Review of Cell Parts and Function
... What does all life have in common? (Modern Cell Theory) 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the base unit of all functions and ...
... What does all life have in common? (Modern Cell Theory) 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the base unit of all functions and ...
BSc.-I Medical - DAV College Jalandhar
... 1. Endoplasmic reticulum is double membrane bound cell organelle. 2. It contains 3 main components like cisternae, vesicles and tubules. 3. ER is of two types i.e., rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). 4. RER is bound by ribosomes. Golgi body 1. It is an importan ...
... 1. Endoplasmic reticulum is double membrane bound cell organelle. 2. It contains 3 main components like cisternae, vesicles and tubules. 3. ER is of two types i.e., rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). 4. RER is bound by ribosomes. Golgi body 1. It is an importan ...
Ch42
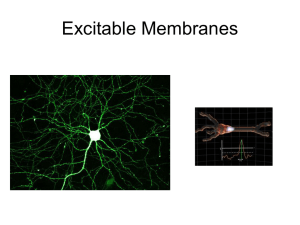
... outside of the cell. The role of the sodium-potassium pump Na+/K+-ATPase transports three sodium ions out and two potassium ions in. this activity maintains the resting potential by restoring the potassium ions that leak out of the neuron. Propagation of the action potential. The action potential st ...
... outside of the cell. The role of the sodium-potassium pump Na+/K+-ATPase transports three sodium ions out and two potassium ions in. this activity maintains the resting potential by restoring the potassium ions that leak out of the neuron. Propagation of the action potential. The action potential st ...
3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life.
... Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. • All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. – All cells are enclosed cell membrane by a membrane. – All cells are filled with cytoplasm. ...
... Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. • All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. – All cells are enclosed cell membrane by a membrane. – All cells are filled with cytoplasm. ...
bio_ch03
... Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. • All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. – All cells are enclosed cell membrane by a membrane. – All cells are filled with cytoplasm. ...
... Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. • All cells share certain characteristics. – Cells tend to be microscopic. – All cells are enclosed cell membrane by a membrane. – All cells are filled with cytoplasm. ...
File
... Lipids are a varied group of compounds made from C, H, and O. Lipids are insoluble in water because they have a high proportion of nonpolar C-H bonds. Fats consist of complex polymers of fatty acids attached to glycerol. - Many lipids exist as triglycerides, three fatty acids connected to a 3-carbon ...
... Lipids are a varied group of compounds made from C, H, and O. Lipids are insoluble in water because they have a high proportion of nonpolar C-H bonds. Fats consist of complex polymers of fatty acids attached to glycerol. - Many lipids exist as triglycerides, three fatty acids connected to a 3-carbon ...
cell membranes
... • Contact between cell and environment • Keeps useful materials inside and harmful stuff outside • Allows transport, communication in both directions ...
... • Contact between cell and environment • Keeps useful materials inside and harmful stuff outside • Allows transport, communication in both directions ...
The Basic Unit of Life
... the slice should be made from the side of the cork, not its top or bottom. The slice must be tissue paper thin. Shavings of cork are ideal size. Caution: Slice away from your fingers, not toward them, to avoid cuts. ...
... the slice should be made from the side of the cork, not its top or bottom. The slice must be tissue paper thin. Shavings of cork are ideal size. Caution: Slice away from your fingers, not toward them, to avoid cuts. ...
02_Classification and functions of simple and complex proteins
... strong fibers. They are water-insoluble and generally have structural functions within the human body. • А globular protein is а protein whose overall shape is roughly spherical or globular. Globular proteins either dissolve in water or form stable suspensions in water, which allows them to travel t ...
... strong fibers. They are water-insoluble and generally have structural functions within the human body. • А globular protein is а protein whose overall shape is roughly spherical or globular. Globular proteins either dissolve in water or form stable suspensions in water, which allows them to travel t ...
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO DET MATEMATISK
... 2) Describe the different mechanisms for reducing the cytosolic Ca2+-concentration back to normal after a transient elevation. When comparing the various mechanisms, Ca2+-affinity and transport (or sequestering) capacity should be emphasized. 3) What physiological problems can we expect that coral r ...
