When Symmetry Breaks Down - School of Natural Sciences
... The one facet of the standard model that we have not yet been able to test experimentally is perhaps the most basic: how is the symmetry broken? However,we have a pretty clear idea of where such information can be found. Just as one can use atomic masses and binding energies to estimate the melting ...
... The one facet of the standard model that we have not yet been able to test experimentally is perhaps the most basic: how is the symmetry broken? However,we have a pretty clear idea of where such information can be found. Just as one can use atomic masses and binding energies to estimate the melting ...
Elements of a Physics Case for HE LHC
... Scalar superpartners are unlikely to be directly produced at LHC in this framework. In general, scalars are heavier than fermion superpartners across many variants of susy model building. Generic prospect. Need high energy to produce directly these heavy squarks. Perhaps best bet is gaugino + squark ...
... Scalar superpartners are unlikely to be directly produced at LHC in this framework. In general, scalars are heavier than fermion superpartners across many variants of susy model building. Generic prospect. Need high energy to produce directly these heavy squarks. Perhaps best bet is gaugino + squark ...
The Royal Society of Edinburgh The Large Hadron Collider – What It
... Greenwood Conference Centre, Dreghorn, Irvine Report by Kate Kennedy There are many things we do not know about the Universe, including what the nature is of the dark matter of which most of it is made; why it seems to be accelerating apart; why there is any matter left in it at all anyway; and, unt ...
... Greenwood Conference Centre, Dreghorn, Irvine Report by Kate Kennedy There are many things we do not know about the Universe, including what the nature is of the dark matter of which most of it is made; why it seems to be accelerating apart; why there is any matter left in it at all anyway; and, unt ...
PHYSICS COLLOQUIUM “What Lurks in the Deep? LHC Run 2 and
... Binghamton University Department of Physics, Applied Physics and Astronomy ...
... Binghamton University Department of Physics, Applied Physics and Astronomy ...
Phenomenology Beyond the Standard Model
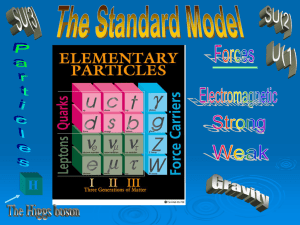
... Summary of the Standard Model • Particles and SU(3) × SU(2) × U(1) quantum numbers: ...
... Summary of the Standard Model • Particles and SU(3) × SU(2) × U(1) quantum numbers: ...
history of particle physics (PowerPoint 13.93MB)
... Particle and Nuclear Physics are the studies to answer this question ...
... Particle and Nuclear Physics are the studies to answer this question ...
The Higgs Boson and Fermion Masses
... • Large number of free parameters • Still unclear mechanism of EW symmetry breaking • CP-violation is not understood • The origin of the mass spectrum in unclear • Flavour mixing and the number of generations is arbitrary • Formal unification of strong and electroweak interactions The way beyond the ...
... • Large number of free parameters • Still unclear mechanism of EW symmetry breaking • CP-violation is not understood • The origin of the mass spectrum in unclear • Flavour mixing and the number of generations is arbitrary • Formal unification of strong and electroweak interactions The way beyond the ...
Muon Lifetime
... Fermi created a theory of beta decay [weak interactions] in 1933 after Pauli’s neutrino hypothesis was publicly presented. It was modified in the later 1950s to include parity violation and works quite well at low energies. It assumes that weak interactions happen at 4 fermion vertex with an interac ...
... Fermi created a theory of beta decay [weak interactions] in 1933 after Pauli’s neutrino hypothesis was publicly presented. It was modified in the later 1950s to include parity violation and works quite well at low energies. It assumes that weak interactions happen at 4 fermion vertex with an interac ...
View Commentary - Journal Club for Condensed Matter Physics
... of the Higgs mode are associated with quantum phase transitions which are fully described by relativistic Lagrangians like those in (1) in both the ordered and disordered phases, and at the quantum critical point between them. Ruegg et al. (Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 205701 (2008)) performed neutron scat ...
... of the Higgs mode are associated with quantum phase transitions which are fully described by relativistic Lagrangians like those in (1) in both the ordered and disordered phases, and at the quantum critical point between them. Ruegg et al. (Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 205701 (2008)) performed neutron scat ...
Slides - uchicago hep
... transparent. They are massless and move with the speed of light. Other particles slow down in the Higgs field, for example matter fields (quarks and leptons), but also the weak force carriers. This is the reason why the weak force is short-ranged! ...
... transparent. They are massless and move with the speed of light. Other particles slow down in the Higgs field, for example matter fields (quarks and leptons), but also the weak force carriers. This is the reason why the weak force is short-ranged! ...
