Löffler`s Endocarditis: First Report of Successful Mitral and
... HES can be further sub-classified as primary, secondary, or complex.4 Primary HES results from underlying stem cell, myeloid, or eosinophilic neoplasm causing clonal expansion. Secondary HES is a reactive type of HE caused by parasites or lymphomas, etc., causing an overproduction of eosinophilopo ...
... HES can be further sub-classified as primary, secondary, or complex.4 Primary HES results from underlying stem cell, myeloid, or eosinophilic neoplasm causing clonal expansion. Secondary HES is a reactive type of HE caused by parasites or lymphomas, etc., causing an overproduction of eosinophilopo ...
Heart
... • Antibiotics are continued for a long time, typically two to six weeks. • Surgical removal of the valve is necessary in patients who fail to clear microorganisms from their blood in response to antibiotic therapy, or in patients who develop cardiac failure resulting from destruction of a valve ...
... • Antibiotics are continued for a long time, typically two to six weeks. • Surgical removal of the valve is necessary in patients who fail to clear microorganisms from their blood in response to antibiotic therapy, or in patients who develop cardiac failure resulting from destruction of a valve ...
01. CVS, Atherosclerosis
... Cardiac abnormalities: chronic valvular diseases, high pressure shunts within the heart (small ventricular septal defects). Prosthetic heart valves. Intravenous drug abusers. ...
... Cardiac abnormalities: chronic valvular diseases, high pressure shunts within the heart (small ventricular septal defects). Prosthetic heart valves. Intravenous drug abusers. ...
Mouth Jewelry - Wellness Proposals
... prevalent form of body art and self-expression in today’s ...
... prevalent form of body art and self-expression in today’s ...
Pacific Coast Society of Orthodontists
... - Endothelium injury induces platelet/fibrin matrix - Bacteria seeds matrix, speeds adhesion formation Staphylococcus (31%) Streptococcus (23%) Enterococcus (10%) Unknown origin (36%) ...
... - Endothelium injury induces platelet/fibrin matrix - Bacteria seeds matrix, speeds adhesion formation Staphylococcus (31%) Streptococcus (23%) Enterococcus (10%) Unknown origin (36%) ...
Bacterial Endocarditis of Systemic Atrioventricular Valve
... with cardiac lesions which cause turbulent flow.3) Cyanotic congenital heart lesions, previous bacterial endocarditis, aortic valve disease, mitral regurgitation and uncorrected left-to-right shunt are high risk diseases for development of endocarditis.4) CCTGA with or without additional cardiac def ...
... with cardiac lesions which cause turbulent flow.3) Cyanotic congenital heart lesions, previous bacterial endocarditis, aortic valve disease, mitral regurgitation and uncorrected left-to-right shunt are high risk diseases for development of endocarditis.4) CCTGA with or without additional cardiac def ...
Traumatic Reticulitis and Heart Conditions in Cattle
... unresponsive to antibiotic therapy although temporary improvement lasting three to five days may be achieved after dexamethasone injection. Necropsy reveals cardiac enlargement and ventricular hypertrophy/dilation. The vegetative lesions are readily demonstrable on the heart valves. Treatment Treatm ...
... unresponsive to antibiotic therapy although temporary improvement lasting three to five days may be achieved after dexamethasone injection. Necropsy reveals cardiac enlargement and ventricular hypertrophy/dilation. The vegetative lesions are readily demonstrable on the heart valves. Treatment Treatm ...
SEPTIC ENDOCARDITIS IN A CARPET PYTHON (Morelia spilota)
... vasculature and evidence of atrial dysfunction. Previously noted vertebral changes were stable. The snake was unresponsive to medical management and was euthanatized 5 mo after presentation. On necropsy the heart was enlarged and an extensive thrombus occupied all chambers of the heart, associated c ...
... vasculature and evidence of atrial dysfunction. Previously noted vertebral changes were stable. The snake was unresponsive to medical management and was euthanatized 5 mo after presentation. On necropsy the heart was enlarged and an extensive thrombus occupied all chambers of the heart, associated c ...
