Effect of Cytochalasin on Average Pseudopodia Length in Amoeba
... 2007) The barbed ends of the actin filaments are where the ATP bound actin monomers bind to the growing polymer. If this end of the filament is capped by cytochalasin, this prevents the cell from polymerizing any new actin filaments and from extending the filaments it already has. (Cooper, 2007) As ...
... 2007) The barbed ends of the actin filaments are where the ATP bound actin monomers bind to the growing polymer. If this end of the filament is capped by cytochalasin, this prevents the cell from polymerizing any new actin filaments and from extending the filaments it already has. (Cooper, 2007) As ...
Oncotic pressure of blood plasma - Lectures For UG-5
... fluid increases. When it becomes clinically detectable, it is called edema Venous obstruction or plasma protein deficiency can lead to edema In conditions where plasma proteins are reduced, e.g. from being lost in the urine (proteinuria) or from malnutrition, there will be a reduction in oncotic ...
... fluid increases. When it becomes clinically detectable, it is called edema Venous obstruction or plasma protein deficiency can lead to edema In conditions where plasma proteins are reduced, e.g. from being lost in the urine (proteinuria) or from malnutrition, there will be a reduction in oncotic ...
The chemical constituents of cells
... Monosaccharides may link by through glycosidic bonds to form a polysaccharide by condensation reactions. They are not sweet, insoluble or slightly soluble in water, non-crystalline. The compact insoluble structure makes it ideal as a storage carbohydrate because they will not diffuse out of the cell ...
... Monosaccharides may link by through glycosidic bonds to form a polysaccharide by condensation reactions. They are not sweet, insoluble or slightly soluble in water, non-crystalline. The compact insoluble structure makes it ideal as a storage carbohydrate because they will not diffuse out of the cell ...
Teacher: Angela Thornton
... energy, exchange of gases, and response to the environment. Identify functions of organelles found in eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. ...
... energy, exchange of gases, and response to the environment. Identify functions of organelles found in eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. ...
mitosis & meiosis
... • Creates new cells for reproduction • One parent cell produces four daughter cells. • Daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes found in the original parent cell ...
... • Creates new cells for reproduction • One parent cell produces four daughter cells. • Daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes found in the original parent cell ...
studies on the intracellular digestive process in mammalian tissue
... phosphatase and an E600-resistant esterase within appeared to be already undergoing hydrolysis as these dense bodies (14). Under normal conditions, evidenced by a uniform loss of density. Some of an average of 2 to 4 dense bodies were found per the vacuoles contained particles in various stages sect ...
... phosphatase and an E600-resistant esterase within appeared to be already undergoing hydrolysis as these dense bodies (14). Under normal conditions, evidenced by a uniform loss of density. Some of an average of 2 to 4 dense bodies were found per the vacuoles contained particles in various stages sect ...
Indian scientists discover how aspirin can kill cancer cells By Dr
... Scientists the world over have been exploring aspirin’s role in killing cancer cells for some time, but the mechanism by which it can do so was not known. Researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology at Chennai have now demonstrated that aspirin preferentially targets cancer cells and kills t ...
... Scientists the world over have been exploring aspirin’s role in killing cancer cells for some time, but the mechanism by which it can do so was not known. Researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology at Chennai have now demonstrated that aspirin preferentially targets cancer cells and kills t ...
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
... • The cells at the tip of the roots are actively dividing, and thus many cells will be in stages of mitosis. • The tips can be prepared in a way that allows them to be flattened on microscopes slide (“squashed”) so that the chromosomes of individual cells can be observed. • The chromosomes can be st ...
... • The cells at the tip of the roots are actively dividing, and thus many cells will be in stages of mitosis. • The tips can be prepared in a way that allows them to be flattened on microscopes slide (“squashed”) so that the chromosomes of individual cells can be observed. • The chromosomes can be st ...
amino sugars - Vitex Nutrition
... Glycoproteins are proteins containing a chain of sugars, usually a dozen or so sugars, called an oligosaccharide chain. This chain modifies the properties of the protein to which it is attached. The sugars are added to newly synthesized protein in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi regions of the c ...
... Glycoproteins are proteins containing a chain of sugars, usually a dozen or so sugars, called an oligosaccharide chain. This chain modifies the properties of the protein to which it is attached. The sugars are added to newly synthesized protein in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi regions of the c ...
16 Chapter
... • The endoplasmic reticulum may be “rough” or “smooth.” • ER that has no attached ribosomes is called smooth endoplasmic reticulum. • This type of ER processes other cellular substances such as lipids that store energy. • Ribosomes are attached to areas on the rough ER where they carry out their job ...
... • The endoplasmic reticulum may be “rough” or “smooth.” • ER that has no attached ribosomes is called smooth endoplasmic reticulum. • This type of ER processes other cellular substances such as lipids that store energy. • Ribosomes are attached to areas on the rough ER where they carry out their job ...
Prokaryotic
... Six characteristics that all cells have in common: 1. Surrounded by a cell membrane. 2. Have ribosomes (make proteins) 3. Contain DNA 4. Have the ability to reproduce 5. Maintain homeostasis 6. Respond to stimuli Write this in the “BOTH” column! ...
