
Unit Title / Grade Level Unit 3: The Basis of Life (Covering Chapters
... LS.3.2 Interactions of Living Systems: Students understand that organisms in all ecosystems interact with and depend on each other, and that organisms with similar needs compete for limited resources. What are the characteristics of a living organism? How are living things classified and why is it i ...
... LS.3.2 Interactions of Living Systems: Students understand that organisms in all ecosystems interact with and depend on each other, and that organisms with similar needs compete for limited resources. What are the characteristics of a living organism? How are living things classified and why is it i ...
Section: Passive Transport
... Complete the table below. In the first column, write two characteristics of cells in endocytosis. In the second column, write two characteristics of cells in exocytosis ...
... Complete the table below. In the first column, write two characteristics of cells in endocytosis. In the second column, write two characteristics of cells in exocytosis ...
The Digestive System
... second, and the same number are born each second. Within a tiny droplet of blood, there are some 5 million red blood cells, 300 000 platelets and 10 000 white cells. It takes about 20 seconds for a red blood cell to circle the whole body. Red blood cells make approximately 250,000 round trips of the ...
... second, and the same number are born each second. Within a tiny droplet of blood, there are some 5 million red blood cells, 300 000 platelets and 10 000 white cells. It takes about 20 seconds for a red blood cell to circle the whole body. Red blood cells make approximately 250,000 round trips of the ...
The Cell - Oakland Schools Moodle
... Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Mitochondria Cytoskeleton ...
... Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Mitochondria Cytoskeleton ...
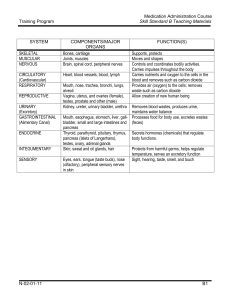
Body Systems, Organs and Functions
... Carries impulses throughout the body Carries nutrients and oxygen to the cells in the blood and removes such as carbon dioxide Provides air (oxygen) to the cells; removes waste such as carbon dioxide Allow creation of new human being ...
... Carries impulses throughout the body Carries nutrients and oxygen to the cells in the blood and removes such as carbon dioxide Provides air (oxygen) to the cells; removes waste such as carbon dioxide Allow creation of new human being ...
Chapter 4 Test - Nutley Public Schools
... Cells & Classification Study Guide Cells were first observed during the 1600’s by Robert Hooke. They were dead cork cells. Most cells are microscopic and can only be seen with a microscope. The Cell Theory States: o All living organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular or multicell ...
... Cells & Classification Study Guide Cells were first observed during the 1600’s by Robert Hooke. They were dead cork cells. Most cells are microscopic and can only be seen with a microscope. The Cell Theory States: o All living organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular or multicell ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... one or more cells. • 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living organisms. • 3. All cells arise from like, pre-existing cells. ...
... one or more cells. • 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living organisms. • 3. All cells arise from like, pre-existing cells. ...
Document
... _____ 9. organisms made up of cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles _____ 10.word that describes most organisms that you can see with your naked Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the i ...
... _____ 9. organisms made up of cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles _____ 10.word that describes most organisms that you can see with your naked Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the i ...
Cells
... Theory – well tested hypothesis. 1.All living things are made up of cells. 2.Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3.New cells come from existing cells. ...
... Theory – well tested hypothesis. 1.All living things are made up of cells. 2.Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3.New cells come from existing cells. ...
Unit B3, B3.2.1 - GCSE Biology Revision
... A ventricle fills with blood by the contraction of .................................................. . When a ventricle contracts, blood is forced into .................................................... . When a ventricle relaxes, the backflow of blood into it is prevented by the closing of ...
... A ventricle fills with blood by the contraction of .................................................. . When a ventricle contracts, blood is forced into .................................................... . When a ventricle relaxes, the backflow of blood into it is prevented by the closing of ...
Skeletal System(Bones), Muscular System (Muscles), and
... •The cell membrane forms the outside boundary of the cell. •The nucleus is the control center that directs the cell’s activities and contains information that determines the cell’s characteristics. •The area between the cell membrane and the nucleus is the cytoplasm. •Cytoplasm contains a clear, jel ...
