study guide for cell energy
... *After all organisms obtain their glucose (either through eating like heterotrophs or through photosynthesis like autotrophs, they must break down the glucose to get the energy out of it. *Glucose is an energy rich sugar. *Cellular Respiration is the process by which cells break down the glucose to ...
... *After all organisms obtain their glucose (either through eating like heterotrophs or through photosynthesis like autotrophs, they must break down the glucose to get the energy out of it. *Glucose is an energy rich sugar. *Cellular Respiration is the process by which cells break down the glucose to ...
Biochemical Evolutdion
... What is the nature of the cell membrane and how does it affect the contents of the cell? ...
... What is the nature of the cell membrane and how does it affect the contents of the cell? ...
Active Transport BioFactsheet
... The sodium concentration is much greater outside the cell than inside it. There is therefore a tendency for sodium ions to diffuse into the cell down their concentration gradient. In order to work against this tendency the cell uses active transport to push out more of the sodium ions. By removing s ...
... The sodium concentration is much greater outside the cell than inside it. There is therefore a tendency for sodium ions to diffuse into the cell down their concentration gradient. In order to work against this tendency the cell uses active transport to push out more of the sodium ions. By removing s ...
1.1 Introduction to Cells
... tissues, tissues form organs etc.) The cell contributes to a greater task Many cells working together and world be useless alone. ...
... tissues, tissues form organs etc.) The cell contributes to a greater task Many cells working together and world be useless alone. ...
Standard II test review Cells
... • What molecule usually helps it? (A word) • ATP • If there things are different on different sides of the membrane, it is usually due to . . . • Active transport • Example brown algae that contain 200 times more iodine than its surroundings. ...
... • What molecule usually helps it? (A word) • ATP • If there things are different on different sides of the membrane, it is usually due to . . . • Active transport • Example brown algae that contain 200 times more iodine than its surroundings. ...
Plant and Animal Cells Lab: A Comparison
... 1. Complete the following chart: Is the cell organelle found in plants, animals, or both. What is their function? nucleus ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------cell wall ------------------------------------------------------------ ...
... 1. Complete the following chart: Is the cell organelle found in plants, animals, or both. What is their function? nucleus ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------cell wall ------------------------------------------------------------ ...
Immunology Lab
... _________________________, the body’s own antigens. This process is known as _________________________ selection. Immature T cells that do not recognize the body’s own antigens are called _________________________ and allowed to mature. ...
... _________________________, the body’s own antigens. This process is known as _________________________ selection. Immature T cells that do not recognize the body’s own antigens are called _________________________ and allowed to mature. ...
Mitosis/Cancer Lecture Notes
... • For many cells, the G1 checkpoint is the most important. • If a cell receives a go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint, it will usually complete the S, G2, and M phases and divide. • If the cell does not receive the go-ahead signal, it will exit the cycle, switching into a non-dividing state called ...
... • For many cells, the G1 checkpoint is the most important. • If a cell receives a go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint, it will usually complete the S, G2, and M phases and divide. • If the cell does not receive the go-ahead signal, it will exit the cycle, switching into a non-dividing state called ...
Organelles In Plant Cell
... into the Golgi lumen. The proteins are then transported through the medial region towards the trans face and are modified on their way. The proteins are also labelled with a sequence of molecules according to their final destination. The transport mechanism itself is not yet clear; it could happen b ...
... into the Golgi lumen. The proteins are then transported through the medial region towards the trans face and are modified on their way. The proteins are also labelled with a sequence of molecules according to their final destination. The transport mechanism itself is not yet clear; it could happen b ...
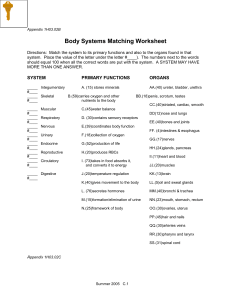
Body Systems Matching Worksheet
... Directions: Match the system to its primary functions and also to the organs found in that system. Place the value of the letter under the letter #____). The numbers next to the words should equal 100 when all the correct words are put with the system. A SYSTEM MAY HAVE MORE THAN ONE ANSWER. ...
... Directions: Match the system to its primary functions and also to the organs found in that system. Place the value of the letter under the letter #____). The numbers next to the words should equal 100 when all the correct words are put with the system. A SYSTEM MAY HAVE MORE THAN ONE ANSWER. ...
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Period 3 - Mercer Island School District
... lymphatic tissue attached to the large intestine. It does not appear to have much lymphatic function in humans minus the ability to release some mucus into the large intestine. ...
... lymphatic tissue attached to the large intestine. It does not appear to have much lymphatic function in humans minus the ability to release some mucus into the large intestine. ...
Jell-O Cells
... represents the cytoplasm within the cell. 2. Put the Jell-O in a refrigerator and let set over night so that it will congeal. 3. Prior to the next class, make a paper plate for each student containing the different candy pieces they will need to create each of their plant and animal cells. 4. Pass o ...
