Cells and Cell Organelle Test Review Sheet
... 10. Which molecules stores and releases energy? 11. Which molecules is the most important molecule in our body? 12. Basic building block is an amino acid. 13. nucleotide-DNA 14. surrounds all living cells 15. What is differentiation? 16. name the three different types of microscopes 17. Be able to l ...
... 10. Which molecules stores and releases energy? 11. Which molecules is the most important molecule in our body? 12. Basic building block is an amino acid. 13. nucleotide-DNA 14. surrounds all living cells 15. What is differentiation? 16. name the three different types of microscopes 17. Be able to l ...
A plant that bends toward to the light is
... c. 10 d. 450 _____ 15. The part of the microscope you look into is called the: a. objective lens b. eyepiece c. stage d. body _____ 16. These are the POWER HOUSES of the cell where energy is released. a. Chloroplasts b. Nucleus c. Lysosomes d. Mitochondria _____ 17. The jelly-like substance composin ...
... c. 10 d. 450 _____ 15. The part of the microscope you look into is called the: a. objective lens b. eyepiece c. stage d. body _____ 16. These are the POWER HOUSES of the cell where energy is released. a. Chloroplasts b. Nucleus c. Lysosomes d. Mitochondria _____ 17. The jelly-like substance composin ...
Day 5, Cell Unit Test
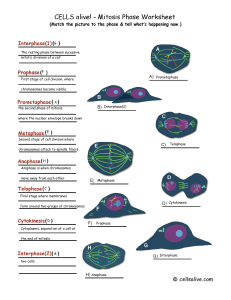
... What phase of mitosis is depicted in the picture above? A. Prophase B. Anaphase C. Metaphase D. Telophase What organelle is the red arrow pointing to in the picture above? A. Cell membrane B. Centriole C. Centromere D. Spindle fiber The hereditary material found in the cell is called what? A. DNA B. ...
... What phase of mitosis is depicted in the picture above? A. Prophase B. Anaphase C. Metaphase D. Telophase What organelle is the red arrow pointing to in the picture above? A. Cell membrane B. Centriole C. Centromere D. Spindle fiber The hereditary material found in the cell is called what? A. DNA B. ...
Notes
... are filled with diffuse chromatin or euchromatin .There are two sex chromosomes designated X chromosome and Y chromosome. Cells from male animals have one X and one Y chromosome, whereas cells from females have a pair of X chromosomes. ...
... are filled with diffuse chromatin or euchromatin .There are two sex chromosomes designated X chromosome and Y chromosome. Cells from male animals have one X and one Y chromosome, whereas cells from females have a pair of X chromosomes. ...
Poor Primitive Prokaryotes
... microscopes, have allowed scientists to study the structure of living cells in increasing detail. In doing so, it was discovered that there are two basic kinds of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or any internal membrane-bound structures. Within these cells, ...
... microscopes, have allowed scientists to study the structure of living cells in increasing detail. In doing so, it was discovered that there are two basic kinds of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or any internal membrane-bound structures. Within these cells, ...
Cell Structure
... proteins stick to the surface of the lipid bilayer, others are free to move around within the bilayer some act as channels through which molecules can pass others act like small pumps, actively pushing molecules from one side of the membrane to the other ...
... proteins stick to the surface of the lipid bilayer, others are free to move around within the bilayer some act as channels through which molecules can pass others act like small pumps, actively pushing molecules from one side of the membrane to the other ...
Notes Chapter 3
... Isotonic Solution = conc of solute particles is the same inside and outside the cell FILTRATION – molecules are forced through a membrane by hydrostatic pressure, Kidneys ACTIVE TRANSPORT – molecules are moved against the concentration gradient. This requires the use of cellular energy, also usually ...
... Isotonic Solution = conc of solute particles is the same inside and outside the cell FILTRATION – molecules are forced through a membrane by hydrostatic pressure, Kidneys ACTIVE TRANSPORT – molecules are moved against the concentration gradient. This requires the use of cellular energy, also usually ...
Chapter 7 Test Review Guide
... 7. List the major differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 8. List the major differences between plant and animal cells. 9. Know the name, location, and function of the following organelles: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nuclear envelope, nuclear pore, nucleolus, vacuole, vesicle, lysoso ...
... 7. List the major differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 8. List the major differences between plant and animal cells. 9. Know the name, location, and function of the following organelles: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nuclear envelope, nuclear pore, nucleolus, vacuole, vesicle, lysoso ...
7.3 Structures and Organelles
... microtubules (long hollow tubes) - act as tracks for organelle movement...also help in cell division microfilaments (tiny threads) - enable cells to move, muscle contraction ...
... microtubules (long hollow tubes) - act as tracks for organelle movement...also help in cell division microfilaments (tiny threads) - enable cells to move, muscle contraction ...
The Cell - Biology Mad
... A chromosome is a ‘condensed chromatin’ thread only visible during mitosis and meiosis. Haploid nuclei (n) have one set of chromosomes i.e. one of each kind of chromosome. Diploid nuclei (2n) have two sets of chromosomes i.e. two of each chromosome. The nuclei of human somatic (= body) cells are dip ...
... A chromosome is a ‘condensed chromatin’ thread only visible during mitosis and meiosis. Haploid nuclei (n) have one set of chromosomes i.e. one of each kind of chromosome. Diploid nuclei (2n) have two sets of chromosomes i.e. two of each chromosome. The nuclei of human somatic (= body) cells are dip ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... I package proteins And other things as well ER I’m full of holes Flexible and thin I control what gets out As well as what comes in Cell Membrane Proteins are made here Even though I’m quite small You can find me in the cytoplasm Or attached to the ER’s wall Ribosomes I’ve been called the storage ta ...
... I package proteins And other things as well ER I’m full of holes Flexible and thin I control what gets out As well as what comes in Cell Membrane Proteins are made here Even though I’m quite small You can find me in the cytoplasm Or attached to the ER’s wall Ribosomes I’ve been called the storage ta ...
Overview of Cell Structure
... Flagella- helps the cell move by using contractile proteins to spin it in a corkscrew motion. Can have one or more and the human sperm cell is an example that uses a flagellum for propulsion. Cilia- shorter hair like structures that are only found in animal cells and have contractile proteins th ...
... Flagella- helps the cell move by using contractile proteins to spin it in a corkscrew motion. Can have one or more and the human sperm cell is an example that uses a flagellum for propulsion. Cilia- shorter hair like structures that are only found in animal cells and have contractile proteins th ...
The work of Schleiden and Schwann can be summarized by saying
... Which organelles help provide cells with energy? a. b. c. d. ...
... Which organelles help provide cells with energy? a. b. c. d. ...
Cells - sandsbiochem
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
Modified Ch. 6 PPT Chou (1)
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY - Eastern Mediterranean University
... – Attach cells to underlying basal lamina – Labile structures associated with actin filaments inside the cell – Play an important role in cell movement ...
... – Attach cells to underlying basal lamina – Labile structures associated with actin filaments inside the cell – Play an important role in cell movement ...
Modification of Genes and Proteins - sharonap-cellrepro-p3
... Cellular response to double stranded RNA (dsRNA) When a cell comes in contact with dsRNA, it is chopped up into smaller segments and then used to identify and destroy any RNA produced by the dsRNA ...
... Cellular response to double stranded RNA (dsRNA) When a cell comes in contact with dsRNA, it is chopped up into smaller segments and then used to identify and destroy any RNA produced by the dsRNA ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.