2.6 The need for transport
... Capillaries • Capillaries allow exchange of materials between the blood and the cells of the body (O2, glucose). • Capillaries are only one cell thick to allow easier/quicker diffusion of materials. •Capillaries also provide a large surface area for exchange. ...
... Capillaries • Capillaries allow exchange of materials between the blood and the cells of the body (O2, glucose). • Capillaries are only one cell thick to allow easier/quicker diffusion of materials. •Capillaries also provide a large surface area for exchange. ...
PowerPoint
... Erythrocytes (red blood cells, RBCs) Contain hemoglobin Non-nucleated in mammals ...
... Erythrocytes (red blood cells, RBCs) Contain hemoglobin Non-nucleated in mammals ...
Protists Topics in Biodiversity
... All five groups of protozoans include some sessile species but most are swimmers. Ciliates use their many tiny cilia, in controlled waves, to propel themselves through the water. Flagellates have a single posterior flagella that pushes them forward in much the same way as a motor boat uses its prope ...
... All five groups of protozoans include some sessile species but most are swimmers. Ciliates use their many tiny cilia, in controlled waves, to propel themselves through the water. Flagellates have a single posterior flagella that pushes them forward in much the same way as a motor boat uses its prope ...
Diffusion and pollutants
... inhale these as well, and that this makes us ill and alters our ability to fully develop. Part 2: In this part, students will be introduced to the Deliver Change AirSensa data. Teachers can either retrieve the data from their school’s own individual device, if applicable, or use a prepared data set ...
... inhale these as well, and that this makes us ill and alters our ability to fully develop. Part 2: In this part, students will be introduced to the Deliver Change AirSensa data. Teachers can either retrieve the data from their school’s own individual device, if applicable, or use a prepared data set ...
Microbes Overview
... Viruses – miniscule, infectious agent with simple acellular organization and pattern of reproduction Viruses can exist – extracellular or intracellular Virion (complete virus particle) consist of : - nucleocapsid (composed of 1 or more DNA or RNA, held within capsid) - in some viruses – envelope (ph ...
... Viruses – miniscule, infectious agent with simple acellular organization and pattern of reproduction Viruses can exist – extracellular or intracellular Virion (complete virus particle) consist of : - nucleocapsid (composed of 1 or more DNA or RNA, held within capsid) - in some viruses – envelope (ph ...
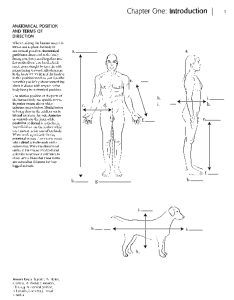
Chapter One: Introduction
... In anatomy the abdomen is divided into nine regions. Write the names of the regions in the spaces indicated. Color both the left and right hypochondriac regions in light blue. Hypochondriac means "below the cartilage." The common use of the word (someone who thinks they are sick all the time) reflec ...
... In anatomy the abdomen is divided into nine regions. Write the names of the regions in the spaces indicated. Color both the left and right hypochondriac regions in light blue. Hypochondriac means "below the cartilage." The common use of the word (someone who thinks they are sick all the time) reflec ...
Chapter 9 Notes
... Circulatory system carries digested food substances to cells of the body Nutrients travel around (over and through each cell) Waste molecules pass from cells back into the bloodstream (through capillary walls) Circulatory system helps dispose of waste products and toxic materials (such as salts) ...
... Circulatory system carries digested food substances to cells of the body Nutrients travel around (over and through each cell) Waste molecules pass from cells back into the bloodstream (through capillary walls) Circulatory system helps dispose of waste products and toxic materials (such as salts) ...
Immune System lecture
... Immune system exposed to harmless version of pathogen triggers active immunity stimulates immune system to produce antibodies to invader rapid response if ...
... Immune system exposed to harmless version of pathogen triggers active immunity stimulates immune system to produce antibodies to invader rapid response if ...
The cytoskeletal system, motor proteins Cyto + SKELETON
... http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/fluorescence/filtercubes/yfp/yfphyq/stains/yfpcy2keratinptk2cells.html http://www.lajollaneuroscience.org/sr/homepage/cell/scientific_art_gallery/pasquale.htm ...
... http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/fluorescence/filtercubes/yfp/yfphyq/stains/yfpcy2keratinptk2cells.html http://www.lajollaneuroscience.org/sr/homepage/cell/scientific_art_gallery/pasquale.htm ...
Notes
... respire through their skins Gills feathery structures that expose a large surface area to the water. Gills are rich in blood vessels that bring blood close to the surface for gas exchange. Book lungs parallel, sheetlike layers of thin tissues that contain blood vessels. Spiracles in in ...
... respire through their skins Gills feathery structures that expose a large surface area to the water. Gills are rich in blood vessels that bring blood close to the surface for gas exchange. Book lungs parallel, sheetlike layers of thin tissues that contain blood vessels. Spiracles in in ...
