The Cell Cycle
... this period, chromosomes are duplicated in preparation for the period of division. ...
... this period, chromosomes are duplicated in preparation for the period of division. ...
Connective Tissue - White Plains Public Schools
... binding. The major classes of cell adhesion molecules are the integrins, cadherins, selectins and the immunoglobulin. These are the glue that holds the cell and tissue together. They become continuous with the basement membrane and the various types of adhesion proteins such as desmosomes. Proteogly ...
... binding. The major classes of cell adhesion molecules are the integrins, cadherins, selectins and the immunoglobulin. These are the glue that holds the cell and tissue together. They become continuous with the basement membrane and the various types of adhesion proteins such as desmosomes. Proteogly ...
Poikilothermic and Homoeothermic Organisms
... to keep their body temperatures constant. Their body temperatures differ in accordance with the temperatures of their surroundings. Homoeothermic is a term that refers to warm-blooded animals. These animals can keep their body temperatures constant regardless of the temperatures around them. They of ...
... to keep their body temperatures constant. Their body temperatures differ in accordance with the temperatures of their surroundings. Homoeothermic is a term that refers to warm-blooded animals. These animals can keep their body temperatures constant regardless of the temperatures around them. They of ...
Electricity Unit Review
... A hair dryer uses 980 W of power when plugged into a 120 V outlet. Calculate the resistance of the element in the hair dryer. (hint: you need to use more than one formula THINK about it!!)) ...
... A hair dryer uses 980 W of power when plugged into a 120 V outlet. Calculate the resistance of the element in the hair dryer. (hint: you need to use more than one formula THINK about it!!)) ...
Cell Biology
... • Water disassociates into H+ and OH• Imbalance of H+ and OH- give rise to “acids and bases” - Measured by the pH • pH influence charges of amino acid groups on protein, causing a ...
... • Water disassociates into H+ and OH• Imbalance of H+ and OH- give rise to “acids and bases” - Measured by the pH • pH influence charges of amino acid groups on protein, causing a ...
the Cell
... oil • Result: ___________________ • _____________________ —those not attached to the cytoskeleton—can move within the fluid lipid bilayer • This “fluidity” is critical to the _________ of proteins, particularly enzymes which speed up chemical reactions ...
... oil • Result: ___________________ • _____________________ —those not attached to the cytoskeleton—can move within the fluid lipid bilayer • This “fluidity” is critical to the _________ of proteins, particularly enzymes which speed up chemical reactions ...
Cell - St. Pius X High School
... 1. What are the two main types of cells? 2. Which one is larger? 3. Which one does not have a membrane bound nucleus? 4. What are the three main parts of the cell (that all cells have)? 5. What are the 3 components of the cell theory? 6. What theory explains how eukaryotes evolved? 7. What limits th ...
... 1. What are the two main types of cells? 2. Which one is larger? 3. Which one does not have a membrane bound nucleus? 4. What are the three main parts of the cell (that all cells have)? 5. What are the 3 components of the cell theory? 6. What theory explains how eukaryotes evolved? 7. What limits th ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. There are 60 questions on this exam. All
... 35) Low density lipoproteins (LDL’s or bad cholesterol) are taken up “in-bulk” into the cytoplasm of a cell. This process is an example of A) endocytosis. B) exocytosis. C) molecular transport. D) osmosis. E) diffusion. 36) Diffusion does not require the cell to expend ATP. Therefore, diffusion is c ...
... 35) Low density lipoproteins (LDL’s or bad cholesterol) are taken up “in-bulk” into the cytoplasm of a cell. This process is an example of A) endocytosis. B) exocytosis. C) molecular transport. D) osmosis. E) diffusion. 36) Diffusion does not require the cell to expend ATP. Therefore, diffusion is c ...
THE CELL KEY
... 25. Glycogen is not normally found in the blood because A. free glucose molecules are stored as starch. B. free glucose molecules are converted to amino acids. C. glycogen can be structurally incorporated directly into the cell wall. D. glycogen molecules are unable to diffuse through the cell membr ...