... •The cell membrane forms the outside boundary of the cell. •The nucleus is the control center that directs the cell’s activities and contains information that determines the cell’s characteristics. •The area between the cell membrane and the nucleus is the cytoplasm. •Cytoplasm contains a clear, jel ...
Additional information
... use bovine-chromaffin cells to study direct effects of channel and exocytotic protein mutants on secretion. We use semliki forest viral infected cells, monitoring direct effects on secretion from as ingle cell and single vesicles by amperometry. 2) We are developing thioredoxin mimetic peptides and ...
... use bovine-chromaffin cells to study direct effects of channel and exocytotic protein mutants on secretion. We use semliki forest viral infected cells, monitoring direct effects on secretion from as ingle cell and single vesicles by amperometry. 2) We are developing thioredoxin mimetic peptides and ...
Organelles Quiz Answers
... Answers may vary. Cells have many different and specific functions/roles, so a cell needs different parts, just like a factory, for these specific functions/roles. ...
... Answers may vary. Cells have many different and specific functions/roles, so a cell needs different parts, just like a factory, for these specific functions/roles. ...
Tissues, Organs, Systems Review Answers
... Blood enters through the right atrium before passing into the left ventricle where it is then pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs for gas exchange. The oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins to the left atria followed by the left ventricle. The blood leaves ...
... Blood enters through the right atrium before passing into the left ventricle where it is then pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs for gas exchange. The oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins to the left atria followed by the left ventricle. The blood leaves ...
Cells and tissues
... oxygen and removal of waste • need to be able to reproduce, called mitosis • tissues are groups of similar cells with specialised function • types are epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous ...
... oxygen and removal of waste • need to be able to reproduce, called mitosis • tissues are groups of similar cells with specialised function • types are epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous ...
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Part 1: Anacaris Reminders!!
... 2. Remove a small leaf from near the tip of an Anacaris plant. 3. Make a wet mount with water of the Anacaris leaf in water 4. Observe the leaf under low power 5. Focus on the leaf carefully, adjusting up and down very slowly 6. Switch to medium power and observe, focusing with the fine adjustment 7 ...
... 2. Remove a small leaf from near the tip of an Anacaris plant. 3. Make a wet mount with water of the Anacaris leaf in water 4. Observe the leaf under low power 5. Focus on the leaf carefully, adjusting up and down very slowly 6. Switch to medium power and observe, focusing with the fine adjustment 7 ...
Animal Structure and Function
... Compare and contrast cartilage, bone, tendons, and ligaments . 6. Learn the basic structure of muscle and the three different types and their function. 7. Learn the structure of nerves and their function. 8. Define an organ and the organization of different tissues within. 9. Learn the 10 organs sys ...
... Compare and contrast cartilage, bone, tendons, and ligaments . 6. Learn the basic structure of muscle and the three different types and their function. 7. Learn the structure of nerves and their function. 8. Define an organ and the organization of different tissues within. 9. Learn the 10 organs sys ...
Chapter 7_The Cell
... 1838 – Scientist discovers plants are made of cells. 1839 – Scientist discovers that animal tissue also consists of individual cells. 1855 – Scientist proposes that all cells are produced from the division of existing cells. The Cell Theory – includes three principles: 1. All living organisms are co ...
... 1838 – Scientist discovers plants are made of cells. 1839 – Scientist discovers that animal tissue also consists of individual cells. 1855 – Scientist proposes that all cells are produced from the division of existing cells. The Cell Theory – includes three principles: 1. All living organisms are co ...
Domains and kingdoms - Peoria Public Schools
... Classified into three groups: Algae (plantlike), Protozoans (animallike) , and fungus-like ...
... Classified into three groups: Algae (plantlike), Protozoans (animallike) , and fungus-like ...
[pdf]
... program highlighted both the physical forces exerted during migration and the signaling pathways involved in the process. Celeste Nelson (Princeton University) presented results suggesting that cells migrate collectively through fibrous extracellular matrix (ECM) by exerting tensile forces at the le ...
... program highlighted both the physical forces exerted during migration and the signaling pathways involved in the process. Celeste Nelson (Princeton University) presented results suggesting that cells migrate collectively through fibrous extracellular matrix (ECM) by exerting tensile forces at the le ...






















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008789103_1-746b7a86138a2a5bab5758b7de85a178-300x300.png)