Simulation of Glucose Diffusion in a Cylindrical Cell
... until the molecules are equally distributed, that is, their concentration is equal throughout the area that contains them. At this point, the molecules continue to move and collide, but their concentration remains the same throughout the area of containment. Diffusion is an example of passive transp ...
... until the molecules are equally distributed, that is, their concentration is equal throughout the area that contains them. At this point, the molecules continue to move and collide, but their concentration remains the same throughout the area of containment. Diffusion is an example of passive transp ...
handout
... Understand how cell cycle is regulated in yeast and multicellular organisms Cancer as a result of deregulated cell proliferation: Beneath the complexity of every cancer lies a limited number of 'critical' events that have propelled the tumour cell and its progeny into uncontrolled expansion and inva ...
... Understand how cell cycle is regulated in yeast and multicellular organisms Cancer as a result of deregulated cell proliferation: Beneath the complexity of every cancer lies a limited number of 'critical' events that have propelled the tumour cell and its progeny into uncontrolled expansion and inva ...
Chapter 11: Cell Communication 10/7/2015
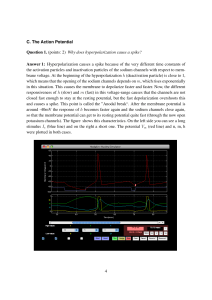
... Many ion channels are gated, i.e., they contain a “gate” which can block the channel. By default, the gate may be closed (or open) only to open (or close) when a soluble signaling molecule is bound to the channel. ...
... Many ion channels are gated, i.e., they contain a “gate” which can block the channel. By default, the gate may be closed (or open) only to open (or close) when a soluble signaling molecule is bound to the channel. ...
Definition Assignment
... (Shrratt, 1990). The cristae are very important structures as they help increase the surface area inside the mitochondria. This increased surface area provides more space for the required chemical reactions to take place (Shrratt, 1990). This essentially parallels the significance of microvilli (mem ...
... (Shrratt, 1990). The cristae are very important structures as they help increase the surface area inside the mitochondria. This increased surface area provides more space for the required chemical reactions to take place (Shrratt, 1990). This essentially parallels the significance of microvilli (mem ...
Tour of Cell Organelles
... build proteins structural proteins (muscle fibers, hair, skin, claws) enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) signals (hormones) & receptors ...
... build proteins structural proteins (muscle fibers, hair, skin, claws) enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) signals (hormones) & receptors ...
Anatomical Organization in Multicellular Organisms is Based on Cell
... • The peptidoglycan layer is substantially thicker in Gram-positive bacteria (20 to 80 nanometers) than in Gram-negative bacteria (7 to 8 nanometers), with the attachment of the S-layer. • Peptidoglycan forms around 90% of the dry weight of Gram-positive bacteria but only 10% of Gramnegative strain ...
... • The peptidoglycan layer is substantially thicker in Gram-positive bacteria (20 to 80 nanometers) than in Gram-negative bacteria (7 to 8 nanometers), with the attachment of the S-layer. • Peptidoglycan forms around 90% of the dry weight of Gram-positive bacteria but only 10% of Gramnegative strain ...
Protein Synthesis: Comprehesive Review PowerPoint Slides
... sequence of amino acids – occur mainly in cytosol // but two different locations for different usage • on surface of rough ER and nuclear envelope (proteins for export) • free rRNA in cytoplasm (proteins for cell use) – consists of two granular subunits, large and small rRNA subunits // each made of ...
... sequence of amino acids – occur mainly in cytosol // but two different locations for different usage • on surface of rough ER and nuclear envelope (proteins for export) • free rRNA in cytoplasm (proteins for cell use) – consists of two granular subunits, large and small rRNA subunits // each made of ...
C. Introduction to Multicellularity
... termites, can digest cellulose with the help of symbiotic micro-organisms that live in their guts. Humans can digest cellulose to some extent,[6][7] however it is often referred to as 'dietary fiber' or 'roughage' (e.g. outer shell of maize) and acts as a hydrophilic bulking agent for feces. ...
... termites, can digest cellulose with the help of symbiotic micro-organisms that live in their guts. Humans can digest cellulose to some extent,[6][7] however it is often referred to as 'dietary fiber' or 'roughage' (e.g. outer shell of maize) and acts as a hydrophilic bulking agent for feces. ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology
... Receptor (Gustatory or Taste) cells – contain gustatory hairs that extend through surface Basal cells - stem cells that divide giving rise to new gustatory cells Supporting ...
... Receptor (Gustatory or Taste) cells – contain gustatory hairs that extend through surface Basal cells - stem cells that divide giving rise to new gustatory cells Supporting ...