Module 5 – Pediatric Cardiac Disorders
... Fever, which often is higher than 101.3 F, and lasts one to two weeks ...
... Fever, which often is higher than 101.3 F, and lasts one to two weeks ...
Week 10 Activity INUR3306
... with rheumatogenic group A streptococci. Damaged valves and endocardium contribute to the development of infective endocarditis. Specifically, the damaged part of a heart valve forms a local blood clot, a condition known as non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE). Inflammation and muscle damage ...
... with rheumatogenic group A streptococci. Damaged valves and endocardium contribute to the development of infective endocarditis. Specifically, the damaged part of a heart valve forms a local blood clot, a condition known as non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE). Inflammation and muscle damage ...
valve replacement for acute left heart endocarditis
... degenerescence (20%) of the aortic and mitral valves. One patient needed valve replacement for recurrent endocarditis on a native valve without any primitive underlying lesion. In the CHD group, 3 bicuspid aortic valves, one hypertrophic cardiomyopathy [HCM], one ventricular septal defect [VSD] asso ...
... degenerescence (20%) of the aortic and mitral valves. One patient needed valve replacement for recurrent endocarditis on a native valve without any primitive underlying lesion. In the CHD group, 3 bicuspid aortic valves, one hypertrophic cardiomyopathy [HCM], one ventricular septal defect [VSD] asso ...
Pediatric Cardiac Conditions
... Surgical valvotomy if the closed procedure does not work – often done when patient is older when severe calcium deposits further obstruct the valve. Recurrent valve obstruction is a complication and if valve replacement is done too early the child may outgrow the valve. ...
... Surgical valvotomy if the closed procedure does not work – often done when patient is older when severe calcium deposits further obstruct the valve. Recurrent valve obstruction is a complication and if valve replacement is done too early the child may outgrow the valve. ...
Blood Velocity and Endocarditis
... surface adjacent to the line of closure. Considerable evidence may be cited to demonstrate that the process is associated with an insufficiency rather than a stenosis. Endocarditis occurs fairly commonly in valves that show no significant stenosis; especially is this so in patients after only a few ...
... surface adjacent to the line of closure. Considerable evidence may be cited to demonstrate that the process is associated with an insufficiency rather than a stenosis. Endocarditis occurs fairly commonly in valves that show no significant stenosis; especially is this so in patients after only a few ...
Systemic lupus erythematosus, eosinophilia and LoÈffler's endocarditis. An unusual association CASE STUDY
... Cardiac involvement or LoÈffler's endocarditis is frequently seen in the hypereosinophilic syndrome [3], an idiopathic syndrome characterized by: 1) a persistent elevation in the total eosinophilic count (>1,500.mm-3) for over 6 months or death within 6 months; 2) associated multiorgan damage; and 3 ...
... Cardiac involvement or LoÈffler's endocarditis is frequently seen in the hypereosinophilic syndrome [3], an idiopathic syndrome characterized by: 1) a persistent elevation in the total eosinophilic count (>1,500.mm-3) for over 6 months or death within 6 months; 2) associated multiorgan damage; and 3 ...
After load
... Ballon valvulopasty ◦ Symptoms on exercise/ high resting pressure gradient(>64mmHg) ◦ High risk of significant valvular insufficiency ...
... Ballon valvulopasty ◦ Symptoms on exercise/ high resting pressure gradient(>64mmHg) ◦ High risk of significant valvular insufficiency ...
Case 5 - Scand
... developed NBTE. Serial blood cultures withdrawn after inoculation were positive in animals with IE, and negative in all other animals. Conclusion: S. aureus endocarditis was successfully induced in pigs with an indwelling cardiac catheter after intravenous inoculation of 107 cfu/kg of S. aureus stra ...
... developed NBTE. Serial blood cultures withdrawn after inoculation were positive in animals with IE, and negative in all other animals. Conclusion: S. aureus endocarditis was successfully induced in pigs with an indwelling cardiac catheter after intravenous inoculation of 107 cfu/kg of S. aureus stra ...