... represents the cytoplasm within the cell. 2. Put the Jell-O in a refrigerator and let set over night so that it will congeal. 3. Prior to the next class, make a paper plate for each student containing the different candy pieces they will need to create each of their plant and animal cells. 4. Pass o ...
Cell Structure
... though they often grow in colonies large enough to see. They have the distinction of being the oldest known fossils, more than 3.5 billion years old, in fact! It may surprise you then to know that the cyanobacteria are still around; they are one of the largest and most important groups of bacteria ...
... though they often grow in colonies large enough to see. They have the distinction of being the oldest known fossils, more than 3.5 billion years old, in fact! It may surprise you then to know that the cyanobacteria are still around; they are one of the largest and most important groups of bacteria ...
cell structure packet
... Cell Theory Questions: 1. Explain why cells are important. 2. Summarize (in one sentence) the cell theory developed by Schwann and Schleiden in 1839. 3. Define unicellular and give an example of something that is unicellular. 4. Define multi-cellular and give an example of something that is multi-ce ...
... Cell Theory Questions: 1. Explain why cells are important. 2. Summarize (in one sentence) the cell theory developed by Schwann and Schleiden in 1839. 3. Define unicellular and give an example of something that is unicellular. 4. Define multi-cellular and give an example of something that is multi-ce ...
DNA Half-Life
... ions and organic molecules. • Control the movement of substances in and out of cells. ...
... ions and organic molecules. • Control the movement of substances in and out of cells. ...
SBI 3C- The Cell: Part One -use this note as a guide to fill in board
... -the cell is the basic structure and function of life -there are many different kinds of cells (ie) muscle cells perform different functions than bone cells Organelle: A specialized structure within a cell that performs a specialized function in the cell. Organelles are the parts of a cell (little o ...
... -the cell is the basic structure and function of life -there are many different kinds of cells (ie) muscle cells perform different functions than bone cells Organelle: A specialized structure within a cell that performs a specialized function in the cell. Organelles are the parts of a cell (little o ...
Intracellular Cytokine staining protocol
... Stimulation of cells 1. Stimulate cells following the appropriate protocols in presence of Brefeldin A (1 µg/ml). Collect the cells and transfer the cell suspension to a centrifuge tube. 2. Centrifuge cell preparations at 828 g for 5 min ...
... Stimulation of cells 1. Stimulate cells following the appropriate protocols in presence of Brefeldin A (1 µg/ml). Collect the cells and transfer the cell suspension to a centrifuge tube. 2. Centrifuge cell preparations at 828 g for 5 min ...
Cells Outline
... 5. Glycocalyx – (sugar coating of plasma membrane) includes glycolipids and glycoproteins are responsible for cell to cell recognition… each glycocalyx is unique to a cell type (Cancer cell glycocalyx changes continuously so immune cells can’t recognize it) 6. Microvilli – increase surface area and ...
... 5. Glycocalyx – (sugar coating of plasma membrane) includes glycolipids and glycoproteins are responsible for cell to cell recognition… each glycocalyx is unique to a cell type (Cancer cell glycocalyx changes continuously so immune cells can’t recognize it) 6. Microvilli – increase surface area and ...
Buckling along boundaries of elastic contrast as a mechanism for
... The problem of animal formation - especially that of vertebrates - is still largely open. In historical times, it was believed that “Bauplans” (body plans) existed [1] for primitive animal forms. In this view, some form of discontinuous evolution acting at the global scale of the animal body, was ne ...
... The problem of animal formation - especially that of vertebrates - is still largely open. In historical times, it was believed that “Bauplans” (body plans) existed [1] for primitive animal forms. In this view, some form of discontinuous evolution acting at the global scale of the animal body, was ne ...
Master of Science in Anatomy
... Thesis Research study on the new interested science in anatomy which is an advantageous knowledge and/or applicable use under supervision of a faculty advisor who also act as the chair of the thesis committee ...
... Thesis Research study on the new interested science in anatomy which is an advantageous knowledge and/or applicable use under supervision of a faculty advisor who also act as the chair of the thesis committee ...
Cell Parts Notes
... c. More active cells like muscle cells have MORE mitochondria d. Both plants & animal cells have mitochondria ...
... c. More active cells like muscle cells have MORE mitochondria d. Both plants & animal cells have mitochondria ...
CH 6 CQ
... Brefeldin A is a drug that disrupts transport from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. What other organelles and membranes are affected? a) lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane b) lysosomes, peroxisomes, plasma membrane c) vacuoles, mitochondria, plasma membrane ...
... Brefeldin A is a drug that disrupts transport from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. What other organelles and membranes are affected? a) lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane b) lysosomes, peroxisomes, plasma membrane c) vacuoles, mitochondria, plasma membrane ...
Levels of Organization
... Epithelial tissue covers and lines the surfaces of your body and organs, inside and out. They primarily serve as protective barriers. Skin is one example. ...
... Epithelial tissue covers and lines the surfaces of your body and organs, inside and out. They primarily serve as protective barriers. Skin is one example. ...