Physiology Acknowledgement Form Review questions provide
... List 4 ways to minimize the risk of lung overexpansion. 42. __________________________________________________________ 43. __________________________________________________________ 44. __________________________________________________________ 45. ___________________________________________________ ...
... List 4 ways to minimize the risk of lung overexpansion. 42. __________________________________________________________ 43. __________________________________________________________ 44. __________________________________________________________ 45. ___________________________________________________ ...
To learn more about preventing skin cancer, click here.
... diagnosed in more than 1 million people in the United States each year. Cancer occurs when normal cells undergo a transformation during which they grow and multiply without normal controls. These cells are only cancerous if they are malignant. Skin cancer has three main types: basal cell, squamous c ...
... diagnosed in more than 1 million people in the United States each year. Cancer occurs when normal cells undergo a transformation during which they grow and multiply without normal controls. These cells are only cancerous if they are malignant. Skin cancer has three main types: basal cell, squamous c ...
H ions
... Carrier Proteins and Ion Channels Glucose, sodium ions and chloride ions are just a few examples of molecules and ions that must efficiently get across the plasma membrane but to which the lipid bilayer of the membrane is impermeable. Their transport must therefore be "facilitated" by proteins that ...
... Carrier Proteins and Ion Channels Glucose, sodium ions and chloride ions are just a few examples of molecules and ions that must efficiently get across the plasma membrane but to which the lipid bilayer of the membrane is impermeable. Their transport must therefore be "facilitated" by proteins that ...
Tissues
... edge are flattened – Function: Protection of underlying areas where friction is common – Present in: • Skin • Mouth • Esophagus ...
... edge are flattened – Function: Protection of underlying areas where friction is common – Present in: • Skin • Mouth • Esophagus ...
Name
... normally. As a result, a person who has emphysema may have high blood acidity levels. The body process that would attempt to return the blood pH to normal so that cells could function properly is called _?_. a. Active transport c. Acidosis b. Adaptation d. Homeostasis ...
... normally. As a result, a person who has emphysema may have high blood acidity levels. The body process that would attempt to return the blood pH to normal so that cells could function properly is called _?_. a. Active transport c. Acidosis b. Adaptation d. Homeostasis ...
Topic Histology of liver And Gall bladder
... These rows are one cell wide and are surrounded by sinusoidal capillaries or sinusoids. This arrangement ensures that each hepatocyte is in very close contact with blood flowing through the sinusoids, i.e. bathed in blood. Hepatocytes They are large cells. Nucleus is large and rounded wit ...
... These rows are one cell wide and are surrounded by sinusoidal capillaries or sinusoids. This arrangement ensures that each hepatocyte is in very close contact with blood flowing through the sinusoids, i.e. bathed in blood. Hepatocytes They are large cells. Nucleus is large and rounded wit ...
Samurai sword protein makes strategic cuts in cell
... But there are many cell types that have ordered microtubule arrays that aren't created by The cells Dixit's lab use are from a lineage of centrosomes. Some nerve cells, for example, have Arabidopsis plants created by Erica Fishel, PhD, very long projections (axons) that are chock full of then a WUST ...
... But there are many cell types that have ordered microtubule arrays that aren't created by The cells Dixit's lab use are from a lineage of centrosomes. Some nerve cells, for example, have Arabidopsis plants created by Erica Fishel, PhD, very long projections (axons) that are chock full of then a WUST ...
Slide 1
... Controlled secretion of H+ and reabsorption of bicarbonate ions help regulate blood pH Secretion also includes active transport of drugs and poisons Reabsorption of salts and urea allow osmotic reabsorption of water ...
... Controlled secretion of H+ and reabsorption of bicarbonate ions help regulate blood pH Secretion also includes active transport of drugs and poisons Reabsorption of salts and urea allow osmotic reabsorption of water ...
Ribosomes
... “optical sectioning” of fluorescently-stained specimens. Only a single plane of focus is illuminated; out-of-focus fluorescence above and below the plane is subtracted by a computer. A sharp image results, as seen in stained nervous tissue (top), where nerve cells are green, support cells are red, a ...
... “optical sectioning” of fluorescently-stained specimens. Only a single plane of focus is illuminated; out-of-focus fluorescence above and below the plane is subtracted by a computer. A sharp image results, as seen in stained nervous tissue (top), where nerve cells are green, support cells are red, a ...
Cell Taxonomy: How are organisms grouped?
... Today, we are going to look at cells from Bacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, and Animals. Based on what you’ve learned about taxonomy and how scientists group things, see if you can figure out the differences (and likenesses) in these cells from different types of organisms. ...
... Today, we are going to look at cells from Bacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, and Animals. Based on what you’ve learned about taxonomy and how scientists group things, see if you can figure out the differences (and likenesses) in these cells from different types of organisms. ...