cell - CSB | SJU Employees Personal Web Sites
... passage of small chemical substances between cells (mostly ions); found in excitable tissues. D. Functions of plasma membrane: functions of proteins found within membrane. 1. Membrane transport. - membrane is selectively permeable. - substances can be transported across either passively or actively. ...
... passage of small chemical substances between cells (mostly ions); found in excitable tissues. D. Functions of plasma membrane: functions of proteins found within membrane. 1. Membrane transport. - membrane is selectively permeable. - substances can be transported across either passively or actively. ...
Human Body Systems PPT
... Lymph nodes contain filtering tissue and a large number of lymph cells. When fighting certain bacterial infections, the lymph nodes swell with bacteria and the cells fighting the bacteria, to the point where you can actually feel them. Swollen lymph nodes may therefore be a good indication that yo ...
... Lymph nodes contain filtering tissue and a large number of lymph cells. When fighting certain bacterial infections, the lymph nodes swell with bacteria and the cells fighting the bacteria, to the point where you can actually feel them. Swollen lymph nodes may therefore be a good indication that yo ...
7.12D: Plant and Animal Cell Organelles A Framework for Funcčon
... fluid substance inside the membrane. An example of a prokaryote is bacteria. Eukaryo>c cells have a much more complex membrane system than prokaryotes, including one around their nucleus. Eukaryotes are the cells that aid in most of your body’s func>ons. Eukaryotes are up to ten >mes larger t ...
... fluid substance inside the membrane. An example of a prokaryote is bacteria. Eukaryo>c cells have a much more complex membrane system than prokaryotes, including one around their nucleus. Eukaryotes are the cells that aid in most of your body’s func>ons. Eukaryotes are up to ten >mes larger t ...
Lab. 2 Cell Division 1. Mitosis Division
... The advantage of having three phases in interphase is that it allows time to check that things are happening as they should. Three checkpoints exist during interphase, during which the cell makes sure that everything has gone as planned and, if needed, fixes errors. The G1-S checkpoint at the end of ...
... The advantage of having three phases in interphase is that it allows time to check that things are happening as they should. Three checkpoints exist during interphase, during which the cell makes sure that everything has gone as planned and, if needed, fixes errors. The G1-S checkpoint at the end of ...
review-notes-on-movement-into-andout-of-cells
... The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer (double membrane), which has embedded proteins and cholesterol It is described as a “fluid mosaic model” because it is always moving and has a mosaic pattern to the way it looks due to the proteins that poke out through it. The phospholipids look lik ...
... The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer (double membrane), which has embedded proteins and cholesterol It is described as a “fluid mosaic model” because it is always moving and has a mosaic pattern to the way it looks due to the proteins that poke out through it. The phospholipids look lik ...
Cell wall
... The area between the outer mebrane and the cytoplasmic membrane is called the periplasmic space. The outer membrane prevents loss of periplasmatic proteins and forms a protective barrier preventing exposure of bacteria to hydrolytic enzymes and toxic substances such as bile in the gastrointestinal t ...
... The area between the outer mebrane and the cytoplasmic membrane is called the periplasmic space. The outer membrane prevents loss of periplasmatic proteins and forms a protective barrier preventing exposure of bacteria to hydrolytic enzymes and toxic substances such as bile in the gastrointestinal t ...
7-1: Life is Cellular
... Coded instructions for making proteins and other molecules • It is surrounded by a nuclear envelope which has pores to let materials in and out • Chromatin is granular material in the nucleus which is made of DNA bound to protein • Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes when the cell divides • The ...
... Coded instructions for making proteins and other molecules • It is surrounded by a nuclear envelope which has pores to let materials in and out • Chromatin is granular material in the nucleus which is made of DNA bound to protein • Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes when the cell divides • The ...
Chapter 7 - North Mac Schools
... Ribosomes make proteins by following coded instructions that come from the nucleus. – These instructions are RNA (ribonucleic acid) Cells that are major protein producers often have numerous ribosomes. ...
... Ribosomes make proteins by following coded instructions that come from the nucleus. – These instructions are RNA (ribonucleic acid) Cells that are major protein producers often have numerous ribosomes. ...
Microbiology 155 Chapter 1 - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... 1883: Carl Zeiss pioneered developments in microscopy (such as immersion lenses and apochromatic lenses which reduce chromatic aberration) which perist until the present day. 1931: Ernst Rusko -constructed the first electron microscope. ...
... 1883: Carl Zeiss pioneered developments in microscopy (such as immersion lenses and apochromatic lenses which reduce chromatic aberration) which perist until the present day. 1931: Ernst Rusko -constructed the first electron microscope. ...
Is the living cell simple or complex?
... Specialized eukaryotic cells have organelles, such as cilia and lysosomes, that enable them to carry out specific functions, such as movement and digestion. Mitochondria are organelles that convert the chemical energy in food to energy the cell can use for life ...
... Specialized eukaryotic cells have organelles, such as cilia and lysosomes, that enable them to carry out specific functions, such as movement and digestion. Mitochondria are organelles that convert the chemical energy in food to energy the cell can use for life ...