The Standard Model and Beyond
... The simplest explanation would be that dark matter consists of ordinary gas (protons, neutrons, electrons) that, for some reason, did not collapse into stars and remained ...
... The simplest explanation would be that dark matter consists of ordinary gas (protons, neutrons, electrons) that, for some reason, did not collapse into stars and remained ...
Beyond the Standard Model at the LHC and Beyond
... What is the origin of matter? LHC Run 2 What is the dark matter that fills the Universe? LHC Run 2 How does the Universe evolve? Why is the Universe so big and old? LHC Run 2 What is the future of the Universe? LHC Run 2 Our job is to ask - and answer - these questions ...
... What is the origin of matter? LHC Run 2 What is the dark matter that fills the Universe? LHC Run 2 How does the Universe evolve? Why is the Universe so big and old? LHC Run 2 What is the future of the Universe? LHC Run 2 Our job is to ask - and answer - these questions ...
The LHC Experiment at CERN
... account interaction of particles with Higgs. In vacuum, photon has zero mass and velocity = c. But in glass velocity < c photon has an effective mass! This is the effect of photon interacting with EM field of matter. Higgs is a quantum field permeating the universe. In analogy, particles acquire m ...
... account interaction of particles with Higgs. In vacuum, photon has zero mass and velocity = c. But in glass velocity < c photon has an effective mass! This is the effect of photon interacting with EM field of matter. Higgs is a quantum field permeating the universe. In analogy, particles acquire m ...
Slide sem título - Instituto de Física / UFRJ
... Higgs summary • Higgs potential is responsible for electroweak symmetry breaking ...
... Higgs summary • Higgs potential is responsible for electroweak symmetry breaking ...
Concepts in Theoretical Physics
... Why do the quarks stick together in this way? It s because the quarks are the only particles to feel the strong nuclear force. To understand this better, we next need to look at the forces. ...
... Why do the quarks stick together in this way? It s because the quarks are the only particles to feel the strong nuclear force. To understand this better, we next need to look at the forces. ...
Proposal of a topic for the PhD schools in Particle Physics Name
... Search with the ATLAS detector for Higgs boson and new physics in high energy proton-proton collisions at the LHC, CERN, Genève. Details of the task : The existence of the Higgs boson is one of the corner stone of the Standard Model (SM) in particle physics not yet confirmed but with already possibl ...
... Search with the ATLAS detector for Higgs boson and new physics in high energy proton-proton collisions at the LHC, CERN, Genève. Details of the task : The existence of the Higgs boson is one of the corner stone of the Standard Model (SM) in particle physics not yet confirmed but with already possibl ...
What is the Higgs? - University of Manchester
... E.g. At Fermilab the collision of a single proton and antiproton is sufficiently energetic to produce over 2000 protons. At CERN, the electron and positron collided with sufficient energy to produce over 200 protons (electrons are more than 1000 times lighter than a proton!) ...
... E.g. At Fermilab the collision of a single proton and antiproton is sufficiently energetic to produce over 2000 protons. At CERN, the electron and positron collided with sufficient energy to produce over 200 protons (electrons are more than 1000 times lighter than a proton!) ...
2009S-FindingHiggs
... •Two up quarks and one down quark are the proton’s “valence quarks” •Gluons traveling between these quarks at the speed of light •Give rise to “sea quarks” that diverge from the gluons, then merge back into gluons ...
... •Two up quarks and one down quark are the proton’s “valence quarks” •Gluons traveling between these quarks at the speed of light •Give rise to “sea quarks” that diverge from the gluons, then merge back into gluons ...
Particle physics today
... Standard Model (SM): successful theory of strong (QCD), weak and electromagnetic (EW) elementary interactions ...
... Standard Model (SM): successful theory of strong (QCD), weak and electromagnetic (EW) elementary interactions ...
PH3520 (Particle Physics) Course Information
... concentrate on broader concepts. That is, we will usually not derive in detail but rather only motivate how theory leads to a certain prediction for the outcome of an experiment. We will, however, compare the prediction with experimental results and see what this implies. The course is intended to p ...
... concentrate on broader concepts. That is, we will usually not derive in detail but rather only motivate how theory leads to a certain prediction for the outcome of an experiment. We will, however, compare the prediction with experimental results and see what this implies. The course is intended to p ...
Physics 120 Homework Set #1 (due Sunday
... interaction energy the strengths of the force get much closer but they do not converge exactly at the same point together. Supersymmetry allows for a perfect matching of the strengths of the strong, weak and electromagnetic force at very high energy, or when the Universe was very hot in the GUT era. ...
... interaction energy the strengths of the force get much closer but they do not converge exactly at the same point together. Supersymmetry allows for a perfect matching of the strengths of the strong, weak and electromagnetic force at very high energy, or when the Universe was very hot in the GUT era. ...