... 25. Glycogen is not normally found in the blood because A. free glucose molecules are stored as starch. B. free glucose molecules are converted to amino acids. C. glycogen can be structurally incorporated directly into the cell wall. D. glycogen molecules are unable to diffuse through the cell membr ...
Movement Through the cell Membrane
... There are three different ways to classify a solution. Hypotonic: contain a low concentration of solute relative to another solution (e.g. the cell's cytoplasm). When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, the water diffuses into the cell, causing the cell to swell and possibly explode. ...
... There are three different ways to classify a solution. Hypotonic: contain a low concentration of solute relative to another solution (e.g. the cell's cytoplasm). When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, the water diffuses into the cell, causing the cell to swell and possibly explode. ...
NAME PRD _____ DATE ______ MULTIPLE CHOICE: Write the
... number of bacteria increased sharply over the first few hours but then tapered off. Which of the following statements about these observations is true? A. ...
... number of bacteria increased sharply over the first few hours but then tapered off. Which of the following statements about these observations is true? A. ...
2-4 summary
... 7. ATP is the only form of energy found in cells. 8. Cellular respiration occurs only in lung cells. ...
... 7. ATP is the only form of energy found in cells. 8. Cellular respiration occurs only in lung cells. ...
Cells are
... Cells need to make more cells! • Making more cells – to replace, repair & grow, the cell must… ...
... Cells need to make more cells! • Making more cells – to replace, repair & grow, the cell must… ...
Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells
... • 250 different kinds of cells in the human body • Through cellular differentiation, different types of cells are created to carry out specific tasks or functions. • In animals the “starter” cells that differentiate are called stem cells • In plants those cells are called meristematic cells ...
... • 250 different kinds of cells in the human body • Through cellular differentiation, different types of cells are created to carry out specific tasks or functions. • In animals the “starter” cells that differentiate are called stem cells • In plants those cells are called meristematic cells ...
There are two types of transport: ACTIVE and PASSIVE
... Ex. Riding up a hill on a bike is an example of Active transport, because you have to use energy to pedal up the hill. However, if you ride down a hill without pedaling, this is an example of passive transport, because you are not using energy. During Active transport, substances move from low conce ...
... Ex. Riding up a hill on a bike is an example of Active transport, because you have to use energy to pedal up the hill. However, if you ride down a hill without pedaling, this is an example of passive transport, because you are not using energy. During Active transport, substances move from low conce ...
The Process of Cell Division (10.2)
... Prophase Prophase: the genetic material inside the nucleus condenses and the duplicate chromosomes become visible. Outside the nucleus, a spindle starts to form. ...
... Prophase Prophase: the genetic material inside the nucleus condenses and the duplicate chromosomes become visible. Outside the nucleus, a spindle starts to form. ...
GOLGI APPARATUS
... ENZYMES PRODUCED ON ROUGH ER - HELPS W/ PHAGOCYTOSIS- CELL INGESTS A FOOD PARTICLE. THIS NEW FOOD VESICLE FUSES W/ LYS. & GETS DIGESTED. - EXAMPLE- TADPOLE TO FROG. TAIL GETS DIGESTED BY LYSOSOMES - TAY-SACHS DISEASE- LIPID-DIGESTING ENZYME IS MISSING OR INACTIVE, BRAIN BECOMES IMPAIRED BY TOO MANY ...
... ENZYMES PRODUCED ON ROUGH ER - HELPS W/ PHAGOCYTOSIS- CELL INGESTS A FOOD PARTICLE. THIS NEW FOOD VESICLE FUSES W/ LYS. & GETS DIGESTED. - EXAMPLE- TADPOLE TO FROG. TAIL GETS DIGESTED BY LYSOSOMES - TAY-SACHS DISEASE- LIPID-DIGESTING ENZYME IS MISSING OR INACTIVE, BRAIN BECOMES IMPAIRED BY TOO MANY ...
Concept Checks: Chapter 6- A Tour of the Cell Concept Check 6.1 1
... 2. Light microscopes magnify <1000x. SEM is used to study the surface of cells. TEM is used to look through cells. EM’s magnify about 1 million times. 3. Similar: nucleus, plasma membrane, mitochondria Differences: cells walls, chloroplasts 4. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus and lack most organell ...