Lab 24 – Mitosis Wheel
... Cells form new cells by a process called cell division or mitosis. During mitosis, one cell divides in half to form two new cells. Suppose you could watch a cell divide. You could see that the cell parts called chromosomes move around the cell during mitosis. Because chromosomes move in particular w ...
... Cells form new cells by a process called cell division or mitosis. During mitosis, one cell divides in half to form two new cells. Suppose you could watch a cell divide. You could see that the cell parts called chromosomes move around the cell during mitosis. Because chromosomes move in particular w ...
Worksheet for video below
... Use with Bozeman Science Video: Transport Across Cell Membranes—13:58 ...
... Use with Bozeman Science Video: Transport Across Cell Membranes—13:58 ...
Class - Educast
... The cork cells studied by Hooke were really empty boxes; they had lost their living matter, the protoplasm. After his discovery, the protoplasm in living cells was largely over looked due to its transparency. Today, with the help of special techniques, we are able to see not only the protoplas ...
... The cork cells studied by Hooke were really empty boxes; they had lost their living matter, the protoplasm. After his discovery, the protoplasm in living cells was largely over looked due to its transparency. Today, with the help of special techniques, we are able to see not only the protoplas ...
28.1 Levels of Organization
... genetic information needed to build an entire organism. However, during determination, they lose their ability to express some of this information. Once a cell is committed to becoming a specialized cell, it will develop into only that type of cell. For instance, a cell that will become a neuron can ...
... genetic information needed to build an entire organism. However, during determination, they lose their ability to express some of this information. Once a cell is committed to becoming a specialized cell, it will develop into only that type of cell. For instance, a cell that will become a neuron can ...
The Three Kingdoms of Life New Eukaryotic Phylogeny Alveolates
... The PV is derived from host cell membrane but behaves different from a phagosome The PV membrane is derived from the host cell plasma membrane The PV is provided by the parasite (e.g. by secretion) Both contribute to the PV ...
... The PV is derived from host cell membrane but behaves different from a phagosome The PV membrane is derived from the host cell plasma membrane The PV is provided by the parasite (e.g. by secretion) Both contribute to the PV ...
3rd Nine Weeks Review
... c) ball and socket—(hip/shoulder)—greatest range of motion—circular d) pivot—(neck)—allows head to turn side to side and up and down 4. Name the three types of muscle tissue. Describe the location and type of movement for each. a) skeletal—attaches to bones; voluntary movement b) smooth—found in res ...
... c) ball and socket—(hip/shoulder)—greatest range of motion—circular d) pivot—(neck)—allows head to turn side to side and up and down 4. Name the three types of muscle tissue. Describe the location and type of movement for each. a) skeletal—attaches to bones; voluntary movement b) smooth—found in res ...
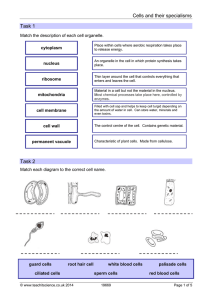
Cells and their specialisms Task 1 Task 2
... Long tail and streamlined head to help it swim towards the egg. Lots of mitochondria to provide energy for movement. Enzymes in head digest through the egg’s cell membrane. ...
... Long tail and streamlined head to help it swim towards the egg. Lots of mitochondria to provide energy for movement. Enzymes in head digest through the egg’s cell membrane. ...
CELL TRANSPORT
... This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with each other. ...
... This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with each other. ...
Comprehensive Review
... a better blood supply and heal faster. SPRAINS: are tears in a ligament, and are fairly serious. When a ligament is sprained, it can take 6 months to heal, and may even need surgery. Even with a partial tear, you have to be careful. STRAIN: is a tear in a muscle, and is not as bad because it has ...
... a better blood supply and heal faster. SPRAINS: are tears in a ligament, and are fairly serious. When a ligament is sprained, it can take 6 months to heal, and may even need surgery. Even with a partial tear, you have to be careful. STRAIN: is a tear in a muscle, and is not as bad because it has ...
Cell structure Part 1
... Phospholipidshas a polar and nonpolar end. The polar end likes water and the nonpolar end hates water. ...
... Phospholipidshas a polar and nonpolar end. The polar end likes water and the nonpolar end hates water. ...
42A Closer Look - Merrillville Community School Corporation
... seen with a light microscope. Some of the jobs performed by these organelles include obtaining and storing energy, helping cells move and divide, and making substances that are either used in the cell or transported to other parts of the body. The organelles that produce energy are called mitochondr ...
... seen with a light microscope. Some of the jobs performed by these organelles include obtaining and storing energy, helping cells move and divide, and making substances that are either used in the cell or transported to other parts of the body. The organelles that produce energy are called mitochondr ...
Document
... SI Bio6 Dr. Wright’s class made by Pyeongsug Kim Revised: 03/14/10 c. What ion enters the cell at the axon terminals and initiates the process of neurotransmitter release? Ca+ d. When acetylcholines(neurotransmitters) bind to muscarinic, Which ion channels will be open? Cause depolarization, repola ...
... SI Bio6 Dr. Wright’s class made by Pyeongsug Kim Revised: 03/14/10 c. What ion enters the cell at the axon terminals and initiates the process of neurotransmitter release? Ca+ d. When acetylcholines(neurotransmitters) bind to muscarinic, Which ion channels will be open? Cause depolarization, repola ...