... 2) Describe the different mechanisms for reducing the cytosolic Ca2+-concentration back to normal after a transient elevation. When comparing the various mechanisms, Ca2+-affinity and transport (or sequestering) capacity should be emphasized. 3) What physiological problems can we expect that coral r ...
chapter39 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... 4. There is then an increase in turgor pressure that makes cell expansion possible. Hager and colleagues found that cells treated with addition IAA increased the number of proton pumps by 80% relative to untreated control cells. They also found that the acidity of the of the cell wall changed from a ...
... 4. There is then an increase in turgor pressure that makes cell expansion possible. Hager and colleagues found that cells treated with addition IAA increased the number of proton pumps by 80% relative to untreated control cells. They also found that the acidity of the of the cell wall changed from a ...
3.2 Cell Organelles Cells have an internal structure.
... processing proteins. • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
... processing proteins. • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
Warm Up (5 minutes)
... (solvent) and substances that are dissolved in water (solutes) In other words, they are located in solutions There are 3 types of solutions in which cells can ...
... (solvent) and substances that are dissolved in water (solutes) In other words, they are located in solutions There are 3 types of solutions in which cells can ...
Biology of Fungi, Lecture 6: Fungal Nutrition
... H+ ions are released via ATPase (ion pump) H+ ions flow into the cell in concert with nutrient through membrane proteins (symporters) ...
... H+ ions are released via ATPase (ion pump) H+ ions flow into the cell in concert with nutrient through membrane proteins (symporters) ...
Lesson Overview
... material can also be actively transported across the cell membrane by processes known as endocytosis and exocytosis. The transport of these larger materials sometimes involves changes in the shape of the cell membrane. ...
... material can also be actively transported across the cell membrane by processes known as endocytosis and exocytosis. The transport of these larger materials sometimes involves changes in the shape of the cell membrane. ...
General Principles of Pathophysiology Definition of basic terms
... be able to derive its pathogenesis, or the development of symptoms An understanding of the disorder in these aspect should lead one to specific therapeutic strategies and measures, and to prognostic conclusions ...
... be able to derive its pathogenesis, or the development of symptoms An understanding of the disorder in these aspect should lead one to specific therapeutic strategies and measures, and to prognostic conclusions ...
Escherichia coli
... Due to hydrophobic and amphiphilic nature Less than 1% of high resolution 3D structures known ...
... Due to hydrophobic and amphiphilic nature Less than 1% of high resolution 3D structures known ...
Cells
... • Composed of double layer of phospholipids and proteins • Surrounds outside of ALL cells • Controls what enters or leaves the cell ...
... • Composed of double layer of phospholipids and proteins • Surrounds outside of ALL cells • Controls what enters or leaves the cell ...
- Triumph Learning
... All organisms share a common feature—the cell. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all organisms. This fact is not obvious, because cells are too small to be seen with the unaided eye. The discovery of the cell, its structure, and its function came about through the work of many ...
... All organisms share a common feature—the cell. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all organisms. This fact is not obvious, because cells are too small to be seen with the unaided eye. The discovery of the cell, its structure, and its function came about through the work of many ...
Chapter 10 Cell Divison
... Eventually fuse into one thin vesicle extending across the mother cell The membranes of the cell plate become the plasma membrane between the daughter cells - Contents of vesicles become the middle lamella between the two daughter cells - Daughter cells later secrete primary cell walls on opposite ...
... Eventually fuse into one thin vesicle extending across the mother cell The membranes of the cell plate become the plasma membrane between the daughter cells - Contents of vesicles become the middle lamella between the two daughter cells - Daughter cells later secrete primary cell walls on opposite ...
Chapter 9
... 1. Each duplicated chromosome (consisting of two sister chromatids) condenses from thread-like form to rod-like form 2. Nuclear envelope and nucleolus disappear 3. Centrioles form and move to opposite ends of the cell and give rise to spindle fibers Spindle – football shaped framework of ...
... 1. Each duplicated chromosome (consisting of two sister chromatids) condenses from thread-like form to rod-like form 2. Nuclear envelope and nucleolus disappear 3. Centrioles form and move to opposite ends of the cell and give rise to spindle fibers Spindle – football shaped framework of ...
ppt
... • Component of cell membranes (bilayer) • 2 fatty acids & phosphate group • Amphipathic behavior in water ...
... • Component of cell membranes (bilayer) • 2 fatty acids & phosphate group • Amphipathic behavior in water ...