... 2. Light microscopes magnify <1000x. SEM is used to study the surface of cells. TEM is used to look through cells. EM’s magnify about 1 million times. 3. Similar: nucleus, plasma membrane, mitochondria Differences: cells walls, chloroplasts 4. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus and lack most organell ...
Cell Structures and Functions
... exocytosis, when other vesicles coming from outside the cell fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents into the cell, this process is called endocytosis. ...
... exocytosis, when other vesicles coming from outside the cell fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents into the cell, this process is called endocytosis. ...
Lesson 1 - d.loft STEM Learning
... • Moving cells! Moving Cells Under Microscope Stock Footage Video | Getty Images • Small analogous picture cards labeled with the part of the cell they represent Cell in the City | Nano-Activities for Kids: Biology - The Center … • Step-by-step “H ...
... • Moving cells! Moving Cells Under Microscope Stock Footage Video | Getty Images • Small analogous picture cards labeled with the part of the cell they represent Cell in the City | Nano-Activities for Kids: Biology - The Center … • Step-by-step “H ...
Concept Checks: Chapter 6- A Tour of the Cell Concept Check 6.1 1
... 2. Light microscopes magnify <1000x. SEM is used to study the surface of cells. TEM is used to look through cells. EM’s magnify about 1 million times. 3. Similar: nucleus, plasma membrane, mitochondria Differences: cells walls, chloroplasts 4. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus and lack most organell ...
... 2. Light microscopes magnify <1000x. SEM is used to study the surface of cells. TEM is used to look through cells. EM’s magnify about 1 million times. 3. Similar: nucleus, plasma membrane, mitochondria Differences: cells walls, chloroplasts 4. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus and lack most organell ...
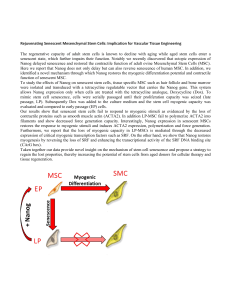
Rejuvenating Senescent Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Implication for
... Here we report that Nanog does not only delay but can also reverse senescence of human MSC. In addition, we identified a novel mechanism through which Nanog restores the myogenic differentiation potential and contractile function of senescent MSC. To study the effects of Nanog on senescent stem cell ...
... Here we report that Nanog does not only delay but can also reverse senescence of human MSC. In addition, we identified a novel mechanism through which Nanog restores the myogenic differentiation potential and contractile function of senescent MSC. To study the effects of Nanog on senescent stem cell ...
File
... The passage below describes how the snake venom travels from the toe to the brain. Use suitable words to complete the sentences in the passage. The venom travels to the heart in the largest vein called the.................................. . The right atrium contracts and pumps the venom through the ...
... The passage below describes how the snake venom travels from the toe to the brain. Use suitable words to complete the sentences in the passage. The venom travels to the heart in the largest vein called the.................................. . The right atrium contracts and pumps the venom through the ...
Tissue Types - Waterford Public Schools
... Apocrine secretion involves the loss of apical cytoplasm. Inclusions, secretory vesicles, and other cytoplasmic components are shed in the process. The gland cell then grows and repairs itself before it releases additional secretions. ...
... Apocrine secretion involves the loss of apical cytoplasm. Inclusions, secretory vesicles, and other cytoplasmic components are shed in the process. The gland cell then grows and repairs itself before it releases additional secretions. ...
A Framework for Function
... cell’s contents. The cytoplasm is held in by the cell membrane. In eukaryotic cells, it is found between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Organelles move about in the cytoplasm, and other cell activity occurs here. In prokaryotic cells, all cellular activities occur in the cytoplasm. 7 Eukaryotic ...
... cell’s contents. The cytoplasm is held in by the cell membrane. In eukaryotic cells, it is found between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Organelles move about in the cytoplasm, and other cell activity occurs here. In prokaryotic cells, all cellular activities occur in the cytoplasm. 7 Eukaryotic ...