THE CELL WHEEL
... For the bottom wheel, divide the circle in half. Divide each half into 20 equal segments. (For a total of 40 segments on entire circle) On one half of the circle, list each of the 20 cell organelles. On the corresponding segment of the other half, list the function of each organelle. Make sure you i ...
... For the bottom wheel, divide the circle in half. Divide each half into 20 equal segments. (For a total of 40 segments on entire circle) On one half of the circle, list each of the 20 cell organelles. On the corresponding segment of the other half, list the function of each organelle. Make sure you i ...
Biology I Outline
... g. Identify the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works h. Explain how the muscular/skeletal system works with other systems to support and allow movement i. Recognize that bones produce both red and white blood cells j. Recognize that communication between c ...
... g. Identify the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works h. Explain how the muscular/skeletal system works with other systems to support and allow movement i. Recognize that bones produce both red and white blood cells j. Recognize that communication between c ...
Inferring cellular response from noise measurements
... observation of the rotational motion of the single motor of individual E.coli cells. To develop this experimental setup, I combined many different devices such as optical lenses, mirrors, light filters, mechanical shutters, a strong UV illuminator and a photo detector with a microscope and controlle ...
... observation of the rotational motion of the single motor of individual E.coli cells. To develop this experimental setup, I combined many different devices such as optical lenses, mirrors, light filters, mechanical shutters, a strong UV illuminator and a photo detector with a microscope and controlle ...
Cell Structure
... 1. How many cm are in a m? 2. What is the difference between resolution and magnification? 3. What measurement system do scientists use? 4. Why can living cells not be viewed under an electron microscope? 5. The English scientist Robert Hooke used a crude microscope to examine these…. ...
... 1. How many cm are in a m? 2. What is the difference between resolution and magnification? 3. What measurement system do scientists use? 4. Why can living cells not be viewed under an electron microscope? 5. The English scientist Robert Hooke used a crude microscope to examine these…. ...
Ch 7-1: Life is Cellular
... Eukaryotic Cells • Nucleus: Contains DNA and controls the cell’s activities -Chromatin: Tightly coiled strands of DNA & protein found within the nucleus. • Nucleolus: Dense small region found within the nucleus that makes ribosomes • Nuclear Envelope: Controls what materials go in and out of the nuc ...
... Eukaryotic Cells • Nucleus: Contains DNA and controls the cell’s activities -Chromatin: Tightly coiled strands of DNA & protein found within the nucleus. • Nucleolus: Dense small region found within the nucleus that makes ribosomes • Nuclear Envelope: Controls what materials go in and out of the nuc ...
Organ/body system
... Phys- = movement/function -ology = the study of Homo- = same -stasis = condition of standing Micro- = small Macro- = large Cyto- = cell Hist- = tissue Path- = disease Ceph(al)- = head/ brain Dorsi/o- = back Dist- = far away Prox(i)- = closer to ...
... Phys- = movement/function -ology = the study of Homo- = same -stasis = condition of standing Micro- = small Macro- = large Cyto- = cell Hist- = tissue Path- = disease Ceph(al)- = head/ brain Dorsi/o- = back Dist- = far away Prox(i)- = closer to ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 8e
... How many chromosomes would be in each of the resulting daughter cells? 2. What happens in interphase to allow the cell to be capable of undergoing future divisions? 3. What is the significance of cytokinesis? What do you think would happen if this process didn’t ...
... How many chromosomes would be in each of the resulting daughter cells? 2. What happens in interphase to allow the cell to be capable of undergoing future divisions? 3. What is the significance of cytokinesis? What do you think would happen if this process didn’t ...
Cell_Structure_post
... If you were a bacterium… – You live in a medium which has the viscosity similar to asphalt. – You have a motor for swimming that only runs in two directions… and you can never stop. – While you can “learn”, you divide @ every 20 minutes and have to restart your education. – You can have “sex”. Howev ...
... If you were a bacterium… – You live in a medium which has the viscosity similar to asphalt. – You have a motor for swimming that only runs in two directions… and you can never stop. – While you can “learn”, you divide @ every 20 minutes and have to restart your education. – You can have “sex”. Howev ...
Cell Dudes From Long Ago - CCA Science
... Rudolf Virchow lived from 1821 until 1902. He was a really good medical doctor. He concluded that all cells come from other cells He pushed the idea that diseases usually result from problems with cells rather than from problems with other bigger parts of the ...
... Rudolf Virchow lived from 1821 until 1902. He was a really good medical doctor. He concluded that all cells come from other cells He pushed the idea that diseases usually result from problems with cells rather than from problems with other bigger parts of the ...