Introduction to Hormone Signalling Receptors and signals theme
... Nature Chem Biol 2:175 (on Weblearn) ...
... Nature Chem Biol 2:175 (on Weblearn) ...
Cell Lab
... All organisms are composed of cells, whether they exist as single cells, colonies of cells, or in multicellular form. Cells are usually very small, and for this reason, a thorough understanding of subcellular structure and function has been possible only through advances in electron microscopy and m ...
... All organisms are composed of cells, whether they exist as single cells, colonies of cells, or in multicellular form. Cells are usually very small, and for this reason, a thorough understanding of subcellular structure and function has been possible only through advances in electron microscopy and m ...
01 Chapter 7 Reading Guide - Student
... 10. Explain the following regions of the prokaryotic chromosome with respect to their role in binary fission: a) ori – b) ter – ...
... 10. Explain the following regions of the prokaryotic chromosome with respect to their role in binary fission: a) ori – b) ter – ...
Biochemical Society Conference Report
... in hyaluronan research. Indeed, the focused nature of the meeting meant that many of the talks were directly relevant to our work at the Institute of Nephrology at Cardiff University School of Medicine. Regulation of gene expression is the basis of much of my group’s research, forming part of an ong ...
... in hyaluronan research. Indeed, the focused nature of the meeting meant that many of the talks were directly relevant to our work at the Institute of Nephrology at Cardiff University School of Medicine. Regulation of gene expression is the basis of much of my group’s research, forming part of an ong ...
Mutations in the VPS45 gene, a SEC1 homologue, result in vacuolar
... 1989), with the exception of DNA fragment isolations carried out by the glass bead method of Vogelstein and Gillespie (1979). The CENbased plasmid pVPS45-10 was generated by inserting the SmaI-PvuII fragment of library plasmid pVPS45-1 (containing VPS45, refer to Fig. 1A) into the SmaI site of pRS41 ...
... 1989), with the exception of DNA fragment isolations carried out by the glass bead method of Vogelstein and Gillespie (1979). The CENbased plasmid pVPS45-10 was generated by inserting the SmaI-PvuII fragment of library plasmid pVPS45-1 (containing VPS45, refer to Fig. 1A) into the SmaI site of pRS41 ...
UlrikPhD2005 - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... Protein Feature Based Identification of Cell Cycle Regulated Proteins in Yeast Ulrik de Lichtenberg, Thomas Skøt Jensen, Lars Juhl Jensen and Søren Brunak Journal of Molecular Biology, 239(4), 663-674, 2003 [PubMed] ...
... Protein Feature Based Identification of Cell Cycle Regulated Proteins in Yeast Ulrik de Lichtenberg, Thomas Skøt Jensen, Lars Juhl Jensen and Søren Brunak Journal of Molecular Biology, 239(4), 663-674, 2003 [PubMed] ...
Ch 10: Cell Division Review
... Identify (specifically) what parts of the cell (and parts of those parts) are involved in cell transport Explain, with or without using diagrams, the different ways that things get into and out of the cell (i.e. the different kinds of cell transport) Explain in detail how each mode of cell transport ...
... Identify (specifically) what parts of the cell (and parts of those parts) are involved in cell transport Explain, with or without using diagrams, the different ways that things get into and out of the cell (i.e. the different kinds of cell transport) Explain in detail how each mode of cell transport ...
Cell Communication
... doesn’t diffuse easily across the cell membrane. • Instead it binds to receptors on the surfaces of nerve cells in the brain. ...
... doesn’t diffuse easily across the cell membrane. • Instead it binds to receptors on the surfaces of nerve cells in the brain. ...
Illustration of Skeletal Muscle Calsequestrin Complex Formation by
... antibodies, the description of materials used and the outline of standard biochemical and cell biological techniques has previously been published [2, 6]. ...
... antibodies, the description of materials used and the outline of standard biochemical and cell biological techniques has previously been published [2, 6]. ...
cell: the basic unit of structure in living things
... cell needs to carry out the life functions. ...
... cell needs to carry out the life functions. ...
Direct Drug Metabolism Monitoring in a Live Single Hepatic Cell by
... cell.11 Weak molecular peaks were also identified by LC-MS/MS with many cells. Besides the peaks of tamoxifen and its metabolites, many peaks were detected at the same time, most of which were found in the control (without tamoxifen). Most of these peaks were hard to identify, however, peak origin w ...
... cell.11 Weak molecular peaks were also identified by LC-MS/MS with many cells. Besides the peaks of tamoxifen and its metabolites, many peaks were detected at the same time, most of which were found in the control (without tamoxifen). Most of these peaks were hard to identify, however, peak origin w ...