Infective Endocarditis - Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
... exclusively for the Yorkshire Heart Centre at Leeds General Infirmary, St James’s hospital and its units within The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust. We were founded in 1989 by a small number of heart patients wishing to return something for the excellent care received. From a small beginning, we ...
... exclusively for the Yorkshire Heart Centre at Leeds General Infirmary, St James’s hospital and its units within The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust. We were founded in 1989 by a small number of heart patients wishing to return something for the excellent care received. From a small beginning, we ...
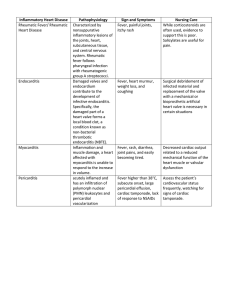
Rheumatic Fever and Heart Disease
... • It is a hypersensitivity reaction induced by group A streptococci. • Antibodies directed against the M proteins of group A streptococci cross-react with normal proteins in the ...
... • It is a hypersensitivity reaction induced by group A streptococci. • Antibodies directed against the M proteins of group A streptococci cross-react with normal proteins in the ...
MED SURGE CARDIAC 4, VALVE DISORDERS
... edges of mitral valve leaflets do not close completely during systole because leaflets and chordae tendineae have thickened and fibrosed, resulting in their contraction. The most common causes of mitral valve regurgitation in developed countries are degenerative changes of the mitral valve (e.g., mi ...
... edges of mitral valve leaflets do not close completely during systole because leaflets and chordae tendineae have thickened and fibrosed, resulting in their contraction. The most common causes of mitral valve regurgitation in developed countries are degenerative changes of the mitral valve (e.g., mi ...
Rheumatic heart disease
... • Increased heart rate –decreased transvalvular gradient ----increased LAP • Lv diastolic pressure in normal in ms • Co is normal at rest ---at exercise –decreased ...
... • Increased heart rate –decreased transvalvular gradient ----increased LAP • Lv diastolic pressure in normal in ms • Co is normal at rest ---at exercise –decreased ...
Food Animal Cardiology
... QRS complex of a PVC is premature, bizarre, prolonged & of larger amplitude Unifocal or multifocal Treat underlying condition or lidocaine ...
... QRS complex of a PVC is premature, bizarre, prolonged & of larger amplitude Unifocal or multifocal Treat underlying condition or lidocaine ...
Journal of the Hoffman - Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
... spectrum of endocarditis, the increased frequency of intravenous drug abusers, the increased prevalence of prosthetic valve endocarditis and older age groups, more recent studies demonstrate less significant differences in the rate of complications among the types of infective organisms with the exc ...
... spectrum of endocarditis, the increased frequency of intravenous drug abusers, the increased prevalence of prosthetic valve endocarditis and older age groups, more recent studies demonstrate less significant differences in the rate of complications among the types of infective organisms with the exc ...
Aortic Regurgitation
... Disclaimer: This article is for information only and should not be used for the diagnosis or treatment of medical conditions. EMIS has used all reasonable care in compiling the information but makes no warranty as to its accuracy. Consult a doctor or other healthcare professional for diagnosis and t ...
... Disclaimer: This article is for information only and should not be used for the diagnosis or treatment of medical conditions. EMIS has used all reasonable care in compiling the information but makes no warranty as to its accuracy. Consult a doctor or other healthcare professional for diagnosis and t ...
Infective endocarditis

Infective endocarditis is a form of endocarditis. It is an inflammation of the inner tissues of the heart, the endocardium (such as its valves). It is caused by infectious agents, or pathogens, which are usually bacterial but other organisms can also be responsible.The valves of the heart do not receive any dedicated blood supply. As a result, defensive immune system mechanisms (such as white blood cells) cannot directly reach the valves via the bloodstream. If an organism (such as bacteria) attaches to a valve surface and forms a vegetation, the host's immune response is blunted. The lack of blood supply to the valves also has implications for treatment, since drugs also have difficulty reaching the infected area.Normally, blood flows smoothly through these valves. If they have been damaged - from rheumatic fever, for example - the risk of bacterial attachment is increased.