Content Outline
... 2. Viruses are often carried to the host through the _____________. 3. The virus and host cell must ____________ together exactly to begin a viral infection. 4. Bacteriophages attach to _______________ and inject their hereditary material. D. Fighting viruses 1. Vaccines–weakened ____________ partic ...
... 2. Viruses are often carried to the host through the _____________. 3. The virus and host cell must ____________ together exactly to begin a viral infection. 4. Bacteriophages attach to _______________ and inject their hereditary material. D. Fighting viruses 1. Vaccines–weakened ____________ partic ...
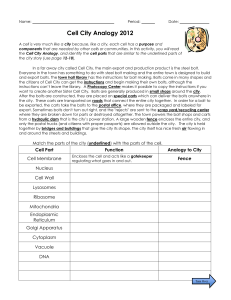
Cell City Analogy - Rochester Community Schools
... A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city story (use page 12-18). ...
... A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city story (use page 12-18). ...
BLOOD
... Keep pH value ( pH = 7,4 ) Important for osmotic pressure ( 0,9% solution of natrium chloride is isotonic to blood plasma of human) Organic substances : a) dissolved proteins : albumin : help to draw the water from tissues into blood globulins : ( immunoglobulins ) : impotant for immunity fibrinogen ...
... Keep pH value ( pH = 7,4 ) Important for osmotic pressure ( 0,9% solution of natrium chloride is isotonic to blood plasma of human) Organic substances : a) dissolved proteins : albumin : help to draw the water from tissues into blood globulins : ( immunoglobulins ) : impotant for immunity fibrinogen ...
Apoptotic cell death signaling in the Human Colon Cancer Cell line
... of cell death. Hence, most anti-cancer treatments aim to eradicate tumor cells through activation of various cell death processes, including apoptosis. Unfortunately, development of resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs during the course of treatment is a substantial problem in the clinics today. The ...
... of cell death. Hence, most anti-cancer treatments aim to eradicate tumor cells through activation of various cell death processes, including apoptosis. Unfortunately, development of resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs during the course of treatment is a substantial problem in the clinics today. The ...
Chemotherapy
... To understand how chemotherapy works as a treatment, it is helpful to understand the normal life cycle of a cell in the body. All living tissue is composed of cells. Cells grow and reproduce to replace cells lost during injury or normal “wear and tear”. The cell cycle is a series of steps that b ...
... To understand how chemotherapy works as a treatment, it is helpful to understand the normal life cycle of a cell in the body. All living tissue is composed of cells. Cells grow and reproduce to replace cells lost during injury or normal “wear and tear”. The cell cycle is a series of steps that b ...
Muscle and Nervous Tissue
... • Functions: Movement of substance within the body (waste, blood, etc) Cannot be contracted consciously – involuntary – Ex of involuntary: smooth muscle moves food through digestive tract ...
... • Functions: Movement of substance within the body (waste, blood, etc) Cannot be contracted consciously – involuntary – Ex of involuntary: smooth muscle moves food through digestive tract ...
cell-defence-animals
... This is why people say that if you catch chickenpox as a child you are unlikely to catch it as an adult. ...
... This is why people say that if you catch chickenpox as a child you are unlikely to catch it as an adult. ...
Cell Organelle Chart
... energy for growth, development, and movement Helps in cell division (mitosis) ...
... energy for growth, development, and movement Helps in cell division (mitosis) ...
BIO 105 S 2013 55244 61816 LAB 1 Mitosis vs. Meiosis and
... osmosis, without being destroyed. An animal cell does not have this cell wall, too much fluid would cause it the cell to pop. Plant cells also are different from animal cells because they have chloroplasts that are used for photosynthesis, which converts sunlight into needed food for the plant. Plan ...
... osmosis, without being destroyed. An animal cell does not have this cell wall, too much fluid would cause it the cell to pop. Plant cells also are different from animal cells because they have chloroplasts that are used for photosynthesis, which converts sunlight into needed food for the plant. Plan ...
1 A Tour of the Cell
... • Explain how the ultrastructure of cilia and flagella relates to their functions. • Describe the basic structure of a plant cell wall. • Describe the structure and function of the extracellular matrix in animal cells. ...
... • Explain how the ultrastructure of cilia and flagella relates to their functions. • Describe the basic structure of a plant cell wall. • Describe the structure and function of the extracellular matrix in animal cells. ...
1 IMMUNE SYSTEM WORKSHEET KEY CONCEPT: The immune
... IMMUNE SYSTEM WORKSHEET KEY CONCEPT: The immune system consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections. VOCABULARY ...
... IMMUNE SYSTEM WORKSHEET KEY CONCEPT: The immune system consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections. VOCABULARY ...