... Six characteristics that all cells have in common: 1. Surrounded by a cell membrane. 2. Have ribosomes (make proteins) 3. Contain DNA 4. Have the ability to reproduce 5. Maintain homeostasis 6. Respond to stimuli Write this in the “BOTH” column! ...
Slide 1
... • The endoplasmic reticulum may be “rough” or “smooth.” • ER that has no attached ribosomes is called smooth endoplasmic reticulum. • This type of ER processes other cellular substances such as lipids that store energy. • Ribosomes are attached to areas on the rough ER where they carry out their job ...
... • The endoplasmic reticulum may be “rough” or “smooth.” • ER that has no attached ribosomes is called smooth endoplasmic reticulum. • This type of ER processes other cellular substances such as lipids that store energy. • Ribosomes are attached to areas on the rough ER where they carry out their job ...
Cell Cycle
... The cell cycle is a series of events that lead to cell division and replication, consisting of four phases: G1, S, G2 and M. The activation of each phase depends on the proper completion of the previous one. The cell cycle commences with the G1 phase, during which the cell increases its size. During ...
... The cell cycle is a series of events that lead to cell division and replication, consisting of four phases: G1, S, G2 and M. The activation of each phase depends on the proper completion of the previous one. The cell cycle commences with the G1 phase, during which the cell increases its size. During ...
Cholesterol
... Transport of Cholesterol Lipoproteins Found in blood plasma Molecules containing a combination of lipids ...
... Transport of Cholesterol Lipoproteins Found in blood plasma Molecules containing a combination of lipids ...
Prokaryotic
... 1. Prokaryotic—no nucleus, no organelles 2. Eukaryotic—plant cells, green discs are ...
... 1. Prokaryotic—no nucleus, no organelles 2. Eukaryotic—plant cells, green discs are ...
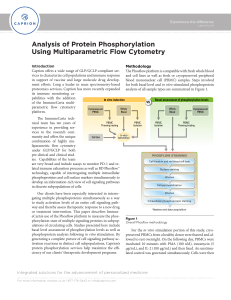
Analysis of Protein Phosphorylation Using Multiparametric Flow
... Drawing from an ever-expanding menu of commerciallyavailable flow cytometry reagents and antibodies, the ImmuneCarta team is capable of interrogating protein phosphorylation states in samples from a wide array of species. It is thus possible to assay phosphoproteins in tandem with cell surface molec ...
... Drawing from an ever-expanding menu of commerciallyavailable flow cytometry reagents and antibodies, the ImmuneCarta team is capable of interrogating protein phosphorylation states in samples from a wide array of species. It is thus possible to assay phosphoproteins in tandem with cell surface molec ...
Cell Cyles
... Centromere – a place to attach the mitotic spindle for chromosome separation Telomere – at end of linear DNA to prevent the chromosome from getting shorter in every round of replication ...
... Centromere – a place to attach the mitotic spindle for chromosome separation Telomere – at end of linear DNA to prevent the chromosome from getting shorter in every round of replication ...
lncreased Expression of Vacuolar Aquaporin and H+
... F-86000 Poitiers, France; Laboratory of Biochemistry, School of Agriculture, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-01 Japan (M.M.);and lnstitut für Botanik, Schnittspahnstrasse, 3-5 Darmstadt, Cermany (R.R.) xenobiotics (Martinoia et al., 1993) are presumed to be stored indefinitely within the vacuole. Beca ...
... F-86000 Poitiers, France; Laboratory of Biochemistry, School of Agriculture, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-01 Japan (M.M.);and lnstitut für Botanik, Schnittspahnstrasse, 3-5 Darmstadt, Cermany (R.R.) xenobiotics (Martinoia et al., 1993) are presumed to be stored indefinitely within the vacuole. Beca ...
Cell Transport PPT 2 File
... concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Diffusion results from the random motion of atoms and molecules due to their kinetic energy. • Diffusion involves the movement of atoms & molecules in gases and liquids ...
... concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Diffusion results from the random motion of atoms and molecules due to their kinetic energy. • Diffusion involves the movement of atoms & molecules in gases and liquids ...
Chapter 3 Body Tissues
... – Single layer, but some cells are shorter than others giving a false (pseudo) impression of stratification – Location: • Respiratory tract, where it is ciliated and known as pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium ...
... – Single layer, but some cells are shorter than others giving a false (pseudo) impression of stratification – Location: • Respiratory tract, where it is ciliated and known as pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium ...
AND C3d-COATED FLUORESCENT
... resuspended in 1.5 ml of 1 OO' BSA/PBS containing 1 .O mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) and sonicated briefly until asingle particle suspension was obtained. A stock solution of 1 15 mM PMSF was first prepared by solubilizing PMSF at 20 mg/ml in 2-propanol. C receptor assays. C receptors were ...
... resuspended in 1.5 ml of 1 OO' BSA/PBS containing 1 .O mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) and sonicated briefly until asingle particle suspension was obtained. A stock solution of 1 15 mM PMSF was first prepared by solubilizing PMSF at 20 mg/ml in 2-propanol. C receptor assays. C receptors were ...