
... A. Classifying reactions • Reactions are classified into several general types B. Combination/Synthesis Reactions • Key Characteristic: 2 or more reactants 1 product • General Form: A + B AB ...
How to Balance Chemical Equations
... involved are set and their formulas can not be altered. Hence, any change to the subscripts is NOT allowed. ONLY COEFFICIENTS ARE ALLOWED TO BE CHANGED!! ...
... involved are set and their formulas can not be altered. Hence, any change to the subscripts is NOT allowed. ONLY COEFFICIENTS ARE ALLOWED TO BE CHANGED!! ...
Chemical Equations & Reactions
... What is the relationship between conservation of mass and the fact that a balanced equation will always have the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of an equation? ...
... What is the relationship between conservation of mass and the fact that a balanced equation will always have the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of an equation? ...
Chemical Names and Formulas
... Copyright © 2004 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in her/his classroom. McGraw-Hill Ryerson shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. ...
... Copyright © 2004 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited. Permission to edit and reproduce this page is granted to the purchaser for use in her/his classroom. McGraw-Hill Ryerson shall not be held responsible for content if any revisions, additions, or deletions are made to this page. ...
Unit 10: Chemical Reactions
... The mole ratio between C3H8 and O2 is __1____C3H8:____5__O2. The mole ratio between C3H8 and CO2 is ___1___C3H8:__3____CO2. The mole ratio between C3H8 and H2O is ___1___C3H8:___4___H2O. The mole ratio between CO2 and O2 is __3____CO2:__5____O2. The mole ratio between H2O and CO2 is __4____H2O:___3_ ...
... The mole ratio between C3H8 and O2 is __1____C3H8:____5__O2. The mole ratio between C3H8 and CO2 is ___1___C3H8:__3____CO2. The mole ratio between C3H8 and H2O is ___1___C3H8:___4___H2O. The mole ratio between CO2 and O2 is __3____CO2:__5____O2. The mole ratio between H2O and CO2 is __4____H2O:___3_ ...
Document
... 2HCl(aq) + Cr(s) H2(g)+ CrCl2(aq) A. composition B. single-displacement C. decomposition D. double-displacement ...
... 2HCl(aq) + Cr(s) H2(g)+ CrCl2(aq) A. composition B. single-displacement C. decomposition D. double-displacement ...
1 - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... 13. Which of the substances below are mixtures, and which are pure substances? a. Gasoline Mixture b. Table sugar (sucrose) Pure Substance c. Garden soil Mixture 14. Which of the mixtures is homogeneous and which is heterogenous? a. Sweetened hot tea Homogenous b. Plastic bag filled with leaves and ...
... 13. Which of the substances below are mixtures, and which are pure substances? a. Gasoline Mixture b. Table sugar (sucrose) Pure Substance c. Garden soil Mixture 14. Which of the mixtures is homogeneous and which is heterogenous? a. Sweetened hot tea Homogenous b. Plastic bag filled with leaves and ...
13.2 Chemical Formulas
... What is a chemical formula? Chemical formulas have two important parts: chemical symbols for the elements in the compound and subscripts that tell how many atoms of each element are needed to form the compound. The chemical formula for water, H2O, tells us that a water molecule is made of the elemen ...
... What is a chemical formula? Chemical formulas have two important parts: chemical symbols for the elements in the compound and subscripts that tell how many atoms of each element are needed to form the compound. The chemical formula for water, H2O, tells us that a water molecule is made of the elemen ...
Chemical plant
A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures (or otherwise processes) chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use specialized equipment, units, and technology in the manufacturing process. Other kinds of plants, such as polymer, pharmaceutical, food, and some beverage production facilities, power plants, oil refineries or other refineries, natural gas processing and biochemical plants, water and wastewater treatment, and pollution control equipment use many technologies that have similarities to chemical plant technology such as fluid systems and chemical reactor systems. Some would consider an oil refinery or a pharmaceutical or polymer manufacturer to be effectively a chemical plant.Petrochemical plants (plants using chemicals from petroleum as a raw material or feedstock ) are usually located adjacent to an oil refinery to minimize transportation costs for the feedstocks produced by the refinery. Speciality chemical and fine chemical plants are usually much smaller and not as sensitive to location. Tools have been developed for converting a base project cost from one geographic location to another.